Human Integrin alphaV beta3 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB3050

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Human Integrin alphaV beta3 Antibody
Detection of Human Integrin alpha V beta 3 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
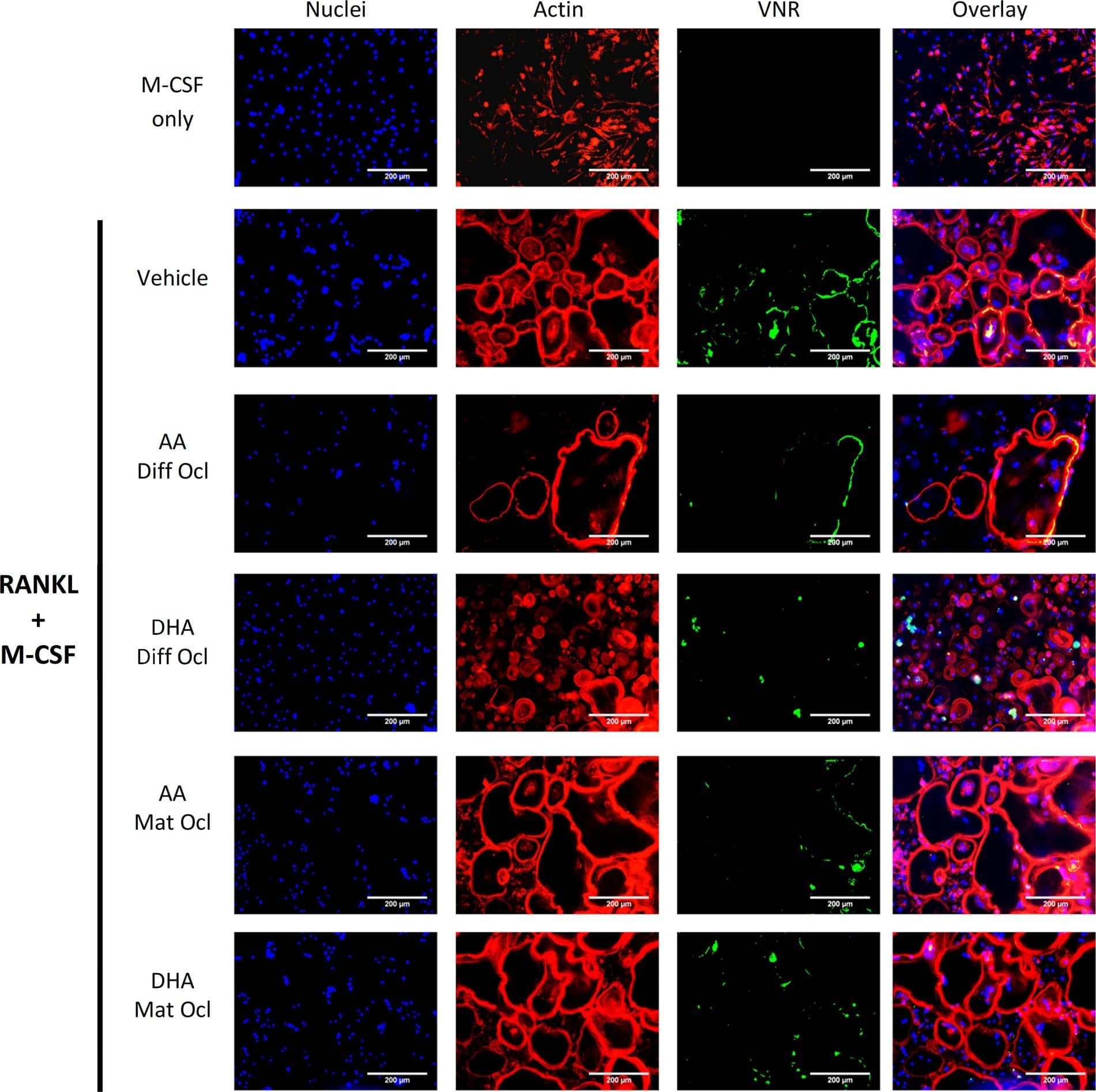
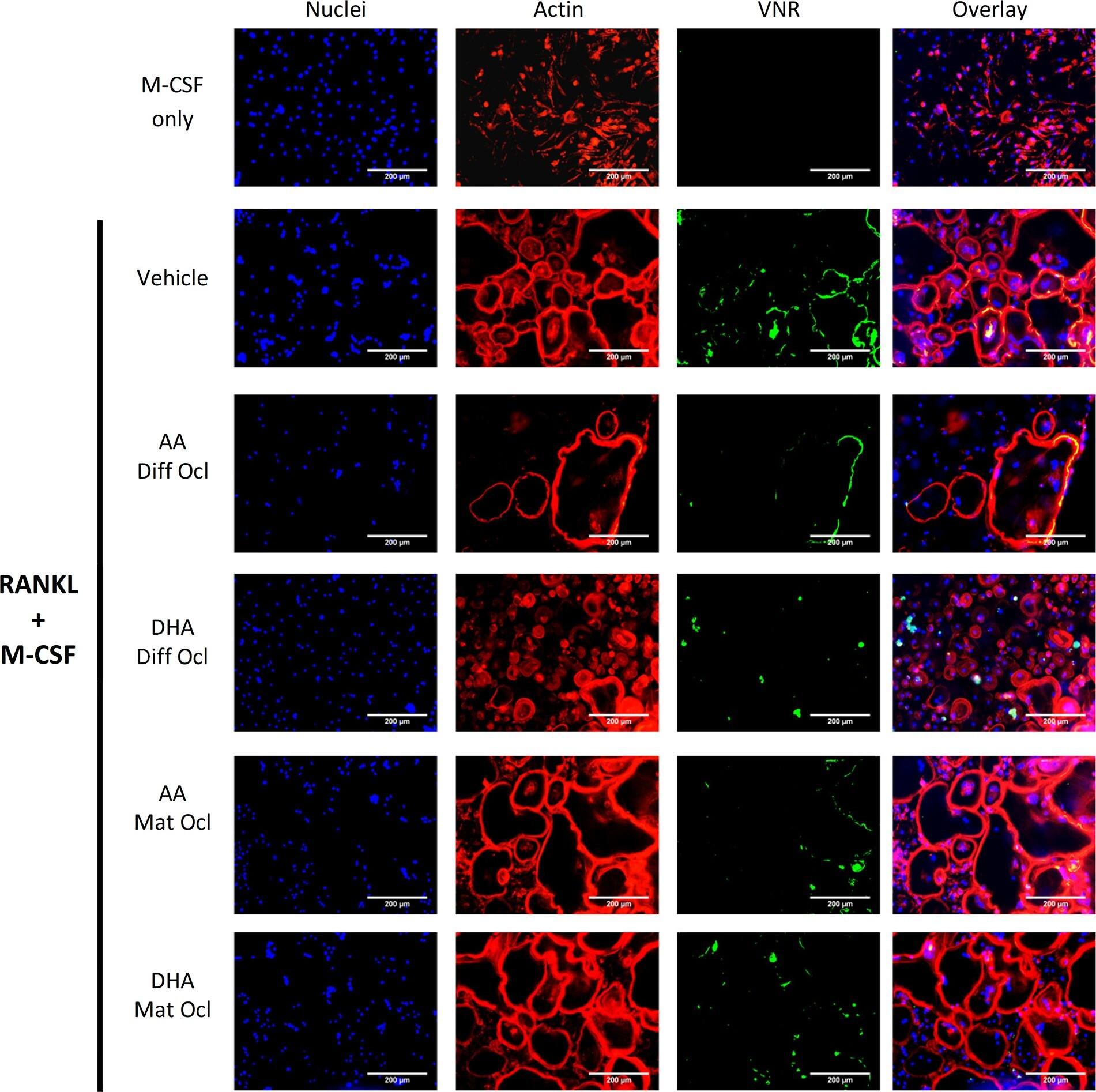
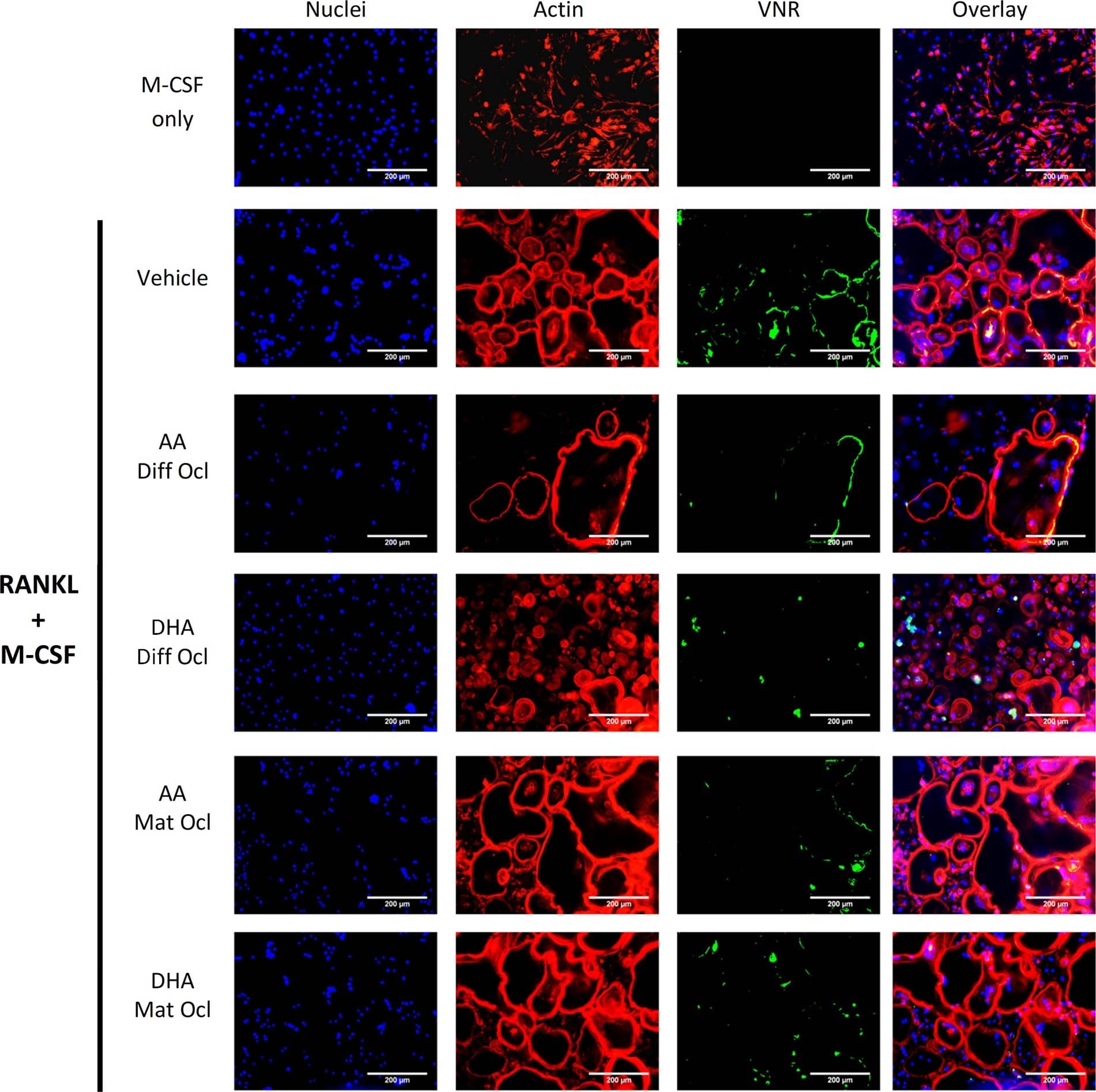
Effects of AA and DHA on actin ring formation and VNR expression.Osteoclast differentiation was stimulated in CD14+ monocytes by the addition of 25 ng ml-1 M-CSF and 30 ng ml-1 RANKL as described in Materials and Methods. Vehicle (0.08% ethanol) or LCPUFAs (40 μorption (day 12–14) in mature osteoclasts. After 3 weeks of culture, cells were fixed and stained with Hoechst (blue) for nuclei, phalloidin (red) for actin rings, and anti-VNR antibody (green). The results are representative of three independent experiments conducted in triplicate. Scale bar = 200 μm. Diff Ocl—differentiating osteoclasts. Mat Ocl—mature osteoclasts. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25867515), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Human Human Integrin alpha V beta 3 Antibody by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence
Effects of AA and DHA on actin ring formation and VNR expression.Osteoclast differentiation was stimulated in CD14+ monocytes by the addition of 25 ng ml-1 M-CSF and 30 ng ml-1 RANKL as described in Materials and Methods. Vehicle (0.08% ethanol) or LCPUFAs (40 μorption (day 12–14) in mature osteoclasts. After 3 weeks of culture, cells were fixed and stained with Hoechst (blue) for nuclei, phalloidin (red) for actin rings, and anti-VNR antibody (green). The results are representative of three independent experiments conducted in triplicate. Scale bar = 200 μm. Diff Ocl—differentiating osteoclasts. Mat Ocl—mature osteoclasts. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25867515), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Human Integrin alpha V beta 3 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence
Effects of AA and DHA on actin ring formation and VNR expression.Osteoclast differentiation was stimulated in CD14+ monocytes by the addition of 25 ng ml-1 M-CSF and 30 ng ml-1 RANKL as described in Materials and Methods. Vehicle (0.08% ethanol) or LCPUFAs (40 μorption (day 12–14) in mature osteoclasts. After 3 weeks of culture, cells were fixed and stained with Hoechst (blue) for nuclei, phalloidin (red) for actin rings, and anti-VNR antibody (green). The results are representative of three independent experiments conducted in triplicate. Scale bar = 200 μm. Diff Ocl—differentiating osteoclasts. Mat Ocl—mature osteoclasts. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25867515), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Human Integrin alphaV beta3 Antibody
Adhesion Blockade
CyTOF-ready
Flow Cytometry
Sample: HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Immunohistochemistry
Immunoprecipitation
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Integrin alpha V beta 3
Integrin alphaV beta3 together with alphaIIb beta3, constitutes the only known beta3 Integrins (1‑3). The non-covalent heterodimer of 170 kDa alphaV/CD51 and 93 kDa beta3/CD61 subunits shows wide expression, notably by endothelial cells and osteoclasts (2‑4). Each subunit has a transmembrane sequence and a short cytoplasmic tail connected to the cytoskeleton. Active cell surface alphaV beta3 adheres to matrix proteins including vitronectin, fibronectin, fibrinogen and thrombospondin (2, 3). The ligand binding site of alphaV beta3 is in the N-terminal head region, formed by interaction of the beta3 vWFA domain with the alphaV beta-propeller structure (4). The alphaV subunit contributes a thigh and a calf region, while the beta3 subunit contains a PSI domain and four cysteine-rich I-EGF folds. The alphaV subunit domains termed thigh, calf-1 and calf-2 generate a “knee” region that is bent when the alphaV beta3 is in its constitutively inactive state. Activation, either by “inside out” signaling or by Mg2+ or Mn2+ binding, extends the Integrin to expose its ligand binding site (1, 4). Two splice variants of beta3 (b and c) diverge over the last 21 amino acids (aa) and lack cytoplasmic phosphorylation sites (5, 6). Another beta3 splice variant diverges after the vWFA domain, producing a soluble 60 kDa form in platelets and endothelial cells (7). alphaV beta3 is essential for the maturation of osteoclasts and their binding and resorption of bone; it also, however, promotes their apoptosis (8, 9). M-CSF R and alphaV beta3 share signaling pathways during osteoclastogenesis, and deletion of either molecule causes osteopetrosis (8, 9). Also cell entry of several viruses is mediated by alphaV beta3 (4, 10). The 962 aa human alphaV ECD (11) shares 92‑95% aa sequence identity with mouse, rat and cow alphaV while the 685 aa human beta3 ECD (12) shares 95% aa identity with horse and dog, and 89‑92% aa identity with mouse, rat and pig beta3.
References
- Hynes, R. O. (2002) Cell 110:673.
- Serini, G. et al. (2006) Exp. Cell Res. 312:651.
- Ross, F. P. and S. L. Teitelbaum (2005) Immunol. Rev. 208:88.
- Xiong, J. et al. (2001) Science 294:339.
- Kumar, C. S. et al. (1987) J. Biol. Chem. 272:16390.
- vanKuppevelt, H. et al. (1989) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:5415.
- Djaffar, I. et al. (1994) Biochem. J. 300:67.
- McHugh, K. P. et al. (2000) J. Clin. Invest. 105:433.
- Faccio, R. et al. (2003) J. Clin. Invest. 111:749.
- Chu, J. J. and M. Ng (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279:54533.
- Suzuki, S. et al. (1987) J. Biol. Chem. 262:14060.
- Fitzgerald, L. A. et al. (1987) J. Biol. Chem. 262:3936.
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
Additional Integrin alpha V beta 3 Products
Product Documents for Human Integrin alphaV beta3 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human Integrin alphaV beta3 Antibody
For research use only