Human CD36/SR-B3 APC-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB19551A

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Gly30-Asn439
Accession # P16671
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human CD36/SR-B3 APC-conjugated Antibody
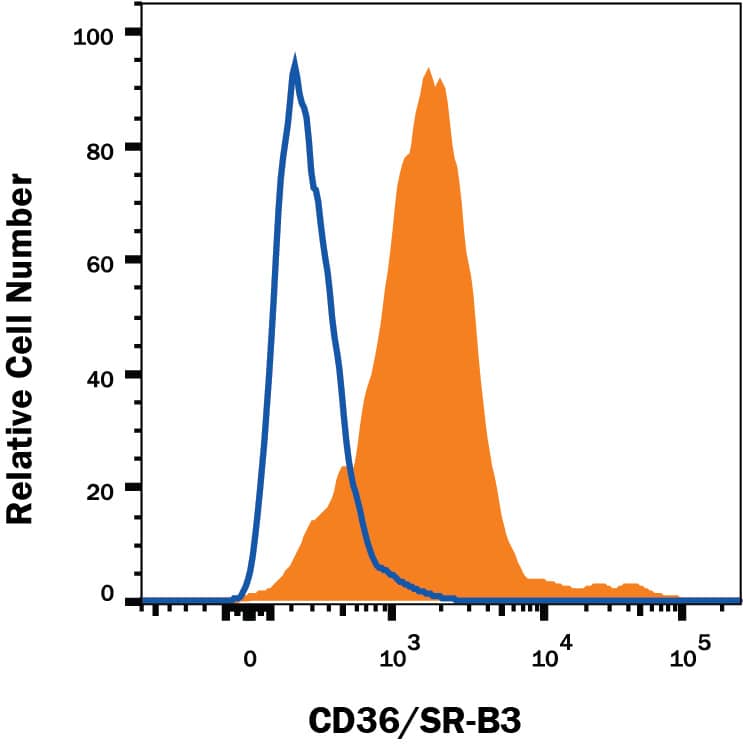
Detection of CD36/SR‑B3 in HepG2 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line was stained with Rat Anti-Human CD36/SR-B3 APC-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB19551A, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC013A, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Human CD36/SR-B3 APC-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
Background: CD36/SR-B3
CD36, alternatively known as platelet membrane glycoprotein IV (GPIV), GPIIIb, thrombospondin receptor, collagen receptor, fatty acid translocase (FAT), and scavenger receptor class B, member 3 (SR-B3), is an integral membrane glycoprotein that has multiple physiological functions (1). It is broadly expressed on a variety of cell types including microvascular endothelium, adipocytes, skeletal muscle, epithelial cells of the retina, breast, and intestine, smooth muscle cells, erythroid precursors, platelets, megakaryocytes, dendritic cells, monocytes/macrophages, and microglia (1, 2). As a member of the scavenger receptor family, CD36 is a multiligand pattern recognition receptor that interacts with a large number of structurally dissimilar ligands, including long chain fatty acid (LCFA), advanced glycation end products (AGE), thrombospondin-1, oxidized low-density lipoproteins (oxLDLs), high density lipoprotein (HDL), phosphatidylserine, apoptotic cells, beta‑amyloid fibrils (fA beta), collagens I and IV, and Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes (3). CD36 is required for the anti-angiogenic effects of thrombospondin-1 in the corneal neovascularization assay (4). It plays a role in lipid metabolism and has been identified as a fatty acid translocase necessary for the binding and transport of LCFA in cells and tissues (5). CD36 has been implicated in the clearance of apoptotic cells and cell debris and has also been shown to mediate the internalization and degradation of a variety of its ligands such as oxLDL, AGE and fA beta (3). Upon ligand binding, CD36 transduces signals that mediate a wide range of pro-inflammatory cellular responses (2). CD36 plays a significant role in the initiation and pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and atherosclerosis (2, 3). The human CD36 gene encodes a single-chain 472 amino acid protein containing both an N- and a C-terminal cytoplasmic tail and an extracellular loop.
References
- Febbraio, M. et al. (2001) J. Clin. Invest. 108:785.
- Khoury, J. et al. (2003) J. Exp. Med. 197:1657.
- Husemann, J. et al. (2002) Glia 40:195.
- Armstrong, L and P. Bornstein (2003) Matrix. Biol. 22:63.
- Febbraio M. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:19055.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional CD36/SR-B3 Products
Product Documents for Human CD36/SR-B3 APC-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human CD36/SR-B3 APC-conjugated Antibody
For research use only