Human IgG is a component of the immune system that protects the body from infection. It is the most abundantly found antibody isotype within the circulatory system of the human body. All antibody isotypes contain two heavy chains and two light chains that are arranged in a Y-shape. The IgG isotpye is found in blood, extracellular fluid, and colostrum among a wide variety of body fluids, and protects the fetus in utero because it is a small monomer capable of crossing the placenta.
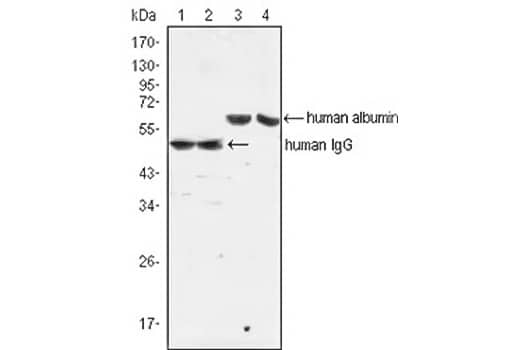
Western blot analysis showing IgG expression (lane 1, 2) and albumin expression (lane 3,4) against human serum (lane 1, 3) and plasma (lane 2, 4) utilizing Mouse anti-Human IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody (4D2D9G8) (Catalog #NBP1-51523).
It functions through multiple mechanisms: opsonization (coating pathogens for phagocytic uptake), activation of the complement signaling cascade, and toxin neutralization through binding. Human IgG antibody has been used to characterize novel classification algorithms for analyzing immunosignature data on complex microarrays in a highly reproducible manner (1). Using human IgG antibody, researchers were able to show that a Niave Bayes algorithm was more simple, robust, fast, and accurate than other widely used methods.
We also offers a wide selection of IgG, IgA, IgD, IgE, IgM and IgY products in the form of primary antibodies, secondary antibodies, isotype controls, kits and more.
- PMID: 22720696