Heparan Sulfate 2-O-Sulfotransferase 1/HS2ST1 Products
Heparan sulfate is a highly sulfated polysaccharide found on the cell surface and within the extracellular matrix. Typically, it is covalently attached to the protein core of proteoglycans, such as syndecans and glypicans. Heparin, on the other hand, can be considered as a highly sulfated version of heparan sulfate that is predominantly found in mast cells. Both heparin and heparan sulfate contain disaccharide repeats of uronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine and are modified by the same sulfotransferases. The uronic acid residues are either glucuronic acid or iduronic acid and maybe sulfated at the 2-O position by heparan sulfate 2-O sulfotransferase 1 (HS2ST1). HS2ST1 physically interacts in the Golgi apparatus with glucuronyl c5-epimerase, which catalyzes the conversion of glucuronic acid to iduronic acid. As a consequence, 2-O sulfation predominantly occurs on iduronic acids naturally and overexpression of HS2ST1 alone causes an increase in 2-O sulfation on glucuronic acid. Our recombinant HS2ST1 was expressed in CHO cells, and the enzyme activity was assayed using an SDS-PAGE-based method.
8 results for "Heparan Sulfate 2-O-Sulfotransferase 1/HS2ST1" in Products
8 results for "Heparan Sulfate 2-O-Sulfotransferase 1/HS2ST1" in Products
Heparan Sulfate 2-O-Sulfotransferase 1/HS2ST1 Products
Heparan sulfate is a highly sulfated polysaccharide found on the cell surface and within the extracellular matrix. Typically, it is covalently attached to the protein core of proteoglycans, such as syndecans and glypicans. Heparin, on the other hand, can be considered as a highly sulfated version of heparan sulfate that is predominantly found in mast cells. Both heparin and heparan sulfate contain disaccharide repeats of uronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine and are modified by the same sulfotransferases. The uronic acid residues are either glucuronic acid or iduronic acid and maybe sulfated at the 2-O position by heparan sulfate 2-O sulfotransferase 1 (HS2ST1). HS2ST1 physically interacts in the Golgi apparatus with glucuronyl c5-epimerase, which catalyzes the conversion of glucuronic acid to iduronic acid. As a consequence, 2-O sulfation predominantly occurs on iduronic acids naturally and overexpression of HS2ST1 alone causes an increase in 2-O sulfation on glucuronic acid. Our recombinant HS2ST1 was expressed in CHO cells, and the enzyme activity was assayed using an SDS-PAGE-based method.
| Reactivity: | Human |
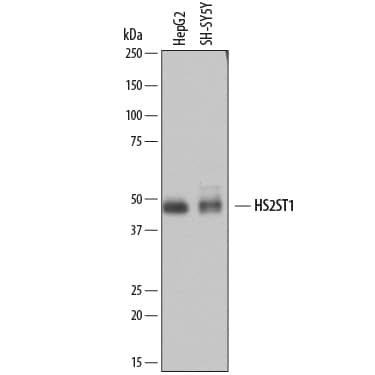
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #738306 |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Applications: | AC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Applications: | WB |
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | Q7LGA3 |
| Applications: | EnzAct |


![Western Blot: Heparan Sulfate 2-O-Sulfotransferase 1/HS2ST1 Antibody [NBP1-79293] Western Blot: Heparan Sulfate 2-O-Sulfotransferase 1/HS2ST1 Antibody [NBP1-79293]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Heparan-Sulfate-2-O-Sulfotransferase-1-HS2ST1-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP1-79293-img0002.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: Heparan Sulfate 2-O-Sulfotransferase 1/HS2ST1 Antibody [NBP1-91982] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: Heparan Sulfate 2-O-Sulfotransferase 1/HS2ST1 Antibody [NBP1-91982]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Heparan-Sulfate-2-O-Sulfotransferase-1-HS2ST1-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-91982-img0009.jpg)
![Western Blot: Heparan Sulfate 2-O-Sulfotransferase 1/HS2ST1 Antibody [NBP1-79294] Western Blot: Heparan Sulfate 2-O-Sulfotransferase 1/HS2ST1 Antibody [NBP1-79294]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Heparan-Sulfate-2-O-Sulfotransferase-1-HS2ST1-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP1-79294-img0003.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: Heparan Sulfate 2-O-Sulfotransferase 1/HS2ST1 Antibody [NBP1-91983] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: Heparan Sulfate 2-O-Sulfotransferase 1/HS2ST1 Antibody [NBP1-91983]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Heparan-Sulfate-2-O-Sulfotransferase-1-HS2ST1-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-91983-img0002.jpg)
![Western Blot: Heparan Sulfate 2-O-Sulfotransferase 1/HS2ST1 Overexpression Lysate [NBL1-11712] Western Blot: Heparan Sulfate 2-O-Sulfotransferase 1/HS2ST1 Overexpression Lysate [NBL1-11712]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Heparan-sulfate-2-O-sulfotransferase-1-Overexpression-Lysate-Adult-Normal-Western-Blot-NBL1-11712-img0002.jpg)
