PD-L1/B7-H1 Products
PD-L1, also known as B7-H1 and CD274, is an approximately 65 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein in the B7 family of immune regulatory molecules. PD-L1 is expressed on inflammatory-activated immune cells including macrophages, T cells, and B cells, keratinocytes, endothelial and intestinal epithelial cells, as well as a variety of carcinomas and melanoma. PD-L1 protein binds to T cell B7-1/CD80 and PD-1.
It suppresses T cell activation and proliferation and induces the apoptosis of activated T cells. It plays a role in the development of immune tolerance by promoting T cell anergy and enhancing regulatory T cell development. PD-L1 favors the development of anti-inflammatory IL-10 and IL-22 producing dendritic cells and inhibits the development of Th17 cells. In cancer, PD-L1 provides resistance to T cell mediated lysis, enhances EMT, and enhances the tumorigenic function of Th22 cells. Many tumors overexpress PD-L1 protein making the PD-1:PD-L1 interaction central to several successful cancer immunotherapy approaches.
Products:
974 results for "PD-L1/B7-H1" in Products
974 results for "PD-L1/B7-H1" in Products
PD-L1/B7-H1 Products
PD-L1, also known as B7-H1 and CD274, is an approximately 65 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein in the B7 family of immune regulatory molecules. PD-L1 is expressed on inflammatory-activated immune cells including macrophages, T cells, and B cells, keratinocytes, endothelial and intestinal epithelial cells, as well as a variety of carcinomas and melanoma. PD-L1 protein binds to T cell B7-1/CD80 and PD-1.
It suppresses T cell activation and proliferation and induces the apoptosis of activated T cells. It plays a role in the development of immune tolerance by promoting T cell anergy and enhancing regulatory T cell development. PD-L1 favors the development of anti-inflammatory IL-10 and IL-22 producing dendritic cells and inhibits the development of Th17 cells. In cancer, PD-L1 provides resistance to T cell mediated lysis, enhances EMT, and enhances the tumorigenic function of Th22 cells. Many tumors overexpress PD-L1 protein making the PD-1:PD-L1 interaction central to several successful cancer immunotherapy approaches.
Products:
Analyzed by SEC-MALS
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | Q9NZQ7 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Flow, IHC, CyTOF-ready, Dual ISH-IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/8222R |
| Applications: | IHC, WB |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | Q9NZQ7 |
| Applications: | Bind |
Luminex High Performance Assays go through rigorous development, validation, and quality control testing to ensure you are getting the best performance out of your multiplex assay. Panels are customizable so you can order a selection of the analytes or the entire panel.
| Applications: | ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/7568R |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 kappa Monoclonal Clone #rPDL1/8825 |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/8591R |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/8809R |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/8408R |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/8222R |
| Applications: | IHC, WB |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/8408R |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/8591R |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/8809R |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/8408R |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/8408R |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/8591R |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/8222R |
| Applications: | IHC, WB |
| Sensitivity: | 4.52 pg/mL |
| Applications: | ELISA |
| Assay Range: | 25 - 1,600 pg/mL (Cell Culture Supernates, Cell Lysates, Serum, EDTA Plasma, Heparin Plasma, Urine) |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/8591R |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/8222R |
| Applications: | IHC, WB |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/7568R |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/8809R |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Kappa Monoclonal Clone #PDL1/7568R |
| Applications: | IHC |


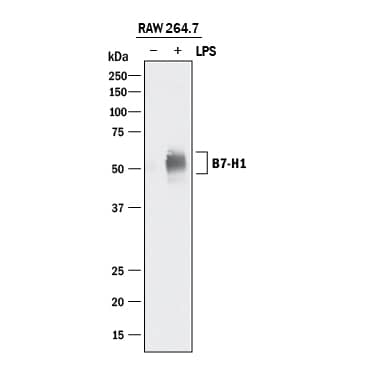

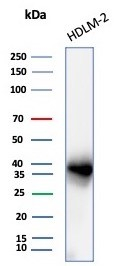
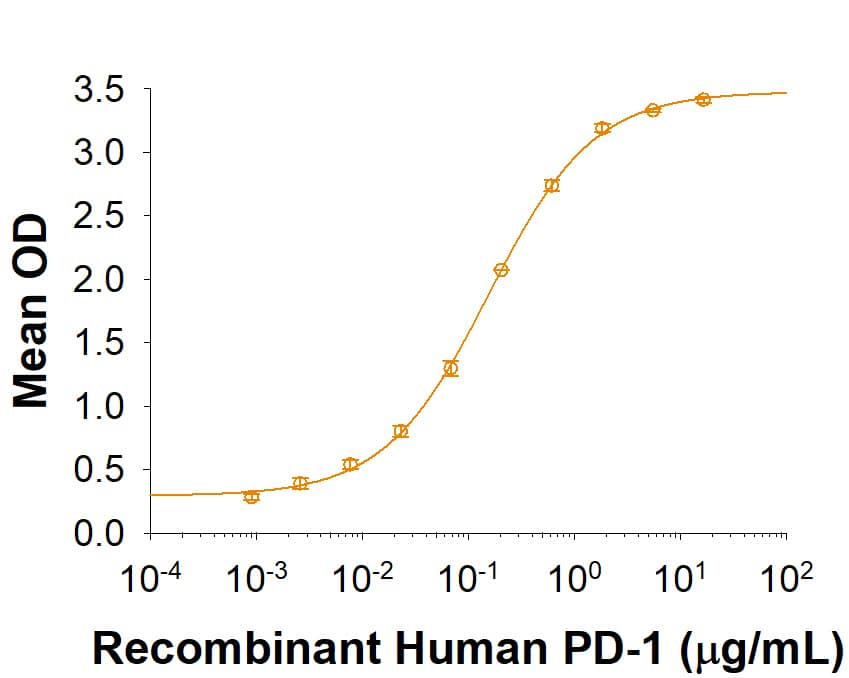

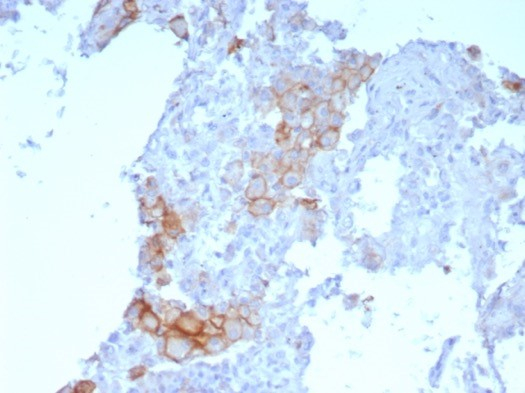

![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: PD-L1 Antibody (PDL1/8591R) [NBP3-23739] - PD-L1 Antibody (PDL1/8591R)](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp3-23739_rabbit-pd-l1-mab-pdl1-8591r-1312202311505320.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: PD-L1 Antibody (PDL1/8809R) [NBP3-23740] - PD-L1 Antibody (PDL1/8809R)](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp3-23740_rabbit-pd-l1-mab-pdl1-8809r-1312202311511035.jpg)

