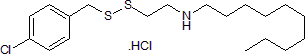Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Products
Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme (UBE1), also known as Ubiquitin-like Modifier Activating Enzyme 1 (UBA1), is a 1058 amino acid (aa) canonical member of the Ubiquitin-activating (E1) enzyme family of proteins with a predicted molecular weight of 118 kDa. It is ubiquitously expressed and highly conserved; mouse and rat UBE1 share 95% and 96% aa sequence identity with the human UBE1 protein, respectively. UBE1 is found in the cytoplasm and nucleus and contains a conserved active-site cysteine residue and ATP-binding site common to E1 enzymes. UBE1 is responsible for the first step in Ubiquitin-protein isopeptide bond formation.
Ubiquitin is activated by UBE1 and thereafter linked to the side chain of a cysteine residue in UBE1, Cys632 in humans, yielding a Ubiquitin-UBE1 conjugate via a thioester bond. The activated Ubiquitin is then transferred to a lysine residue on the target protein via the Ubiquitin-conjugating - Ubiquitin ligase enzyme cascade. UBE1 is required for cell cycle progression and has been linked to cellular responses to DNA damage such as nucleotide excision repair. Mutations in UBE1 are associated with X-linked lethal infantile spinal muscular atrophy. UBE1 is a critical component for the initiation of in vitro ubiquitin conjugation reactions.
Products:
29 results for "Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1" in Products
29 results for "Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1" in Products
Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Products
Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme (UBE1), also known as Ubiquitin-like Modifier Activating Enzyme 1 (UBA1), is a 1058 amino acid (aa) canonical member of the Ubiquitin-activating (E1) enzyme family of proteins with a predicted molecular weight of 118 kDa. It is ubiquitously expressed and highly conserved; mouse and rat UBE1 share 95% and 96% aa sequence identity with the human UBE1 protein, respectively. UBE1 is found in the cytoplasm and nucleus and contains a conserved active-site cysteine residue and ATP-binding site common to E1 enzymes. UBE1 is responsible for the first step in Ubiquitin-protein isopeptide bond formation.
Ubiquitin is activated by UBE1 and thereafter linked to the side chain of a cysteine residue in UBE1, Cys632 in humans, yielding a Ubiquitin-UBE1 conjugate via a thioester bond. The activated Ubiquitin is then transferred to a lysine residue on the target protein via the Ubiquitin-conjugating - Ubiquitin ligase enzyme cascade. UBE1 is required for cell cycle progression and has been linked to cellular responses to DNA damage such as nucleotide excision repair. Mutations in UBE1 are associated with X-linked lethal infantile spinal muscular atrophy. UBE1 is a critical component for the initiation of in vitro ubiquitin conjugation reactions.
Products:
| Source: | Sf 21 (baculovirus) |
| Accession #: | P22314.3 |
| Applications: | EnzAct |
| Source: | Sf 21 (baculovirus) |
| Accession #: | P22314.3 |
| Applications: | EnzAct |
| Source: | Sf 9 (baculovirus) |
| Accession #: | P22314.3 |
| Applications: | EnzAct |
Will be discontinued when existing inventory is gone.
| Source: | Sf 21 (baculovirus) |
| Accession #: | P22515.2 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Applications: | AC |
| Applications: | AC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #6H2I9 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, IP |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Kappa Monoclonal Clone #2B6 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, IP |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #05 |
| Applications: | ELISA, IP |
| Applications: | WB |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #05 |
| Applications: | ELISA, IP |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #05 |
| Applications: | ELISA, IP |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #05 |
| Applications: | ELISA, IP |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #05 |
| Applications: | ELISA, IP |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #05 |
| Applications: | ELISA, IP |
Ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1) inhibitor
| Chemical Name: | N-[2-[[(4-Chlorophenyl)methyl]dithio]ethyl]-1-decanamine hydrochloride |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #05 |
| Applications: | ELISA, IP |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #05 |
| Applications: | ELISA, IP |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #05 |
| Applications: | ELISA, IP |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #05 |
| Applications: | ELISA, IP |



![Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Antibody (6H2I9) [NBP3-16792] Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Antibody (6H2I9) [NBP3-16792]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Ubiquitin-activating-Enzyme-UBE1-Antibody-6H2I9-Western-Blot-NBP3-16792-img0003.jpg)
![Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Antibody [NB600-472] Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Antibody [NB600-472]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Ubiquitin-activating-Enzyme-UBE1-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB600-472-img0004.jpg)
![Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Antibody [NB100-58804] Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Antibody [NB100-58804]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Ubiquitin-activating-Enzyme-UBE1-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB100-58804-img0002.jpg)
![Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Antibody (2B6) [H00007317-M02] Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Antibody (2B6) [H00007317-M02]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Ubiquitin-activating-Enzyme-UBE1-Antibody-2B6-Western-Blot-H00007317-M02-img0002.jpg)
![Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Antibody [NBP1-90307] Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Antibody [NBP1-90307]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Ubiquitin-activating-Enzyme-UBE1-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP1-90307-img0016.jpg)
![Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Antibody [NBP2-20779] - Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp2-20779_rabbit-polyclonal-ubiquitin-activating-enzyme-ube1-antibody-91020242021911.jpg)
![Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Antibody (05) [NBP3-05789] Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Antibody (05) [NBP3-05789]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Ubiquitin-activating-Enzyme-UBE1-Antibody-05-Western-Blot-NBP3-05789-img0001.jpg)
![Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Overexpression Lysate [NBL1-17495] Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Overexpression Lysate [NBL1-17495]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/UBE1-Overexpression-Lysate-Adult-Normal-Western-Blot-NBL1-17495-img0002.jpg)
![Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Overexpression Lysate [NBL1-17494] Western Blot: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme/UBE1 Overexpression Lysate [NBL1-17494]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/UBE1-Overexpression-Lysate-Adult-Normal-Western-Blot-NBL1-17494-img0002.jpg)