CNPase Antibody - BSA Free
Novus Biologicals, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # NB100-1935

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Format
Concentration
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Localization
Marker
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Theoretical MW
Disclaimer note: The observed molecular weight of the protein may vary from the listed predicted molecular weight due to post translational modifications, post translation cleavages, relative charges, and other experimental factors.
Scientific Data Images for CNPase Antibody - BSA Free
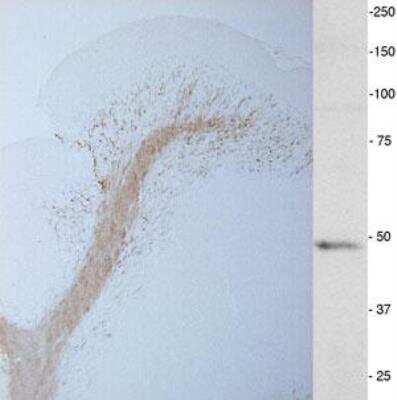
Immunohistochemistry: CNPase Antibody [NB100-1935]
Immunohistochemistry: CNPase Antibody [NB100-1935] - A tissue section through an adult mouse brain showing CNPase (brown staining) in white matter tracts and the granule cell layer of the cerebellum.Applications for CNPase Antibody - BSA Free
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence
Immunohistochemistry
Western Blot
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Format
Preservative
Concentration
Shipping
Stability & Storage
Background: CNPase
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional CNPase Products
Product Documents for CNPase Antibody - BSA Free
Product Specific Notices for CNPase Antibody - BSA Free
Chicken products cannot be exported to Canada.
Purification Notes
After repeated injections, immune eggs were collected, the IgY fractions were purified from the yolks, and then affinity-purified using a peptide column. The concentrations of the eluates were then adjusted to 100 ug/ml, and the preparation was filter-sterilized.
Storage Notes
Store at 4C in the dark. Under these conditions, the antibodies should have a shelf life of at least 12 months (provided they remain sterile). Do not freeze these antibodies unless you want to store them for longer periods of time. Note, however, that each time an antibody preparation is frozen, about half of its binding activity is lost.
This product is for research use only and is not approved for use in humans or in clinical diagnosis. Primary Antibodies are guaranteed for 1 year from date of receipt.
![Immunohistochemistry: CNPase Antibody [NB100-1935] Immunohistochemistry: CNPase Antibody [NB100-1935]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/CNPase-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-NB100-1935-img0001.jpg)