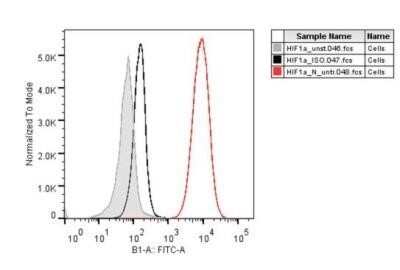
HIF-1 alpha Antibody (H1alpha67) - Azide and BSA Free
Novus Biologicals, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # NBP2-80760

Conjugate
Catalog #
Key Product Details
Validated by
Biological Validation
Species Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat, Porcine, Bovine, Canine, Feline, Ferret, Monkey, Primate, Rabbit, Sheep, Xenopus
Applications
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation, Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP), CyTOF-ready, ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Gel Super Shift Assays, Immunoassay, Immunoblotting, Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Immunohistochemistry-Frozen, Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin, Immunoprecipitation, In vitro assay, Knockdown Validated, Knockout Validated, Ligand Activation, Proximity Ligation Assay, Tissue Culture Substratum, Western Blot
Label
Unconjugated
Antibody Source
Monoclonal Mouse IgG2B Clone # H1alpha67
Format
Azide and BSA Free
Concentration
1 mg/ml
Product Specifications
Immunogen
This HIF-1 alpha Antibody (H1alpha67) was developed against a fusion protein containing amino acids 432 - 528 of human HIF-1 alpha [Uniprot# Q16665].
Reactivity Notes
Xenopus reactivity was reported in scientific literature (PMID: 18303027). Please note that this antibody is reactive to Mouse and derived from the same host, Mouse. Additional Mouse on Mouse blocking steps may be required for IHC and ICC experiments. Please contact Technical Support for more information. Canine reactivity reported in scientific literature (PMID: 24153191, 29974500). Feline reactivity reported in scientific literature (PMID: 30419801).
Localization
HIF-1 is a nuclear protein
Clonality
Monoclonal
Host
Mouse
Isotype
IgG2B
Theoretical MW
93 kDa.
Disclaimer note: The observed molecular weight of the protein may vary from the listed predicted molecular weight due to post translational modifications, post translation cleavages, relative charges, and other experimental factors.
Disclaimer note: The observed molecular weight of the protein may vary from the listed predicted molecular weight due to post translational modifications, post translation cleavages, relative charges, and other experimental factors.
Scientific Data Images for HIF-1 alpha Antibody (H1alpha67) - Azide and BSA Free
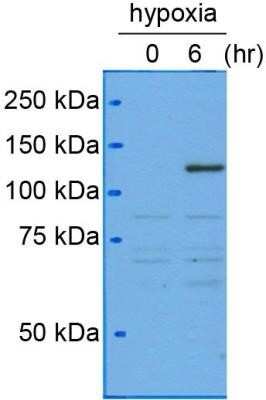
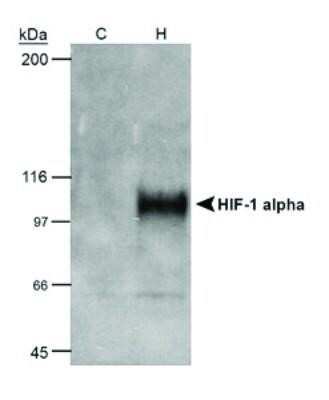
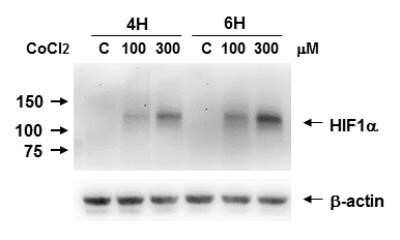
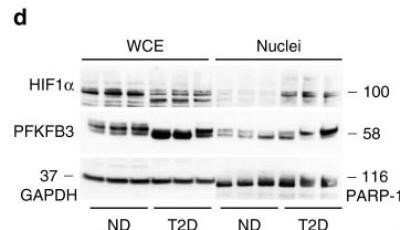
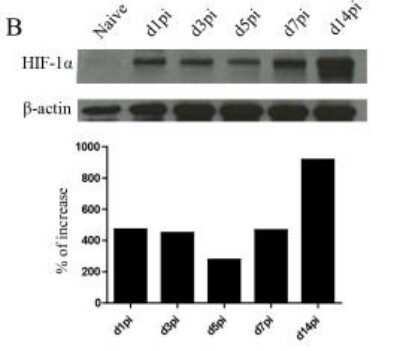
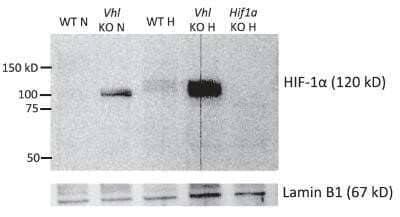
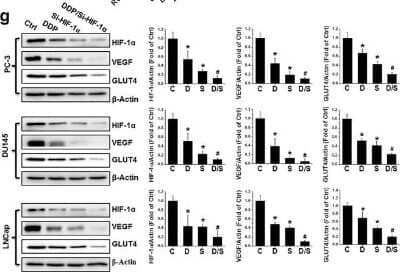
Detection of HIF-1 alpha by Western Blot in Multiple Cells Lines with Various Treatments
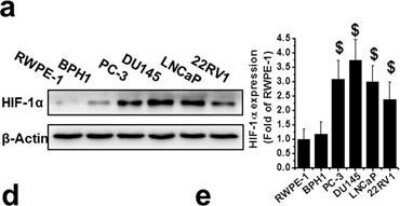
Upregulation of HIF-1alpha in human PCa. Protein expression of HIF-1alpha, VEGF, and GLUT4 were examined with western blot, in PC-3, DU145, and LNCaP cells after various treatments as indicated. Data are expressed as mean +/- SD of seven independent experiments. $p < 0.05 versus RWPE-1 or BPH1 cells or normal tissue. *p < 0.05 versus control group. #p < 0.05 versus si-HIF-1alpha or DDP group. Original blots are shown in Supplementary Figure 5. C: Ctrl; D: DDP; S: si-HIF-1alpha; D/S: DDP/si-HIF-1alpha. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-07973-4), licensed under a CC-BY license. Image from the standard format of this antibody.Staining of HIF-1 alpha in DFOA Treated and non-Treated HeLa Cells
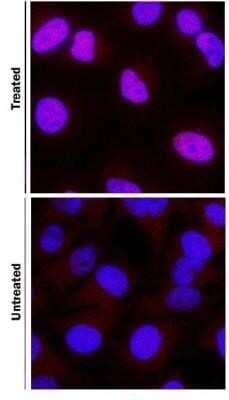
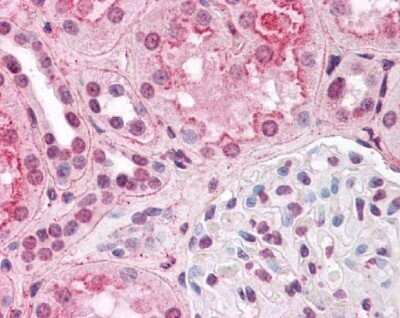
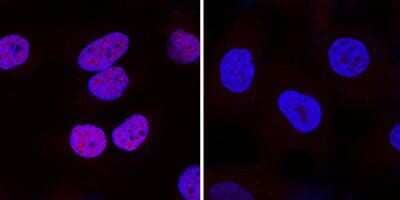
HIF-1 alpha was detected in immersion fixed HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cell line treated with DFOA using 1 ug/mL of mouse anti-HIF-1 alpha monoclonal antibody NB100-105. Cells were stained using a donkey anti-rabbit secondary antibody and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Image from the standard format of this antibody.Immunohistological Staining of HIF-1 alpha in Paraffin Embedded Human Glioblastoma Multiforme
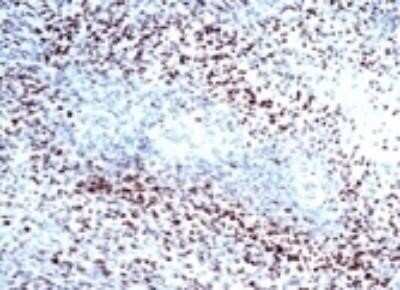
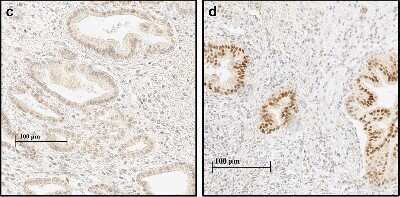
Analysis using the biotin conjugate of NB100-105. Staining of human glioblastoma multiforme.Applications for HIF-1 alpha Antibody (H1alpha67) - Azide and BSA Free
Application
Recommended Usage
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
1 - 5 ug/IP. Use reported in scientific literature
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
1-5 ug/IP
ELISA
1:100 - 1:2000. Use reported in scientific literature (PMID 20042684)
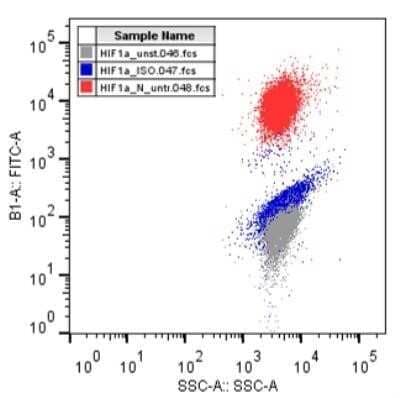
Flow Cytometry
1:10 - 1:1000
Gel Super Shift Assays
1:1 - 1:100. Use reported in scientific literature (PMID 22411794)
Immunoassay
reported in scientific literature (PMID 26147748)
Immunoblotting
reported in multiple pieces of scientific literature
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence
1:50
Immunohistochemistry-Frozen
1:20 - 1:50
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin
1:20 - 1:50
Immunoprecipitation
1:10 - 1:500
In vitro assay
reported in multiple pieces of scientific literature
Knockout Validated
reported in scientific literature (PMID 26861754)
Ligand Activation
reported in scientific literature (PMID 26147748)
Proximity Ligation Assay
reported in scientific literature (PMID 27595394)
Application Notes
In WB, a band can be seen at 120 kDa representing HIF-1 alpha in induced tissues and cells. Multiple bands may be seen at 100-120 kDa representing post-translational modification of HIF-1 alpha. For WB, testing on nuclear extracts is recommended. We recommend the use of a highly sensitive ECL reagent, such as West Pico PLUS, for Western blot detection.
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Protein G purified
Formulation
PBS
Format
Azide and BSA Free
Preservative
No Preservative
Concentration
1 mg/ml
Shipping
The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below.
Stability & Storage
Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
Background: HIF-1 alpha/HIF1A
HIF-1 or hypoxia inducible factor 1 (predicted molecular weight 93kDa), is a transcription factor commonly referred to as a "master regulator of the hypoxic response" for its central role in the regulation of cellular adaptations to hypoxia. In its active form under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1 is stabilized by the formation of a heterodimer of HIF-1 alpha and ARNT/HIF-1 beta subunits. Nuclear HIF-1 engages p300/CBP for binding to hypoxic response elements (HREs). This process induces transcription and regulation of genes including EPO, VEGF, iNOS2, ANGPT1 and OCT4 (4,5).
Under normoxic conditions, the HIF-1 alpha subunit is rapidly targeted and degraded by the ubiquitin proteasome system. This process is mediated by prolyl hydroxylase domain enzymes (PHDs), which catalyze the hydroxylation of key proline residues (Pro-402 and Pro-564) within the oxygen-dependent degradation domain of HIF-1 alpha. Once hydroxylated, HIF-1 alpha binds the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein (pVHL) for subsequent ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation (4). pVHL dependent regulation of HIF-1 alpha plays a role in normal physiology and disease states. Regulation of HIF-1 alpha by pVHL is critical for the suppressive function of FoxP3+ regulatory Tcells (6). Repression of pVHL expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) B cells leads to HIF-1 alpha stabilization and increased VEGF secretion (7).
References
1. Semenza, G. L., Agani, F., Feldser, D., Iyer, N., Kotch, L., Laughner, E., & Yu, A. (2000). Hypoxia, HIF-1, and the pathophysiology of common human diseases. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology.
2. Muz, B., de la Puente, P., Azab, F., & Azab, A. K. (2015). The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia. https://doi.org/10.2147/hp.s93413
3. Huang, Y., Lin, D., & Taniguchi, C. M. (2017). Hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) in the tumor microenvironment: friend or foe? Science China Life Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-017-9178-y
4. Koyasu, S., Kobayashi, M., Goto, Y., Hiraoka, M., & Harada, H. (2018). Regulatory mechanisms of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activity: Two decades of knowledge. Cancer Science. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13483
5. Dengler, V. L., Galbraith, M. D., & Espinosa, J. M. (2014). Transcriptional regulation by hypoxia inducible factors. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. https://doi.org/10.3109/10409238.2013.838205
6. Lee, J. H., Elly, C., Park, Y., & Liu, Y. C. (2015). E3Ubiquitin Ligase VHL Regulates Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 alpha to Maintain Regulatory T Cell Stability and Suppressive Capacity. Immunity. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2015.05.016
7. Ghosh, A. K., Shanafelt, T. D., Cimmino, A., Taccioli, C., Volinia, S., Liu, C. G., ... Kay, N. E. (2009). Aberrant regulation of pVHL levels by microRNA promotes the HIF/VEGF axis in CLL B cells. Blood. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-10-185686
Long Name
Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1 Subunit Alpha
Alternate Names
BHLHE78, HIF 1A, HIF-1a, HIF1 alpha, HIF1A, MOP1, PASD8
Gene Symbol
HIF1A
Additional HIF-1 alpha/HIF1A Products
Product Documents for HIF-1 alpha Antibody (H1alpha67) - Azide and BSA Free
Product Specific Notices for HIF-1 alpha Antibody (H1alpha67) - Azide and BSA Free
This product is for research use only and is not approved for use in humans or in clinical diagnosis. Primary Antibodies are guaranteed for 1 year from date of receipt.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...