Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Mouse Brain, Neurons 40X
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Detection of human HIF1-alpha by immunohistochemistry. Sample: FFPE section of renal cell carcinoma. Antibody: Affinity purified rabbit anti-HIF1-alpha antibody (NB110-58773). Detection: DAB
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Detection of Human HIF-1 alpha by Western Blot and Immunoprecipitation. Samples: Whole cell lysate (5, 15 and 50 ug for WB; 1 mg for IP, 20% of IP loaded) from HeLa cells that were either treated with cobalt chloride (+; 200 uM) or mock treated (-). Antibodies: Affinity purified rabbit anti-HIF1 alpha antibody used for WB at 0.1 ug/mL(A) and 1 ug/mL (B) and used for IP at 3 ug/mg lysate. HIF-1 alpha was also immunoprecipitated by a previous lot of this antibody. Detection: Chemiluminescence with exposure times of 30 seconds (A) and 10 seconds (B).
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Blot showing the effect of hypoxia on the protein expression levels of the purine biosynthetic enzymes. HIF-1 alpha is stabilized in hypoxia as expected, and no significant increase in the purine enzymes was detected between normoxic (21% oxygen) and hypoxic (1% oxygen) growth conditions. The positions of molecular markers surrounding each band of interest are shown for each blot. ADSL (NBP2-03107), ATIC (NBP2-01941), FGAMS (NBP1-84691), GART (H00002618-M01), HIF-1a (NB100-449), PAICS (NBP2-02817), PPAT (NBP2-02056). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (//pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32439803/) licensed under a CC-BY license.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Murine primary bone marrow derived macrophages stained with HIF1-alpha antibody (red). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Image from verified customer review.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Analysis of microvascular density and HIF-1alpha activity. Low, homogenous expression of HIF-1alpha was detected in the tumors of NNK treated mice (40X, scale bar = 25 um). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1476-4598-11-4), licensed under a CC-BY license.
Flow Cytometry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Flow Cytometry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HeLa cells were treated for 15 hrs with 200 uM CoCl2, fixed in PFA, and permeabilized in 90% MeOH. 1 X 10^6 cells were stained with 0.125 ug anti-HIF-1 alpha and secondary FITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit (in a 150 uL reaction). Black: treated, anti-KLH control IgG; Red: untreated, anti-HIF-1 alpha; Blue: treated, anti-HIF-1 alpha.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Analysis of HIF-1 alpha in human myeloma cell lysate using anti-HIF-1 alpha. Cells were untreated or treated with IGF-1, IL-6 or CoCl2. Image from verified customer review.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Detection of HIF-1 alpha in a hypoxic sample. Lane 1: CoCl2 treated Cos-7 nuclear extract (hypoxic). Lane 2: Untreated Cos-7 nuclear extract (normoxic).
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Detection of mouse HIF-1 alpha on hypoxia treated MEFs
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Samples: Whole cell lysate (5, 15 and 50 ug) from HeLa cells that were treated with cobalt chloride (+; 200 uM) or mock treated (-). Antibodies: Affinity purified rabbit anti-HIF1 alpha antibody NB100-449 used for WB at 0.1 ug/ml. Detection: Chemiluminescence with exposure times of 30 seconds.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - BMDM were seeded at 0.5x10^6 overnight. Cells were treated with 10 ng/ml LPS for 24 hrs. Image from verified customer review.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Analysis of total protein using anti-HIF-1 alpha, -CAIX, -ISCU antibodies and VDACs antibody (PMID: 29596470).
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Analysis of total protein using anti-HIF-1 alpha, -ISCU, -FXN antibodies. CoCl2 was used to treat or not HeLa cells for 2 days (PMID: 29596470).
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Detection of human HIF1 alpha by western blot. Samples: Whole cell lysate (15 and 50 ug) from HEK293T cells that were either treated with 200 uM cobalt chloride (+) or mock treated (-). Antibodies: Affinity purified rabbit anti-HIF1 alpha antibody NB100-449 used for WB at 0.1 ug/ml. Detection: Chemiluminescence with exposure times of 3 minutes.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - 3T3-L1 mouse embryonic fibroblast adipose-like cell line. Antibody at 1:2000. WB image submitted by a verified customer review.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Formaldehyde-fixed asynchronous HeLa cells.
Immunoprecipitation: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Immunoprecipitation: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha analysis in HEK293 cells. Image from verified customer review.
Immunoprecipitation: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]
Immunoprecipitation: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Detection of human HIF1 alpha by western blot of immunoprecipitates. Samples: Whole cell lysate (1 mg for IP, 20% of IP loaded) from HEK293T cells that were treated with 200 uM cobalt chloride. Antibodies: Affinity purified rabbit anti-HIF1 alpha antibody NB100-449 used for WB at 1 ug/ml and for IP at 6 ug/mg lysate. Detection: Chemiluminescence with exposure times of 3 minutes.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
beta-Glucan size affects the requirement for reactive oxygen species (ROS) in IL-1 beta induction.(B) Human mDCs from healthy donors or chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) patients were stimulated with curdlan or glucan-mp for 8 h. HIF-1 alpha and pro-IL-1 beta protein expression measured by immunoblot (n = 2 donors).
Western Blot: Rabbit Polyclonal HIF-1 alpha Antibody -
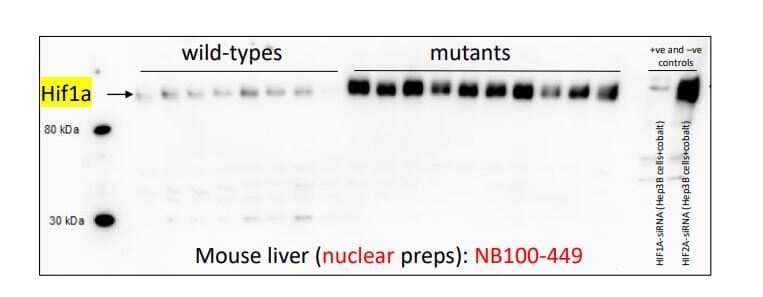
Western Blot: Rabbit Polyclonal HIF-1 alpha Antibody - Analysis of HIF-1 alpha antibody on mouse liver nuclear extracts. Image from a verified customer review.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
HIF-1 alpha/2 alpha expression in myeloid-specific KO mice targeting the HIF pathway. (A) Images of the colon of wild-type (WT), myeloid-specific Hif-1a KO (hMRP8 Hif-1a KO) or von Hippel Lindau (Vhl) KO (hMRP8 Vhl KO) mice, immunostained for MRP8 (green) & the DNA-binding regions of Hif-1a mRNA (red). Mice were fed with 5% DSS for 4 days prior to immunostaining analyses. Note that there were no MRP8-positive cells that were positive for Hif-1a mRNA in hMRP8 Hif-1a KO (middle column) mice, but we observed many cells that were double positive for MRP8 & Hif-1a mRNA in hMRP8 Vhl KO mice (right column). (B) Images of the colon of hMRP8 Vhl KO mice fed with 5% DSS as in A, immunostained for MRP8 (green) & HIF-1 alpha (red, upper row) or HIF-2 alpha (red, bottom row). DAPI-stained nuclei are shown in blue. White boxes in A & B indicate the regions magnified in the lower or right images, respectively. Yellow arrowheads in A & B indicate cells positive for both markers. Scale bars: 100 μm. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29967068), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Analysis of microvascular density & HIF-1 alpha activity. Microvascular density of pulmonary tumors was significantly higher in hyperplastic (B) & tumoral lesions (D) of NNK/NTHi treated mice compared to the NNK treated mice (A, & C) detected by CD105 immunostaining (10X, scale bar = 100 μm). HIF-1 alpha immunostaining after NNK/NTHi combined treatment showed hot-spots of high stromal expression in tumors (F), & high expression in perivascular-peribronchiolar lymphocytes (H). In contrast, low, homogenous expression of HIF-1 alpha was detected in the tumors (E) & perivascular-peribronchiolar lymphocytes (G) of NNK treated mice (40X, scale bar = 25 μm). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1476-4598-11-4), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Chronic ethanol feeding enhances tumorigenesis markers during AOM/DSS-induced tumorigenesis. AOM/DSS-induced colonic tumorigenesis was induced with (EF) or without (PF) 4 % ethanol feeding as described in Methods section. Cryosections of distal colon were stained for VEGF (a) pSmad (b), or HIF1 alpha (c), & co-stained for F-actin & nucleus. Images presented are representative of n of 5 for each group Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26951793), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Treatment with HBOT or PFD decreased HIF-1 alpha expression in the AD lesions.IHC for HIF-1 alpha (A). Scale bar is 100 µm. HIF-1 alpha+ area was measured in five fields chosen at random by using image analysis software (B). RT-PCR for HIF-1 alpha (C). NT, not treated. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 12). *P<0.05, compared with the control group; ¶P<0.05, compared with the AD-NT group; §, P<0.05, compared with the AD-Steroid group. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25275529), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Elevated PIK3/AKT/HIF-1 alpha pathways in KL SqCC tumours.(a,b) Analysis of TCGA gene expression (normalized TPM) & PIK3CA (a) & PTEN (b) genomic copy number alteration profiles. Each dot represents one SqCC patient (n=501). Boxes represent the interquartile range & whiskers are drawn to the minimum & maximum. Kruskal–Wallis non-parametric ANOVA, ****P<0.0001, ***P<0.001, **P<0.01. (c) IHC analysis (top) & quantification (bottom) of p63, p-AKT, p-S6, p-4EBP1, HIF-1 alpha & GLUT1 in KL tumours (n=6 each group). Two-tailed t-test, ****P<0.0001, ***P<0.001, **P<0.01. Scale bar, 50 μm. (d) Immunoblot analysis of HIF-1 alpha & GLUT1 in control shGFP & shHIF-1 alpha knockdown SqCC cell lines, HCC95 & HCC1588. All error bars represent the mean±s.e.m. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28548087), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Analysis of microvascular density & HIF-1 alpha activity. Microvascular density of pulmonary tumors was significantly higher in hyperplastic (B) & tumoral lesions (D) of NNK/NTHi treated mice compared to the NNK treated mice (A, & C) detected by CD105 immunostaining (10X, scale bar = 100 μm). HIF-1 alpha immunostaining after NNK/NTHi combined treatment showed hot-spots of high stromal expression in tumors (F), & high expression in perivascular-peribronchiolar lymphocytes (H). In contrast, low, homogenous expression of HIF-1 alpha was detected in the tumors (E) & perivascular-peribronchiolar lymphocytes (G) of NNK treated mice (40X, scale bar = 25 μm). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1476-4598-11-4), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Immunolocalization of HIF1A in limbs.Immunoreactivity was detected in control limbs in the apical ectodermal ridge & interdigital regions (I.R.). The mesenchymal condensations/developing cartilaginous anlagen (Digits) were not immunoreactive. 4-OOHCPA treatment resulted in a concentration- & time-dependent increase in HIF1A immunoreactivity in this area in the 3 & 6 h exposure groups; staining was diminished by 24 h. Four separate replicates were done. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0051937), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Effects of cell stress on VEGF-A & HIF1 alpha expression in Müller cells & Y79 photoreceptors. (A) VEGF-A was measured by ELISA using conditioned media collected from MIO-M1 & Y79 cells, n = 4–5/group in Müller cells & n = 8/group in Y79 photoreceptors, ** p < 0.01; (B) Western blots for HIF1 alpha using cellular proteins, n = 4/group, ** p < 0.01. For MIO-M1 Müller cells: Grey bars: 5 mM glucose. Black bars: 25 mM glucose. For Y79 photoreceptors: Grey bars: 11 mM glucose. Black bars: 25 mM glucose. NS, not significant; LG, low glucose; HG, high glucose. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (http://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/18/3/533), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Analysis of microvascular density & HIF-1 alpha activity. Microvascular density of pulmonary tumors was significantly higher in hyperplastic (B) & tumoral lesions (D) of NNK/NTHi treated mice compared to the NNK treated mice (A, & C) detected by CD105 immunostaining (10X, scale bar = 100 μm). HIF-1 alpha immunostaining after NNK/NTHi combined treatment showed hot-spots of high stromal expression in tumors (F), & high expression in perivascular-peribronchiolar lymphocytes (H). In contrast, low, homogenous expression of HIF-1 alpha was detected in the tumors (E) & perivascular-peribronchiolar lymphocytes (G) of NNK treated mice (40X, scale bar = 25 μm). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1476-4598-11-4), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Phenylhydrazine administration results in hypoxia in retinal vessels & in HIF-1 alpha & HIF-2 alpha stabilization in peripheral blood leukocytes.(A) 3-dimensional reconstructed imaging of the superficial vascular plexus of flat mounted retinae of mice (steady state, treated with PHZ & treated with PHZ & peak EIU induction) stained with DAPI, hypoxyprobe & Isolectin B4. (B) Representative analysis of HIFs by western blot: 50ug of protein from total cell lysate of blood leukocytes isolated from mice treated with PHZ compared to untreated; (C) relative densitometry quantification of HIF western blots from PBMC showing mean, n = 3, error bar showing SD, unpaired t test, ***P < 0.001. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28112274), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunohistochemistry-Frozen: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Immunohistochemistry-Frozen: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Ethanol elevates tumorigenic markers & nuclear localization of HIF1 alpha in colonic crypts during AOM/DSS-induced tumorigenesis: AOM/DSS-induced colonic tumorigenesis was induced with or without 4 % ethanol feeding as described in Methods section. a & b Colonic mucosal extracts were immunoblotted for pSmad & VEGF (a), & the band density evaluated using Image J software (b). Values are mean ± SE (n = 3). Asterisks indicate the values that are significantly different (p < 0.05) from corresponding values for AOM/DSS group. c Cryosections of colon were stained for HIF1 alpha (red) & nucleus (blue). Sections of the images from Fig. 2c are enlarged to show the detailed localization of HIF1 alpha in the nucleus. While arrows indicate nuclear co-localization of HIF1 alpha Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26951793), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Dectin-1-induced NADPH oxidase-derived ROS is required for augmented IL-1 beta during TSLPR inhibition. (A) Human mDC derived from healthy donors (HD) or CGD patients were stimulated with SC glucan for 8 h (n = 2 representative donors presented, three separate experiments performed). Pro-IL-1 beta, IL-1 beta, HIF-1 alpha, phospho-AMPK, AMPK & beta-actin were measured by immunoblot. (B–E) Densitometry of cumulative data was performed using Image Studio Lite software with pro-IL-1 beta, IL-1 beta & HIF-1 alpha normalized to beta-actin & phospho-AMPK normalized to total AMPK. Data is reported as percentage of maximal signal observed within each donor (n = 3 independent donors, presented as pooled data). (F–H) Human mDC derived from HD or CGD patients were stimulated with SC glucan, CA glucan or heat killed C. albicans hyphae with anti-TSLPR or IgG isotype control antibodies for 24 h (n = 3 independent donors, presented as pooled data). IL-1 beta was measured in 24-h cell culture supernatants by ELISA. Cumulative data displayed as mean +SEM. Statistical analysis calculated using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests (***p = 0.001,*p = 0.05). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31139177), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Reactive oxygen species production & expression of stabilized HIF1 alpha & AMPK subunit alpha2 & in H1299 & H1299r cells(A) H1299, H1299r, P31 & P31r cell were seeded at a density of 250,000 cells/well & left for 24 h. The cells were then stained with 10 μmol/L dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA). Fluorescence was analysed for 10,000 events. Whole cell lysates were prepared from confluent cultures of H1299, H1299r cells. Proteins (90 μg) were resolved in 10% SDS-PAGE gels & transferred to a PVDF membrane. (B) Representative blot of HIF1 alpha protein expression. (C) Representative blot of AMPK subunit alpha2 protein expression from four independent experiments. (D) Bar chart of AMPK subunit alpha2 mean for four separate measurements. Statistical analyses was carried out using the student t-test. ** = p<0.01, * = p<0.05. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.oncotarget.com/lookup/doi/10.18632/oncotarget.21885), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Pyruvate kinase isoform M2 (PKM2) & hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (Hif-1 alpha) bind directly to the promoter region of PDL1 in primary murine BMDM cells. BMDM cells were treated with TEPP-46 at 50 µM for 1 h prior to stimulation with LPS (100 ng/ml, 24 h) (A). Binding of PKM2 (left) or Hif-1 alpha (right) to HRE1 or HRE4 of the PD-L1 promoter was detected by incubating cell lysates with biotinylated oligonucleotides spanning the relevant HRE promoter region. Protein–oligonucleotide complexes were isolated using streptavidin agarose beads, & proteins were detected by western blotting. Representative of n = 3. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-PCR (B) using PKM2 & HIF-1 alpha antibodies & primers specific for three promoter regions of PD-L1 (HRE1, 2–3, & 4) & a known Hif-1 alpha binding region of vascular endothelial growth factor as a positive control showing binding of Hif-1 alpha (left) & PKM2 (right) to the PD-L1 promoter in LPS-treated BMDMs (100 ng/ml, 24 h). (C) Sequential ChIP assays measuring simultaneous endogenous binding of PKM2 & Hif-1 alpha to chromatin in response to LPS (100 ng/ml, 24 h) ±TEPP-46 (pretreatment using 50 µM, 60 min). ChIP data are calculated as percent of input, error bar represents mean ± SEM, & statistics are performed as two-tailed unpaired t-test *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, & ***P < 0.001. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29081778), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Changes in Hepatic Oxygen Saturation & Hypoxia-related Protein Expression. (A) In the representative case, the hepatic oxygen saturation in the experimental group was lower than that in the control group at four, six, & eight weeks (51.6 vs. 54.5%, 48.4 vs. 53.9%, 32.3 vs. 43.2%, & 31.2 vs. 42.9%). (B) There was significant decrease of oxygen saturation of liver parenchyma in the experimental group compared to those of control group (45.2 vs. 51.9%, 43.0 vs. 49.0%, & 31.3 vs. 49.7%) at the four, six, & eight weeks, respectively (P < 0.001). (C) In the Western blot analysis, the experimental group was relatively higher expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1 alpha) & vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) protein than the control group at eight weeks. The full-length blots with these antibodies were presented in supplementary Figure S1. (D,E) The experimental group showed significantly higher expression of HIF-1 alpha & VEGF protein than the control group at eight-week (1.47 ± 0.48 vs. 0.19 ± 0.08 & 0.96 ± 0.23 vs. 0.33 ± 0.06, P = 0.019 & P < 0.018). *P < 0.05. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29079853), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - BCAT1 expression & inhibition in human macrophages.(a) RNA-sequencing in human monocyte-derived macrophages (hMDMs) shows mRNA copies of BCAT enzymes in normalized counts. n=14 healthy donor hMDMs were used for RNA-seq. (b) Chemical structure of ERG240 & leucine. (c) Enzymatic activity of recombinant human BCAT1 & BCAT2 in presence of ERG240. (d) Relative expression of IRG1, HIF1A & IL1B measured by qRT-PCR in control, ERG240-treated (20 mM, 3 h), LPS treated (100 ng ml−1, 3 h), & LPS+ERG240 treated (LPS, 100 ng ml−1; ERG240, 20 mM for 3 h) hMDMs. ns, non-significant. All expression values are normalized to those obtained for HPRT gene expression. n=3 healthy donor hMDMs were used in each group. (e) Western blot analysis of IRG1, IL-1 beta, HIF-1 alpha & beta-actin (ACTB) in control (untreated), ERG240-treated (20 mM, 3 h), LPS treated (100 ng ml−1, 3 h) & LPS+ERG240 treated (LPS, 100 ng ml−1; ERG240, 20 mM for 3 h) hMDMs. The experiment is representative of three independent experiments using n=3 healthy donor hMDMs each. (f) GC/MS results showing itaconic acid production in hMDMs in presence or absence of ERG240 (20 mM). LPS treatment was for 8 h (100 ng ml−1). GC/MS plot for each donor is shown separately where itaconate abundance denotes arbitrary units. Error bars are s.e.m. Significance was tested using two-tailed Student’s t-test or one-way ANOVA. * P<10−3 following two-way ANOVA. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms16040), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha/2 alpha expression in myeloid-specific KO mice targeting the HIF pathway. (A) Images of the colon of wild-type (WT), myeloid-specific Hif-1a KO (hMRP8 Hif-1a KO) or von Hippel Lindau (Vhl) KO (hMRP8 Vhl KO) mice, immunostained for MRP8 (green) & the DNA-binding regions of Hif-1a mRNA (red). Mice were fed with 5% DSS for 4 days prior to immunostaining analyses. Note that there were no MRP8-positive cells that were positive for Hif-1a mRNA in hMRP8 Hif-1a KO (middle column) mice, but we observed many cells that were double positive for MRP8 & Hif-1a mRNA in hMRP8 Vhl KO mice (right column). (B) Images of the colon of hMRP8 Vhl KO mice fed with 5% DSS as in A, immunostained for MRP8 (green) & HIF-1 alpha (red, upper row) or HIF-2 alpha (red, bottom row). DAPI-stained nuclei are shown in blue. White boxes in A & B indicate the regions magnified in the lower or right images, respectively. Yellow arrowheads in A & B indicate cells positive for both markers. Scale bars: 100 μm. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29967068), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Increased infiltration of myeloid cells expressing HIF-1 alpha in DSS-induced colitis. (A) Western blot analysis of MRP8, F4/80 or actin using the whole colon tissue lysate from mice fed with water or 5% DSS for 4 days. (B) Images of the colon of mice fed with water or 5% DSS, immunostained for myeloid cells using anti-MRP8 (green) or anti-HIF-1 alpha (red) antibodies. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. White rectangles indicate the areas magnified in the images shown below. Yellow arrowheads indicate cells with colocalization of MRP8 & HIF-1 alpha. Quantification of MRP8-positive cells & percentage of those expressing HIF-1 alpha are shown as bar graphs on the right-hand side. Data are mean±s.e.m. for at least three independent fields examined per mouse (n≥3 per group). **P<0.01 & ***P<0.001, assessed by Student's t-test. HPF, high-powered field. (C) Images of the colon of mice fed with 5% DSS, immunostained for MRP8 (red) & CD11b (green). DAPI-stained nuclei are shown in blue & a merged image is also shown. Scale bars: 100 μm. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29967068), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Increased HIF-1 alpha expression is regulated by TSLPR inhibition & not IL-1 beta secretion (A) Human mDC were stimulated with SC glucan with either anti-TSLPR or IgG isotype control antibodies for 8 h in the presence or absence of IL-1 beta neutralization antibodies (n = 1 representative donor presented, three separate experiments performed). Pro-IL-1 beta, IL-1 beta, HIF-1 alpha, phospho-p38 MAPK, p38 MAPK, phospho-AMPK, AMPK & beta-actin were measured by immunoblot. (B,C) Densitometry of cumulative data was performed using Image Studio Lite software with HIF-1 alpha normalized to beta-actin & phospho-AMPK normalized to AMPK. Data is reported as percentage of maximal signal observed within each donor (n = 3 independent donors, presented as pooled data). Cumulative data displayed as mean +SEM. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31139177), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - miR-18b (miR-18b-5p) regulates Hif1 alpha & reduces apoptosis in mtNSC-34 cells. a Overexpressed miR-18b (miR-18b-5p) decreased Hif1 alpha & Mef2c proteins. Both Mctp1 & Rarb expression were increased by miR-18b (miR-18b-5p). Downregulated Bax & upregulated Bcl2 by miR-18b (miR-18b-5p) diminished apoptosis in mtNSC-34 cells. b RT-qPCR analysis showed low expression of Hif1 alpha & Mef2c mRNAs. c Mctp1 & Rarb transcripts were highly expressed by miR-18b (miR-18b-5p). d Bax mRNAs were decreased & Bcl2 mRNAs were increased by overexpressed miR-18b. e miR-18b (miR-18b-5p) was overexpressed in mtNSC-34 cells. f miR-206 was reduced by miR-18b (miR-18b-5p). g LDH release analysis explained that transfected miR-18b (miR-18b-5p) restores apoptosis. h Luciferases assay with 3′ UTR of Hif1 alpha showed that Hif1 alpha is target of miR-18b in contNSC-34 cells. i & j Overexpression of miR-18b (miR-18b-5p) enhanced neuronal differentiation (MAP2) & attenuated intracellular Ca2+ levels (Cont (0.098) versus miR-18b (miR-18b-5p) (0.051) in fluorescence intensities from baseline 490/525 ratio) in mtNSC-34 cells. Empty vector served as a negative control (Cont). Arrow represents SOD1 aggregation (green). Scale bar, 40 μm. Significantly different at *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005. The experiments were replicated 5 times Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32605607), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Hypoxic conditions upregulate CNN3 in BeWo cells.BeWo cells were cultured either under normoxic or under hypoxic conditions for 24(A) Total protein lysates were examined with the Western Blot technique to detect CNN3 protein levels. For normalization, HPRT was stained on the same membrane. As hypoxia marker, HIF-1 alpha was detected as well. (B) Protein bands of CNN3 & HPRT were densitometrically measured on the Western Blot membrane & CNN3/HPRT levels are plotted in the graph (white column: normoxia; black column: hypoxia). n = 3. (C) BeWo cells were serum starved for 16 h & then treated with either PBS as control or 200 µM CoCl2 for 6 h in serum free medium. Then total protein was isolated & a Western Blot was performed. The HIF-1 alpha, CNN3 & HPRT protein was detected on the membrane with specific antibodies. (D) A densitometric analysis was performed to determine CNN3/HPRT levels (white column: normoxia; black column: hypoxia). n = 3. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25050546), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Dynamics of the hypoxia-triggered decrease in MET phosphorylation & its reversal upon reoxygenation(A) MCF10A cells were incubated under normoxia or hypoxia for 1 h. They were then treated, under the same oxygen pressure, with 10 ng/mL HGF/SF for 5, 10, 20, 30, 60, 90 & 120 minutes. A control (Ctrl) without any HGF/SF stimulation was also performed. The same amount of protein was analyzed by western blotting with antibodies directed against: phosphorylated residues in the MET kinase domain, the MET kinase domain, the hypoxia marker HIF1a, phosphorylated Akt, Akt, Erk2, phosphorylated Erk, & actine. The positions of prestained molecular weight markers are indicated. Arrows indicate the positions of precursor & mature full-length MET. (B) MCF10A cells were incubated under hypoxia for 5, 10, 15 or 30 minutes. Another set of cells were incubated under hypoxia for 1 h & then returned to normoxia for 5, 10, 15 or 30 min (re-oxygenation). A control under normoxic (N) conditions was also included. The same amount of protein was analyzed by western blotting as previously described with the addition of GAB1 & its phosphorylated form. (C) MCF10A cells were placed under normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 1 h or hypoxia for 1 h & then normoxia for 10 minutes (reoxygenation). Cells were then treated at the indicated time with 10 ng/mL of HGF/SF. Cell lysates were incubated for AlphaScreen specific phospho-Erk & phospho-Akt quantitation. Error bars represent standard deviations (n = 3; ± SD). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29930749), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - The role of HIF-1 in purinosome formation.a, quantifying the number of purinosome-containing cells in normoxia or hypoxia (24 h) in purine-rich medium & normoxia in purine-depleted medium (purine -ve), cells in hypoxia transfected with siRNA to HIF-1 alpha (+ siRNA), & cells in purine-rich medium supplemented with DFX. Data shown are n = 3, mean ± S.E., total number of cells counted are shown in parentheses. b, time course of purinosome formation in hypoxia shows the number of purinosome-containing cells steadily increases after 3 h in hypoxia. Re-oxygenation of the samples after hypoxic incubation for 10 h reverts the number purinosome-containing cells back to normoxic levels. Data shown is n = 3, mean ± S.E., total number of cells counted are shown in parentheses. c, time course of HIF-1 alpha stabilization in hypoxia shows maximum HIF-1 alpha protein expression levels at 3 h in hypoxia, after which the HIF-1 alpha expression decreases. The positions of molecular markers are shown for each blot; uncropped blots with overlaid markers are deposited in the raw data files. d, the effect of hypoxia on the transcription of purine biosynthesis enzymes measured by qPCR. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) & HIF-1 alpha are controls. Data shown are n = 5, mean ± S.E. e, the effect of hypoxia on the protein expression levels of the purine biosynthetic enzymes. HIF-1 alpha is stabilized in hypoxia as expected, & no significant increase in the purine enzymes was detected between normoxic (21% oxygen) & hypoxic (1% oxygen) growth conditions. The positions of molecular markers surrounding each band of interest are shown for each blot; uncropped blots with overlaid markers are deposited in the raw data files. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32439803), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - C/EBP delta promotes HIF-1 alpha expression in macrophages through inhibition of FBXW7 alphaa) RT-PCR analysis of FBXW7 isoform expression from different sources as follows. 1, primary peritoneal macrophages (PPMs); 2, RAW 264.7 cells; 3, MMTV-Neu mammary tumour tissue; 4, primary mouse embryo fibroblasts. Numbers indicate the position of size markers in base pairs. (b) RT-qPCR analysis of Fbxw7 transcript levels in PPMs from WT & Cebpd−/− KO mice, cultured +/− LPS (100 ng/ml, 24 h), compared to WT untreated (n=4, *P<0.05; **P<0.001). (c) Western analysis of nuclear extract (NE) from primary human monocytes nucleofected with siRNA oligos (C, control; D, CEBPD; F, FBXW7) & treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) & 1%O2 (16 h) as indicated. SE, short exposure; LE, long exposure. (d) RT-qPCR analysis of FBXW7 & CEBPD transcripts in primary human monocytes as in panel (c) (n=3, *P<0.05; **P<0.001). (e) Western analysis of NE from PPMs nucelofected with siRNA oligos & treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) & 1%O2 for 16 h as indicated. SE, short exposure; LE, long exposure.Where applicable, data are mean±S.E.M., evaluated by two-tailed unequal variance t-test. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23575666), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Hypoxia downregulates CFTR expression. (a) Phase-contrast photographs of MDCK cells treated with normoxia & hypoxia conditions; (b) Western blot showing downregulation of CFTR in the MDCK cells by hypoxia (Full-length blot is shown in Supplementary Figure S7b.); (c) Real time-PCR assay showing decreased mRNA expression of CFTR induced by hypoxia in HK-2 cells,*p < 0.05; (d) Western blot showing decreased expression of CFTR induced by hypoxia in HK-2 cells (Full-length blot is shown in Supplementary Figure S7c.); (e) Western blot showing the expression changes of HIF-1 alpha & EMT markers induced by hypoxia in MDCK cells, quantification analysis is shown in the lower panel, *p < 0.05; (Full-length blot is shown in Supplementary Figure S7d.) (f) Immunofluorescent staining showing dramatically increased HIF-1 alpha & reduced CFTR protein levels in tubular epithelial cells at inner cortices in UUO kidney (arrow). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28701694), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - NRP1 & MET on HT1080 cells are accessible for blood-borne rhodocetin-alpha beta(A) expression of NRP1 & MET by HT1080 cells was proven by flow cytometry. Gray, isotype-matched controls. (B) flow cytometry of NRP1-knockout HT1080 cells demonstrating their NRP1-deficiency & unaffected MET expression. (C) treatment with CoCl2, mimicking a hypoxic tumor micro-environment, induced upregulation of HIF-1 alpha. (D) NRP1, as a downstream target of HIF-1 alpha, is upregulated in HT1080 cells but not in NRP1-knockout HT1080 cells. beta-actin immunoblots show even loading. (E) increased HIF-1 alpha (red) levels in hypoxic tumor regions, which also contained partly (arrows) or completely (open arrows) EC-deficient VM vessels. ECs are stained green & nuclei blue. (F) immunostaining of NRP1 (red) & MET (blue) showed that both proteins were present on HT1080 cells & ECs in tumor tissue. Note the continuity between EC-lined vasculature & EC marker-deficient vessels (arrows in F’). F’, F’’, in oblique view, gating of the green CD31 signal also showed an apical absence of NRP1 on ECs in contrast to MET (open arrows). (G) the fluorescence intensity along a traceroute, averaged over a width of 5 pixels, (rectangle in F) through the endothelium revealed that in ECs NRP1, unlike MET, is absent from the apical side & restricted to the basolateral side. In contrast, on ATV/VM-lining cells (F’, arrows) both NRP1 & MET are accessible from the bloodstream (H). Vertical gray lines in G & H indicate the position of the apical cell border. Original magnification was 400× (E) & 630× (F-F’’). Representative images are shown. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.oncotarget.com/lookup/doi/10.18632/oncotarget.25032), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - NRP1 & MET on HT1080 cells are accessible for blood-borne rhodocetin-alpha beta(A) expression of NRP1 & MET by HT1080 cells was proven by flow cytometry. Gray, isotype-matched controls. (B) flow cytometry of NRP1-knockout HT1080 cells demonstrating their NRP1-deficiency & unaffected MET expression. (C) treatment with CoCl2, mimicking a hypoxic tumor micro-environment, induced upregulation of HIF-1 alpha. (D) NRP1, as a downstream target of HIF-1 alpha, is upregulated in HT1080 cells but not in NRP1-knockout HT1080 cells. beta-actin immunoblots show even loading. (E) increased HIF-1 alpha (red) levels in hypoxic tumor regions, which also contained partly (arrows) or completely (open arrows) EC-deficient VM vessels. ECs are stained green & nuclei blue. (F) immunostaining of NRP1 (red) & MET (blue) showed that both proteins were present on HT1080 cells & ECs in tumor tissue. Note the continuity between EC-lined vasculature & EC marker-deficient vessels (arrows in F’). F’, F’’, in oblique view, gating of the green CD31 signal also showed an apical absence of NRP1 on ECs in contrast to MET (open arrows). (G) the fluorescence intensity along a traceroute, averaged over a width of 5 pixels, (rectangle in F) through the endothelium revealed that in ECs NRP1, unlike MET, is absent from the apical side & restricted to the basolateral side. In contrast, on ATV/VM-lining cells (F’, arrows) both NRP1 & MET are accessible from the bloodstream (H). Vertical gray lines in G & H indicate the position of the apical cell border. Original magnification was 400× (E) & 630× (F-F’’). Representative images are shown. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.oncotarget.com/lookup/doi/10.18632/oncotarget.25032), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - C/EBP delta promotes HIF-1 alpha expression in macrophages through inhibition of FBXW7 alphaa) RT-PCR analysis of FBXW7 isoform expression from different sources as follows. 1, primary peritoneal macrophages (PPMs); 2, RAW 264.7 cells; 3, MMTV-Neu mammary tumour tissue; 4, primary mouse embryo fibroblasts. Numbers indicate the position of size markers in base pairs. (b) RT-qPCR analysis of Fbxw7 transcript levels in PPMs from WT & Cebpd−/− KO mice, cultured +/− LPS (100 ng/ml, 24 h), compared to WT untreated (n=4, *P<0.05; **P<0.001). (c) Western analysis of nuclear extract (NE) from primary human monocytes nucleofected with siRNA oligos (C, control; D, CEBPD; F, FBXW7) & treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) & 1%O2 (16 h) as indicated. SE, short exposure; LE, long exposure. (d) RT-qPCR analysis of FBXW7 & CEBPD transcripts in primary human monocytes as in panel (c) (n=3, *P<0.05; **P<0.001). (e) Western analysis of NE from PPMs nucelofected with siRNA oligos & treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) & 1%O2 for 16 h as indicated. SE, short exposure; LE, long exposure.Where applicable, data are mean±S.E.M., evaluated by two-tailed unequal variance t-test. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23575666), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Dectin-1-induced TSLP negatively regulates pro-IL-1 beta & HIF-1 alpha. (A) Human mDC were stimulated with SC glucan, CA glucan or heat killed C. albicans hyphae with anti-TSLPR antibodies or IgG isotype control for 24 h (n = 6 independent donors, presented as pooled data). Lactate production was measured in cell-culture supernatants using colourmetric L-lactate detection kit. (B) Human mDC were stimulated SC glucan with either anti-TSLP, anti-TSLPR or IgG isotype control antibodies for 8 h (n = 1 representative donor presented, three separate experiments performed). Pro-IL-1 beta, IL-1 beta, HIF-1 alpha, phospho-p38 MAPK, p38 MAPK, phospho-AMPK, AMPK & beta-actin were measured by immunoblot. (C–G) Densitometry of cumulative data was performed using Image Studio Lite software with pro-IL-1 beta, IL-1 beta & HIF-1 alpha normalized to beta-actin & phospho-p38 MAPK & phospho-AMPK normalized to total p38 MAPK & AMPK respectively. Data is reported as percentage of maximal signal observed within each donor (n = 3 independent donors, presented as pooled data). Cumulative data displayed as mean +SEM. Statistical analysis calculated using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests (***p = 0.001). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31139177), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - Involvement of MET in Akt & Erk pathway activation under hypoxiaMCF10A cells were transfected with a pool of three MET-targeting siRNAs (20 nM) or a control siRNA (siCtrl). A control without siRNA was also included (Ctrl) (A). MCF10A cells were transfected with two HIF1a-targeting siRNAs (20 nM), independently or together, or a control siRNA (siCtrl) (B). The cells were then placed for 1 h under normoxic or hypoxic conditions & treated or not for 10 min with 10 ng/mL HGF/SF. In each experiment, the same amount of protein was analyzed by western blotting with antibodies directed against: phosphorylated residues in the MET kinase domain, the MET kinase domain, phosphorylated Akt, Akt, phosphorylated Erk, Erk2, phosphorylated GAB1, GAB1, or hypoxia marker HIF1a. The positions of prestained molecular weight markers are indicated. Arrows indicate the positions of precursor & mature full-length MET & Erk1/2 proteins. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29930749), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - beta-Glucan size affects the requirement for reactive oxygen species (ROS) in IL-1 beta induction. (A) Human monocyte-derived dendritic cell (mDC) stimulated with curdlan or glucan-mp for 8 h. ROS were detected by incubating cells with CellRox Green fluorescence dye & analysis by flow cytometry (representative experiment of two) presented, (B) Human mDCs from healthy donors or chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) patients were stimulated with curdlan or glucan-mp for 8 h. HIF-1 alpha & pro-IL-1 beta protein expression measured by immunoblot (n = 2 donors). (C–L) Human mDC from healthy donors or CGD patients were stimulated with curdlan or glucan-mp for 24 h (n = 6 donors). IL-1 beta, IL-6, IL-23, TSLP, & CCL22 secretion were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, with cumulative data displayed as mean ± SEM. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00791/full), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.

![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB100-449-img0015.jpg)
![Simple Western: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Simple Western: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Simple-Western-NB100-449-img0032.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-NB100-449-img0034.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Knockdown Validated: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Knockdown-Validated-NB100-449-img0050.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-NB100-449-img0047.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB100-449-img0038.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB100-449-img0053.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NB100-449-img0039.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NB100-449-img0052.jpg)
![Flow Cytometry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Flow Cytometry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Flow-Cytometry-NB100-449-img0035.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB100-449-img0033.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB100-449-img0036.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB100-449-img0037.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB100-449-img0042.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB100-449-img0043.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB100-449-img0044.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB100-449-img0045.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB100-449-img0046.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB100-449-img0051.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NB100-449-img0006.jpg)
![Immunoprecipitation: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Immunoprecipitation: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Immunoprecipitation-NB100-449-img0005.jpg)
![Immunoprecipitation: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] Immunoprecipitation: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HIF-1-alpha-Antibody-Immunoprecipitation-NB100-449-img0048.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-271220231253349.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-210202423452449.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415284545.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415304212.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415363719.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241534344.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415384135.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415293325.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415394514.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415291950.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415304256.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Frozen: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241553383.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415532021.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415525284.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241612685.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241552391.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241554543.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241554544.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241612613.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241612635.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-3102024155453.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241554521.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241552522.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241682187.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241683944.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241612654.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415533837.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241612628.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415533827.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241682146.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241682155.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody [NB100-449] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-449_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415541992.jpg)