Staining of HIF-1 alpha in Paraffin Embedded Mouse Kidney with and without Blocking Peptide
Staining in normal mouse kidney showing (A) staining with HIF-1 alpha antibody and (B) blocking peptide used at 10-fold excess concentration. Images provided by Dr Yves Heremans. Please see the product review of NBC1-18422 for additional details.
Detection of HIF-1 alpha in Mouse Hepatocytes in Western Blot
Analysis of HIF-1 alpha in mouse hepatocytes (left lane: normoxic and right lane: hypoxic) using HIF-1 alpha antibody. Western blot image submitted by a verified customer review.
Immunohistological Staining of HIF-1 alpha in Paraffin Embedded Mouse Skin Wound
Analysis in paraffin section of mouse skin wound using NB100-479 at 1:6000. Image courtesy of product review by Ian Darby of RMIT University.
Immunofluorescence Labeling and Confocal Microscopy Analysis of the Distribution of HIF-1 alpha and Abeta in APPsw Cells
Immunofluorescence (IF) labeling and confocal microscopy analysis of the distribution of HIF-1alpha (A1-D1) and Abeta (A2-D2) in APPsw cells. DFO treatment significantly increased HIF-1alpha IF (D1) and reduced the Abeta IF (D2) in APPsw cells compared with controls (A1,A2). (A3-D3) DAPI was used to detect the nucleus (blue). (A4-D4) Merged images from the double channels indicated that DFO has an inhibitory effect on Abeta formation, and is involved in HIF-1alpha stabilization in APPsw cells. Fe treatment (100 uM) decreased HIF-1alpha (B1) and increased the Abeta levels (B2). DFO treatment reversed the reduction of HIF-1alpha (C1) and the increase of Abeta (C2) in cultures pretreated with 100 uM Fe. Scale bar = 20 um. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://journal.frontiersin.org/Article/10.3389/fnagi.2015.00104/abstract) licensed under a CC-BY license.
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Using HIF-1 alpha Antibody in MDA-MB-231 Cells
MDA-MB-231 cells were exposed to 20% or 1% O2 for 16 hours, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) was performed with the indicated antibody (Ab). Primers flanking the HIF binding site in the S100A10 gene were used for qPCR. ChIP image submitted by a verified customer review.
Western Blot Analysis of HIF-1 alpha in PC12 Cells at 20% and 1% Oxygen
Analysis in A. PC12 (rat) cells, 20% oxygen and B. PC12 (rat) cells, 1% oxygen.
Western Blotting of HIF-1 alpha in Treated and Untreated Cos-7 Nuclear Extract
Analysis in a hypoxic sample. Lane 1: CoCl2 treated Cos-7 nuclear extract (50 ug, hypoxic). Lane 2: Untreated Cos-7 nuclear extract (50 ug, normoxic). 10 second ECL exposure.
Detection of HIF-1 alpha in U251 Cells by Western Blot
U251 cells exposed to 4 hour hypoxia (0.5% oxygen) incubation. Western blot image submitted by a verified customer review.
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Staining of HIF-1 alpha in RCC4 Cells
Detection of HIF-1 Alpha (green) in RCC4 cells using NB100-479. Nuclei (Blue) were counterstained using Hoechst 33258.
Immunohistological Staining of HIF-1 alpha in Paraffin Embedded Human Kidney Tumor
Analysis of HIF-1 alpha in human kidney tumor.
Immunohistological Staining of HIF-1 alpha in Human Placenta
Staining of human placenta, villi.
Staining of HIF-1 alpha in i.v. CDDP and i.a. CDDP Administered Tumor Tissue
Effects of different routes of CDDP administration on remaining viable tumor tissue. Representative images of tumor tissue (i.v. CDDP, i.a. CDDP) stained for HIF-1alpha (20X). Scale bar corresponds to 100 um. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://jeccr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13046-016-0392-1), licensed under a CC-BY license.
Immunohistological Imaging of HIF-1 alpha in Preimplantation Embryos
Hif1alpha expression in preimplantation embryos. Co-staining of OCT4 and Hif1alpha in inner cell mass of blastocyst (top) and negative control images without primary antibodies (bottom). Scale bar: 30um. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0154309) licensed under a CC-BY license.
Simple Western Analysis of HIF-1 alpha in MSCs
Simple Western lane view shows lysates of MCF +/- DMOG, BioSpherix MSCs in hypoxic conditions, and BioSpherix MSCs in normoxic conditions loaded at 0.5 mg/ml. A band was detected for HIF-1 alpha at approximately 116 kDa (as indicated) using NB100-479 (1:100 dilution) followed by Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody (042-206, ProteinSimple). This experiment was conducted under standard assay conditions, and using the 12-230 kDa separation module (SW-W004). Non-specific interaction with the 230 kDa Simple Western standard seen with this antibody. Image from an internal validation.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Cofilin phosphorylation is HIF-1 alpha dependent.Wt, shC, and the HIF-1 alpha knock down cell clones c1 and c2 cells were lysed after 24 hrs of normoxia (20% O2) or hypoxia (1% O2). Cell extracts were analysed by Western blots. Note that p-cofilin levels are reduced in c2 and c2 cells compared to wt and shC cells at 20% O2 and 1% O2.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hypoxic markers accumulate in miR-29-sponge Zebrafish hearts. (A) Representative western blot analysis of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF1 alpha) expression in Wild Type & miR-29-sponge Zebrafish heart. In each condition, alpha-tubulin was used as loading control. Three independent experiments were performed. Full-length blot is presented in Supplementary Figure 6.(B) qRT-PCR mRNA analysis of hypoxia associated genes: erythropoietin alpha (epoa); hexokinase2 (hk2); heme oxygenase1a (hmox1a); lactate dehydrogenase A (ldha); cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (p27) in Wild Type (black circles; n = 4) & miR-29-sponge (gray squares; n = 4) Zebrafish hearts expressed as fold-change versus Wild Type samples. *p < 0.05 Vs Wild Type. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-16829-w), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - (a,b) Immunofluorescence staining of (a) HIF-1 alpha (green), the macrophage marker F4/80 (red) & DAPI nuclear stain (blue), & (b) lactate dehydrogenase (LDH, green), F4/80 (red) & DAPI (blue) in WAT of lean & obese mice. Colocalization is shown in the merged image (arrows). Scale bar = 100 µm. (c,d) Relative mRNA expression of (c) Hif1a & Hif2a, & the HIF target genes (d) Vegfa & Glut1 in ATM isolated from lean & obese mice (n = 3). (e) Levels of succinate in ATM of lean & obese mice (n = 6). (f) Relative mRNA levels of the glutamate transporter Slc3a2 in ATM from lean & obese (n = 3). Data is expressed as mean ± s.e.m. *p < 0.05. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32221369), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Increased expression of HIF alpha and/or Twist in A549 & H441 cells induced by the inhibition of PIMT & Thapsigargin(A) Immunoblotting of Slug, ZEB1, Snail1, Twist, & HIF1 alpha in A549 sh-PIMT & sh-control cells. (B, C) Immunoblotting & relative intensity of HIF1 alpha in A549 cells treated with Tg. (D) Immunoblotting of Slug, ZEB1, Snail1, Twist, & HIF1 alpha in si-control cells & si-PIMT H441 cells. (E, F) Immunoblotting & relative intensity of HIF1 alpha in H441 cells treated with Tg. #1 & #2 indicates si-RNA of J-010000-05-0002 & J-010000-07-0002, respectively. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.oncotarget.com/lookup/doi/10.18632/oncotarget.24324), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Histology & immunofluorescence in rat corneal sections. a Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E), b VEGF-A (green); c CCL2 (green); d TNF-alpha (green); e CXCL5 (green); f CD45 (green) & g HIF-1 alpha (green) staining in rat cornea tissue. Nuclear counterstaining by DAPI (blue) in fluorescent images Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10456-018-9594-9), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Increased expression of HIF alpha and/or Twist in A549 & H441 cells induced by the inhibition of PIMT & Thapsigargin(A) Immunoblotting of Slug, ZEB1, Snail1, Twist, & HIF1 alpha in A549 sh-PIMT & sh-control cells. (B, C) Immunoblotting & relative intensity of HIF1 alpha in A549 cells treated with Tg. (D) Immunoblotting of Slug, ZEB1, Snail1, Twist, & HIF1 alpha in si-control cells & si-PIMT H441 cells. (E, F) Immunoblotting & relative intensity of HIF1 alpha in H441 cells treated with Tg. #1 & #2 indicates si-RNA of J-010000-05-0002 & J-010000-07-0002, respectively. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.oncotarget.com/lookup/doi/10.18632/oncotarget.24324), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - White-jaded spleen & muscle in another NOD/SCID mouse model. One-week-old NOD/SCID mice were i.p. infected with EV-A71, & scarified after disease manifestation. aUpper panel: An atrophic & discolored spleen was identified in EV-A71-infected mice. Viral protein (VP1) & HIF1A were both expressed in the infected spleen. Lower panel: A saline control showed a normal-sized spleen with no VP1 & less expression of HIF1A. b Both HIF1A & VEGFA were strongly expressed in the whitened muscles infected with EV-A71, but not detectable in the saline control Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31711481), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - The Neutralizing antibody against nucleolin eliminate HDGF-stimulated AKT/HIF-1 alpha/NF-kappa B/VEGF signaling in SCC4 oral cancer cells. a-d SCC4 cells were treated with recombinant HDGF protein (100 ng/ml) in the presence of anti-NCL or anti-IgG antibody (5 μg/ml) for 24 h before total protein extraction. Cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. beta-actin was used as an internal control for loading & transfer. Data were mean of three experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ns, not statistically significant Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31711427), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hif1 alpha expression in neonatal & adult ovary.(A) Section of P5 ovary showing MVH expression in all oocytes & Hif1 alpha expression only in small oocytes (primary follicles; top). Negative control images without primary antibodies (bottom). Scale bar: 50μm. (B) Section of adult ovary showing absence of Hif1 alpha expression in primary follicles detected with MVH staining (top). Negative control without primary antibody (bottom). Scale bar: 50μm. (C) Section of adult ovary showing Hif1 alpha expression in mature primary oocyte (arrow). Negative control without primary antibody (bottom). Scale bar: 100μm. (D) Image of a Metaphase II oocyte from superovulated three-month-old female showing Hif1 alpha expression. Scale bar: 50μm. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27148974), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Effect of alpha-MSH on HIF-1 alpha expression & activity in B16-F10 melanoma cells during hypoxia.a, b alpha-MSH increased HIF-1 alpha mRNA & protein expression levels during hypoxia. c Cells were transfected with luciferase reporter driven by a promoter region containing HIF-1 alpha-specific binding sites before alpha-MSH treatment at the indicated time & concentration. The luciferase activities were measured immediately & expressed as means ± SD from triplicate experiments. d Relative mRNA expression levels were analyzed by real-time PCR. Data are expressed as fold change compared with control (means ± SD of triplicate experiments). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. alpha-MSH elevated the Bcl-2 family gene expression levels by HIF-1 alpha activation Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30062060), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Increased expression of HIF alpha and/or Twist in A549 & H441 cells induced by the inhibition of PIMT & Thapsigargin(A) Immunoblotting of Slug, ZEB1, Snail1, Twist, & HIF1 alpha in A549 sh-PIMT & sh-control cells. (B, C) Immunoblotting & relative intensity of HIF1 alpha in A549 cells treated with Tg. (D) Immunoblotting of Slug, ZEB1, Snail1, Twist, & HIF1 alpha in si-control cells & si-PIMT H441 cells. (E, F) Immunoblotting & relative intensity of HIF1 alpha in H441 cells treated with Tg. #1 & #2 indicates si-RNA of J-010000-05-0002 & J-010000-07-0002, respectively. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.oncotarget.com/lookup/doi/10.18632/oncotarget.24324), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - (a) Immunofluorescence staining for HIF-1 alpha (red), hypoxia probe pimonidazole (green) & DAPI nuclei (blue) in WAT of obese mice. Boxed region in the merged image shows HIF-1 alpha-positive cells in crown-like structures that are Pimo− (arrows). (b) HIF-1 alpha protein levels in BMDM treated with BSA (control) or BSA-conjugated palmitate (Palm) for 6, 12 & 24 hours. Tubulin is shown as an internal loading control. (c) Fold change in mRNA expression of Hif1a, Vegfa & Il1b in BMDM treated with palmitate or BSA. (d) Relative mRNA expression in BMDM treated as indicated in the presence or absence of a HIF-1 alpha inhibitor. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments & are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. *p < 0.05. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32221369), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hif1 alpha mediates Glut1 induction downstream of Bmp-mTORC1 signaling. a–c Western blot (a, c) or RT-qPCR (b) analyses in primary chondrocytes after 24 h of BMP2 treatment with or without mTOR inhibitors. Rapa: rapamycin. d Western blot analyses in primary chondrocytes in response to BMP2 with or without the Hif1 alpha inhibitors for 24 h. Quantification of all western blots denotes average fold change over vehicle control after normalization to beta-actin (±SD, n = 3). *p < 0.05, n = 3, error bar indicates SD, two-tailed Student’s t-test Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30446646), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Tamoxifen administration-induced PHD2 deletion in skeletal muscle in Phd2f/f/Rosa26CreERT2 mice. a. PHD1, 2, & 3 deletion efficiency in the gastrocnemius muscles of tamoxifen-treated Phd2f/f/Rosa26CreERT2 mice was determined using qRT-PCR. Relative gene expression was determined using gastrocnemius muscle tissue cDNA (n = 3–4 mice per group). b. Anti-PHD2 & PHD3 Western blotting of gastrocnemius & soleus muscles at 6 weeks after tamoxifen administration. c. The expression of HIF-1 alpha in gastrocnemius & soleus at 5 weeks after tamoxifen administration. d. The level of hif-1 alpha mRNA in gastrocnemius at 5 weeks after tamoxifen administration. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 compared to control. Values are means ± SEM Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26949511), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hif1 alpha expression in neonatal & adult ovary.(A) Section of P5 ovary showing MVH expression in all oocytes & Hif1 alpha expression only in small oocytes (primary follicles; top). Negative control images without primary antibodies (bottom). Scale bar: 50μm. (B) Section of adult ovary showing absence of Hif1 alpha expression in primary follicles detected with MVH staining (top). Negative control without primary antibody (bottom). Scale bar: 50μm. (C) Section of adult ovary showing Hif1 alpha expression in mature primary oocyte (arrow). Negative control without primary antibody (bottom). Scale bar: 100μm. (D) Image of a Metaphase II oocyte from superovulated three-month-old female showing Hif1 alpha expression. Scale bar: 50μm. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27148974), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - FASN Regulates HIF-alpha Protein Stability & HIF Target Gene Expression. (A) FASN siRNA downregulates HIF-alpha protein levels. PREC, HeLa & HCT116 cells treated with FASN (+) or control (−) siRNA & harvested after 72 h. Cells exposed to hypoxia (1% oxygen) or maintained in normoxia (21% oxygen) 4 h before harvesting & subjecting WCEs to WB analysis. Unmodified (250 kDa) & modified (larger) FASN bands indicated by large arrowheads, REDD1 by a small arrowhead, & HIF-1 alpha & HIF-2 alpha by arrows. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28775317), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hif1 alpha expression in neonatal & adult ovary.(A) Section of P5 ovary showing MVH expression in all oocytes & Hif1 alpha expression only in small oocytes (primary follicles; top). Negative control images without primary antibodies (bottom). Scale bar: 50μm. (B) Section of adult ovary showing absence of Hif1 alpha expression in primary follicles detected with MVH staining (top). Negative control without primary antibody (bottom). Scale bar: 50μm. (C) Section of adult ovary showing Hif1 alpha expression in mature primary oocyte (arrow). Negative control without primary antibody (bottom). Scale bar: 100μm. (D) Image of a Metaphase II oocyte from superovulated three-month-old female showing Hif1 alpha expression. Scale bar: 50μm. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27148974), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - FASN Regulates HIF-alpha Protein Stability & HIF Target Gene Expression. (B) Downregulation of HIF-1 alpha & HIF-2 alpha in HCT116 cell clones carrying the FASN gene mutagenized using CRISPR-Cas9 (See Supplementary Fig. S3 for genomic DNA information). Protein samples prepared in normoxia (left column) or hypoxia (right column) for WB analysis. Asterisk indicates a non-specific band. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28775317), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Effect of silencing Cx43 on the expression of HIF-1 alpha in astrocytes.Astrocytes were transfected with NT-siRNA or with Cx43-siRNA. At the indicated times the expression of HIF-1 alpha & Cx43 was analysed by Western blot. A) Representative Western blot of HIF-1 alpha, Cx43 & GAPDH showing that the decrease in Cx43 expression was concomitant with HIF-1 alpha up-regulation. B) HIF-1 alpha quantification. C) Cx43 quantification. The results are expressed as percentages of the level found in the NT-siRNA condition at time 0. ***p<0.001 versus the corresponding NT-siRNA values. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0032448), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HDGF triggered AKT/HIF-1 alpha/NF-kappa B signaling in SCC4 oral cancer cells. a-d Cells were treated with recombinant HDGF (1–100 ng/ml) for 24 h & then harvested for total protein extraction. The cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE & detected by Western blotting with the indicated primary antibodies. beta-actin was used as an internal control for loading & transfer. Data were mean of three experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ns, not statistically significant Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31711427), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Cofilin phosphorylation is HIF-1 alpha dependent.Wt, shC, & the HIF-1 alpha knock down cell clones c1 & c2 cells were lysed after 24 hrs of normoxia (20% O2) or hypoxia (1% O2). Cell extracts were analysed by Western blots. Note that p-cofilin levels are reduced in c2 & c2 cells compared to wt & shC cells at 20% O2 & 1% O2. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069128), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Genotyping of transgenes.PCR genotyping was performed for all four transgenes as described in materials & methods. Sizes of the amplified products obtained are: 240 bp for Hif-1 alpha (wild type); 274 bp for Hif-1 alphaflox/flox; 410 bp for Hif-2 alpha (wild type); 444bp for Hif-2 alphaflox/flox; 370 bpfor Cre transgene; 350 bpfor rtTA transgene. One representative sample was genotyped for the four transgenes from each of three generated mouse strains: SPC-rtTA-/tg/(tetO)7-Cre-/tg/Hif-1 alphafl/fl (Lane 1), SPC-rtTA-/tg/(tetO)7-Cre-/tg/Hif-2 alphafl/fl mouse (Lane 2), & SPC-rtTA-/tg/(tetO)7-Cre-/tg/Hif-1 alpha/2 alphafl/fl (Lane 3)). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139270), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Effect of 24 h UO on renal HIF-1 alpha/2 alpha expression.WT mice were exposed to either sham-operation or left UO, which continued for 24 hours, & then was released. The left kidneys were harvested immediately (d0), 2, 4 or 7 days after release of obstruction (n = 4 at each time point). Immunoblot analyses of HIF-1 alpha & HIF-2 alpha in left kidneys were then performed & co-detection of TBP was performed to assess equal loading. HIF protein bands were quantified & normalized to TBP. Data were expressed as mean ± SD, & the mean value obtained from non-operated control mice was arbitrarily defined as 1. *, p<0.05 versus sham-operated controls; **, p<0.05 versus all the other groups. C, non-operated controls; S, sham-operated controls. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22295069), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hif1 alpha expression in 15.5dpc germ cells.(A) Sections of male (top) & female (bottom) gonads from 15.5 dpc Oct4-GFP embryos showing Oct4-GFP & Hif1 alpha expressions in germ cells. Scale bars: 50μm (male) & 20μm (female). (B) FACS-sorted male (top) & female (bottom) 15.5dpc germ cells showing Oct4-GFP & Hif1 alpha expressions. Scale bars: 100μm (male) & 50μm (female). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27148974), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Effect of ET-1 on glucose uptake in HIF-1 alpha-silenced astrocytes.Astrocytes were transfected with NT-siRNA or with HIF-1 alpha-siRNA. After 48 h, astrocytes were incubated in the absence (control, C) or presence of 0.1 µM ET-1 for 24 h. A) HIF-1 alpha, Hx-1, GLUT-3, Hx-2, GLUT-1 & GAPDH Western blots & quantification. The results are the means ± SEM of at least three independent experiments & they are expressed as percentages of the level found in the control NT-siRNA. B) Glucose uptake expressed as pmol of 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG) taken up per hour & per milligram of protein. The results show that the down-regulation of HIF-1 alpha levels promoted by HIF-1 alpha-siRNA decreased the rate of glucose uptake & the expression of GLUT-1, GLUT-3, Hx-1 & Hx-2, both in the control & in the ET-1 treated astrocytes. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01 & *p<0.05 versus the corresponding controls (C); ###p<0.001, ##p<0.01 & #p<0.05 versus the corresponding NT-siRNA. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0032448), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Effect of ET-1 & Cx43 on HIF-1 alpha expression & glucose uptake when c-Src is inhibited.Astrocytes were preincubated with 100 ng/µL PP2 (c-Src inhibitor) or 100 ng/µL PP3 (inactive analogue) for 1 h. Then, cells were incubated in the absence (control) or presence of 0.1 µM ET-1 for 24 h. A) HIF-1 alpha Western blot & quantification. The results are expressed as percentages of the level found in the controls treated with PP3 & they show that the inhibitor of c-Src PP2 prevented the up-regulation of HIF-1 alpha promoted by ET-1. ***p<0.001 versus the absence of ET-1. B) Glucose uptake expressed as pmol of 2-deoxyglucose taken up per hour & per milligram of protein. The results show that the inhibitor of c-Src PP2 prevented the increase in the rate of glucose uptake promoted by ET-1. ***p<0.001 versus the absence of ET-1. C) Astrocytes were preincubated with 100 ng/µL PP2 or 100 ng/µL PP3 for 1 h. Then, cells were transfected with NT-siRNA or with Cx43-siRNA & after 48 h HIF-1 alpha was analysed by Western blot. The results are expressed as percentages of the level found in the PP3 NT-siRNA & they show that the inhibitor of c-Src PP2 prevented the up-regulation of HIF-1 alpha promoted by silencing Cx43. ***p<0.001 versus the corresponding NT-siRNA. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0032448), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hypoxia reduces inflammatory processes & induces autophagy in Il-10−/− mice. a, b, c, d, e, f & g WT, Nrlp3−/−,Il-10−/−, & Il-10−/−Nrlp3−/−double knockout mice were subjected to normoxia (N, 21% O2) or hypoxia (H, 8% O2). After 18 h, mice were killed & colon biopsies were collected. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-test. Results represent mean + s.e.m., WT mice under normoxia: n = 5, WT mice under hypoxia: n = 5; Nrlp3−/− mice under normoxia: n = 4; Nrlp3−/− mice under hypoxia: n = 5; Il-10−/− mice under hypoxia: n = 4; Il-10−/− mice under hypoxia: n = 4; Il-10−/−Nrlp3−/− mice under normoxia: n = 7; Il-10−/−Nrlp3−/− mice under hypoxia: n = 9, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. h Total protein was isolated & western blot performed. LC3-I & LC3-II bands were quantified, & autophagy was measured by variations in the ratio of LC3-II/LC3-I & the total amount of LC3 (LC3-I plus LC3-II) relative to beta-actin Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28740109), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hypoxia reduces inflammatory processes & induces autophagy in the DSS mouse model of colitis. a, b, c, d, e, f & g WT & Nrlp3−/− mice were administered with DSS or DSS-free water & subjected to normoxia (N, 21% O2) or hypoxia (H, 8% O2). After 18 h, mice were killed & colon biopsies were collected. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-test. Results represent mean + s.e.m., WT mice under normoxia: n = 5, WT mice under normoxia: n = 5, DSS-treated WT mice under normoxia: n = 6; Nrlp3−/− mice under normoxia: n = 5; DSS-treated Nrlp3−/− mice under normoxia: n = 6; WT mice under hypoxia: n = 4, DSS-treated WT mice under hypoxia: n = 5; Nrlp3−/− mice under hypoxia: n = 3; DSS-treated Nrlp3−/− mice under hypoxia: n = 3, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. h Total protein was isolated & western blot performed. LC3-I & LC3-II bands were quantified, & autophagy was measured by variations in the ratio of LC3-II/LC3-I & the total amount of LC3 (LC3-I plus LC3-II) relative to beta-actin Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28740109), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Effect of HIF-1 alpha silencing on alpha-MSH-induced apoptosis in B16-F10 melanoma cells during hypoxia.a Cells were transfected with shLacZ or shHIF-1 alpha plasmids for 48 h before harvest. HIF-1 alpha shRNA reduced the basal HIF-1 alpha mRNA & protein expression levels. b, c Relative mRNA expression levels were analyzed by real-time PCR. Data are expressed as fold change compared with control (means ± SD of triplicate experiments). d Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblot using the indicated antibodies. beta-Actin was used as an internal control for loading & transfer. e The population of apoptotic cells was analyzed by flow cytometry & qualified as mean ± SD from triplicate experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Knockdown of HIF-1 alpha diminished alpha-MSH-induced apoptosis in B16-F10 melanoma cells during hypoxia Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30062060), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - FASN & CAD Binding Specificity of pVHL Mutants Derived from VHL Patients. (A) Schematic representation of pVHL domains. Dotted lines indicate the approximate positions of the HIF-1 alpha & Elongin C binding domains. The alpha & beta structural domains are also indicated. (B) Effects of pVHL mutations on interactions with E3 ligase components, HIF-alpha & other interacting proteins including FASN. pVHL mutants were stably expressed by lentiviral vectors in HCT116 cells, & WCEs were tested in precipitation assays. Note that the mutant pVHL-W88S almost completely lost the ability to bind to HIF-1 alpha & HIF-2 alpha, whereas pVHL-Y112H retains this ability almost completely. However, both pVHL-W88S & pVHL-Y112H show significantly reduced binding to FASN & CAD, as indicated by small & large asterisks, respectively. Arrows indicate HIF-1 alpha & HIF-2 alpha bands. Long arrows & arrowheads indicate unmodified & modified forms of FASN, respectively. Protein samples prepared from hypoxia (1% oxygen)-exposed cells were added as positive control in left-end extra lanes. (C) The same samples as used in B were analyzed by silver staining. The E3 ligase components appear as major bands as indicated. (D) Subcellular localization of stably expressed pVHL mutants in 786-O. pVHL-Y112H & pVHL-W88S showed preferential nuclear localization, whereas pVHL-WT & pVHL-H115Q which both strongly bind to FASN & CAD, showed cytoplasmic localization. Cells showing clear nuclear (C < N) or cytoplasmic (C > N) localization in three microscopic viewing areas were counted as shown in the lower panel. The total counted cell numbers ranged from 35 to 64. The experiments were repeated more than twice, except for the cell localization count, & the results were reproduced. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28775317), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hypoxia signaling & cytotoxicity to CdCl2. (a) Wild-type (WT) cells were left untreated (Ctrl) or exposed to 150 μM CoCl2 (Co2+), 1, 5 or 10 μM CdCl2 (Cd2+) or 150 μM CoCl2 & 10 μM CdCl2 for 24 hours. HIF1 alpha −/− cell extract treated with 150 μM CoCl2 was used as a negative control. Nuclear protein was extracted & separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose membrane & probed with a HIF1 alpha (upper panel) or beta-actin (lower panel) specific antibody. The bands observed in the cadmium only WT cells are nonspecific as they are also observed in the HIF1 alpha −/− cells. (b) BNip3 mRNA expression levels were analyzed by qRT-PCR in wild type (WT, white bars) & HIF1 alpha −/− cells (black bars). Cells were left untreated (0), or exposed to 5 μM CdCl2 (Cd2+) or 150 μM CoCl2 (Co2+) for 24 hours. Each value was normalized to the control level in the corresponding cell line. *P < 0.05 compared to the corresponding controls, n = 4. (c) BNIP3 protein levels were determined in wild type & HIF1 alpha −/− cells after treatment with 150 μM CoCl2 (Co2+) or 5 μM CdCl2 (Cd2+) for 24 hours using a BNIP3 specific antibody & beta-actin was used as a loading control (lower Panel). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21811500), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - FIH exits the nucleus via a Leptomycin B-sensitive exportin1-dependent pathway. (A) Immunofluorescence staining of FIH (green) & HIF1 alpha (red) in MCF7 cells after the indicated hypoxia (0.5% O2) & re-oxygenation treatments. TO-PRO-3 (blue) was used to stain nuclei. (B) Total cell lysates from U2OS cells were immunoprecipitated with an anti-exportin1 antibody or control IgG. FIH, exportin1 & beta-tubulin levels are indicated. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of FIH (green) in FIH-null mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) transfected with HA-FIH 1–349 or HA-FIH deltaNES followed by normoxia, hypoxia (1% O2, 3 h) or 3 h of hypoxia followed by re-oxygenation for 1 h. TO-PRO-3 (blue) was used to stain nuclei. Arrows indicate nuclear localization of signal. (D) Total cell lysates from U2OS cells transfected with control vector, HA-FIH 1–349 or HA-FIH deltaNES were immunoprecipitated with an anti-exportin 1 antibody. HA-FIH, exportin1 & beta-tubulin levels are indicated. FL, full length; IgGL, IgG light chain. Scale bars: 20 µm. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30333145), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Phagocyte infiltration contributes to the respiratory burst & consequent EPO signalling activation during inflammation resolution.ZymA (i.p., 1 mg per mouse) was applied to induce peritonitis in male WT mice. (a–c) Mice were treated with either 0.5 mg per mice i.p. of anti-Ly6G antibody or control (isotype control rat IgG2a) 1.5 day before zymA injection, & exudate leucocytes, peritoneum & peritoneal fluid were collected for analysis of ROS (a, n=3), hypoxia, HIF-1 alpha (b, n=3) & EPO (c, n=3) at 6 24 h. (d–f) Mice were treated with either anti-Ly6G antibody (0.5 mg per mice) plus clodronate liposomes (0.2 ml per 10 g) or control (isotype antibody+empty liposome) before zymA injection, & exudate leucocytes, peritoneum & peritoneal fluid were collected for analysis of ROS (d, n=3), hypoxia, HIF-1 alpha (e, n=3) & EPO (f, n=3) at 24 h. Representative data from two independent experiments are shown. For flow cytometry data, black numbers refer to the percentage of positive cells & red numbers refer to the mean fluorescent intensity. Error bars represent the s.e.m. *P<0.05, two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test. Full-size images for b & e are shown in Supplementary Fig. 12. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27397585), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hypoxia reduces inflammatory signaling pathways & NLRP3 expression & induces autophagy in IECs. a HT-29 cells were subjected to normoxia & hypoxia at the indicated times in the absence or presence of 10 µg/ml LPS. Autophagy was measured by variations in the ratio of LC3-II/LC3-I & the total amount of LC3 (LC3-I plus LC3-II) relative to beta-actin. Results are representative of two independent experiments. b, c & d HT-29 cells were subjected to normoxia & hypoxia for the indicated periods in the absence or presence of 10 µg/ml LPS, followed by transcript analysis. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-test. Results represent mean + s.e.m. of two independent experiments done in triplicate, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns not significant. e HT-29 cells were subjected to normoxia or hypoxia in the presence & absence of 10 µg/ml LPS & 20 µM of MG132. Results are representative of two independent experiments. f & g Putative binding sites for HIF-1 alpha & NF-kappa B were found in the p62 f & NLRP3 g promoters using Genomatix software tools. Numbers under the boxes indicate the distance from the transcription start site. HT-29 cells were subjected to normoxia (21% O2) or hypoxia (0.2% O2) for 6 h & 24 h. ChIP analysis was performed using antibodies against HIF-1 alpha & NF-kappa B for immunoprecipitation. PCR was performed using the promoter-specific primers for the p62 f & NLRP3 g promoter binding sites of HIF-1 alpha & NF-kappa B. Aliquots taken prior to immunoprecipitation were used as input control. PCR products were run on 2% agarose gel. The results are representative of three independent experiments. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28740109), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Effect of Hif1a deletion upon growth & invasion. (A) Wild-type (WT) mammary tumor epithelial cells (MTECs) grown to 80% confluence subjected to hypoxic culture for the indicated times up to 24 hours, or cells continued to be cultured under normoxic conditions such that the time t = 0 sample harvested on the same day as the time t = 24 hours hypoxic condition sample. High-salt enriched whole-cell extracts resolved on 3% to 8% Tris-acetate gels & blotted onto polyvinylidene fluoride membrane, which divided horizontally at approximately 60 kDa. The top half of the blot used to detect HIF-1 alpha, & the lower portion used to detect lamin (loading control) to avoid the need to strip & reprobe the blot. (B) Growth curve of WT & knockout (KO) MTECs cultured at normoxia (Nor) or hypoxia (Hyp) in growth medium supplemented w/ 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS) + epidermal growth factor (EGF) (left) or w/ 2% FBS (right). For cells grown in 5% FBS + EGF, a representative graph is shown in which the mean ± SEM of cell number per time point of quadruplicate wells per genotype/oxygen tension is plotted per time point. For cells grown in 2% FBS, the grand mean ± SEM of cell number is presented, which calculated as an average of the mean cell number observed per replicates per time point as observed in three replicate experiments. All data analyzed by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA, *P < 0.05). (C) The mean fold change (FC) in invasion normalized to invasion index observed for WT cells cultured at normoxia (FC = 1.0). Data represent the mean FC in invasion observed in three independent experiments. All columns compared using one-way ANOVA w/ a Bonferroni posttest. *P < 0.05. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (http://breast-cancer-research.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/bcr3087), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Involvement of HIF-1 alpha in alveolar epithelial cell phenotypic changes induced by hypoxia. Primary rat AECs were cultured in normoxia (Nx) (21% O2) or hypoxia (Hx) (1.5% O2) during 6 days in presence or absence of 10 µM YC-1. (A) Immunostaining of ZO-1 (magenta) & TTF1 (cyan) were performed. n = 4 experiments were performed. Isolated primary rat AECs were cultured in normoxia (Nx) (21% O2) or hypoxia (Hx) (1.5% O2) during 6 h in the presence or absence of 100 mM 4-phenylbutyrate (4-PBA) or pre-treated or not with 1 µM BAPTA-AM 90 min before exposition to hypoxia. A representative picture of at least n = 4 independent experiments for each condition has been presented & scale bar represents 50 µm. (B) Western blot of HIF-1 alpha protein levels was performed. Representative blot of n = 5 experiments is shown. Expression levels of HIF-1 alpha were quantified & reported to beta-actin expression for each condition. Primary rat AECs were transfected with plasmid coding for luciferase reporter activity of hypoxia responsive element (HRE: i.e., HIF-luc), & cultured as described. (C) Luciferase activity corresponding to the transcriptional capacity of HIF was reported (n = 4 experiments). Raw data were submitted a Kruskal-Wallis test. * & ** indicate a significant difference as compared with normoxic value with p < 0.05 & p < 0.01 respectively. # & ## indicate a significant difference as compared with value in untreated hypoxic cells with p < 0.05 & p < 0.01, respectively. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30875855), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Pharmacological inhibition of ABCC3 reduces cell proliferation through STAT3 & HIF1 alpha dysregulation & induction of apoptosis. a Representative Western blot images show the effects of pharmacological inhibition of ABCC3 with MCI-715 on the expression of pSTAT3 Y705 & HIF1 alpha in three PDAC cell lines (AsPC1, HPAFII, CFPAC-1). Cells were treated with MCI-715 at the concentration of 10 μM & collected after 24 h (CFPAC-1) or 48 h (AsPC1, HPAFII). The quantitative analysis of n = 3 separate experiments is presented in Additional file 1: Figure S2; b The effects of the treatment of AsPC1, HPAFII & CFPAC-1 cell lines with 10 μM MCI-715 on the Caspase 3/7 activity (72 h post treatment) measured with Caspase 3/7 fluorigenic probe; c Representative Western blotting images & quantitative analysis of cleaved caspase 3 expression following treatment of indicated PDAC cell lines with 10 μM MCI-715. All results are presented as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. The quantitative analysis was performed with the use of ImageJ & Image Lab software, unpaired Student’s t-test was performed for statistical analysis, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31378204), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Normoxic pretreatment sensitizes glioma cells to radiation after rapid acute hypoxic (RAH) exposure.(A) The rapid acute hypoxia (RAH) protocol is shown depicting the timing & severity of hypoxic exposure. Cells either remain in a continuous hypoxic environment (–) or are transiently (25 min) exposed to normoxia 25 min prior to radiation (+). Continuously normoxic cells (NOx) were irradiated as a positive control. (B) The results of anchorage-independent colony forming assays are shown for U87, U87-luc, GL261 glioma cells & 0308 GSCs after 5 Gy radiation exposure under varying oxygen conditions. To allow for ease of comparisons among cell types, raw values are expressed as a percentage of the corresponding cell type’s negative (non-irradiated) control & the means & SEMs are plotted. Each result represents at least three independent samples, plated in triplicate. Holm-Sidak comparisons for multiple groups were used for statistical comparisons of raw values (**p<0.01). Also shown are Western blots of nuclear HIF-1 alpha at the time of irradiation for each cell type. Corresponding Western blots of lamin A/C are shown as a loading control. All lanes shown that are non-adjacent to the negative control (NOx) are denoted with a separating black line. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25350400), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Multiple distinct mechanisms for downregulation of AKT activity in TSC1/2-deficient SCs. A-F: Western blots of sciatic nerve lysates from control & TSC2-SCKO/TSC1-SCKO mice at age P28 (A-E) or P14 (F) (3 mice per group), probed with the indicated antibodies. G: Immunofluorescence of longitudinal frozen sciatic nerve sections from control & TSC2-SCKO mice (age P28) showing greatly increased immunoreactivity of PTEN in the mutant (cytoplasmic signals surrounding DAPI+ nuclei). Scale bars: 50 µm H: Schematic summarizing distinct mechanisms underlying the downregulation of AKT activity in SCs from TSC1/2-SCKO nerves. Components highlighted in red are upregulated while blue highlighting depicts downregulation in mutant nerves. Note downregulation of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) by constitutively active S6 kinases downstream of mTORC1. This leads to attenuated activation of PI3K/AKT. Lack of mTORC2 stimulation occurs through abolished TSC1/2 which results in reduced AKT phosphorylation in position Ser473 as well as through feedback inhibition by S6 kinases. Lastly, hyperactive mTORC1 promotes Hif1 alpha transcription factor expression which results in increased PTEN transcription, & thus attenuated PI3K/AKT signaling. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29497474), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - DLK1 cleavage is dependent on HIFs & ADAM 17 activity.a, b Representative images & densitometric analysis of western blots showing HIF-1 alpha, HIF-2 alpha, & DLK1 expression & cleavage in U3082MG cells after siRNA targeting of HIF1A & HIF2A in hypoxia. c, d Representative images & densitometric analysis of western blots showing the effects of ADAM inhibition by pre-treatment with 20 µM TAPI-2 on DLK1 cleavage in U3082MG cells grown at 21% or 1% O2 for 48 h. SDHA was used as loading control. e, f Representative images & densitometric analysis of western blots showing the effects of ADAM17 inhibition by pre-treatment with 0.5 μM TMI-1 on DLK1 cleavage in U3082MG cells grown at 21% or 1% O2 for 48 h. SDHA was used as loading control. Statistical analysis: b has 3 independent experiments while d & f have four independent experiments, all data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. In the whole figure significance is represented as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, & ***p < 0.001 vs. respective 21% O2 controls or as indicated by straight lines. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32205867), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hypoxia downregulates MHC class I expression via HIF transcription factors.(A-C): siRNA mediated knockdown of HIF-1 alpha reversed hypoxic downregulation of MHC class I expression as compared with the scrambled, non-targeting (NT) siRNA control. MCA205 tumor cells were reverse transfected with scrambled siRNA (NT; red histogram) or with HIF-1 alpha specific siRNA (blue histogram) & cultured as 3D spheroids under 1% (A) or 21% (B) oxygen for 48h. Levels of MHC class I surface expression was determined using flow cytometry. Efficacy of gene knockdown was assessed using Western blot (C). beta-Actin was used as the loading control. Representative data of 3 independent experiments shown. (D-F): Flow cytometry assessment of surface expression of HLA-ABC on paired isogenic renal cell carcinoma cell lines RCC4 (D), UMRC2 (E) & CAKI2 (F). Each pair had the parental cell line that lacked endogenous wild-type VHL (VHL null, transfected with empty vector) & one with vector stably expressing functional VHL (VHL restored). Restoring VHL function & thereby reducing HIF expression, significantly increased HLA-ABC expression on the cells. Representative histograms of 4 independent experiments are shown. Grey filled: unstained control; red: VHL null genotype; blue: VHL restored genotype. (D1-F1): Inactivation of HIF-1 alpha by restoring VHL expression was verified by Western blotting for RCC4 (D1), UMRC2 (E1) & CAKI2 (F1) cells. beta-Actin was used as the loading control. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187314), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Effect of ET-1 & Cx43 on HIF-1 alpha expression & glucose uptake when c-Src is inhibited.Astrocytes were preincubated with 100 ng/µL PP2 (c-Src inhibitor) or 100 ng/µL PP3 (inactive analogue) for 1 h. Then, cells were incubated in the absence (control) or presence of 0.1 µM ET-1 for 24 h. A) HIF-1 alpha Western blot & quantification. The results are expressed as percentages of the level found in the controls treated with PP3 & they show that the inhibitor of c-Src PP2 prevented the up-regulation of HIF-1 alpha promoted by ET-1. ***p<0.001 versus the absence of ET-1. B) Glucose uptake expressed as pmol of 2-deoxyglucose taken up per hour & per milligram of protein. The results show that the inhibitor of c-Src PP2 prevented the increase in the rate of glucose uptake promoted by ET-1. ***p<0.001 versus the absence of ET-1. C) Astrocytes were preincubated with 100 ng/µL PP2 or 100 ng/µL PP3 for 1 h. Then, cells were transfected with NT-siRNA or with Cx43-siRNA & after 48 h HIF-1 alpha was analysed by Western blot. The results are expressed as percentages of the level found in the PP3 NT-siRNA & they show that the inhibitor of c-Src PP2 prevented the up-regulation of HIF-1 alpha promoted by silencing Cx43. ***p<0.001 versus the corresponding NT-siRNA. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0032448), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha protein increases in HCT116 cells exposed to rapid intermittent hypoxia. Increased HIF-1 alpha increases HIF-1 transactivation, leading to increased expression of HIF-1 target genes at both the mRNA & protein level. (A) Rapid intermittent hypoxia increases HIF-1 alpha protein after 6 h of exposure. (B) Rapid intermittent hypoxia increases the mRNA expression of genes involved in glycolysis, extracellular matrix remodeling & the HIF pathway after 18 h of exposure. (C) Additional genes with known hypoxia response elements (HRE) binding sites for HIF-1 were measured & all tested genes showed an increase in both chronic hypoxia & intermittent hypoxia after 18 h. All values were normalized to normoxic expression levels, which is equivalent to 0 on the Log2 scale. Results are the mean ± SEM of independent experiments run in duplicate (n ≥ 3). (D) The increase in mRNAs is also reflected in an increase in the protein levels of Glut1, HK2, LDHA & PHD2. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 & **** p < 0.0001. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30669593), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hif1 alpha expression in neonatal & adult testis.(A) Section of testis from 5-day old (P5) male new born pups showing Hif1 alpha expression in MVH+ gonocytes within the seminiferous tubules (top) & negative control images without primary antibodies (bottom). Scale bar: 50μm. (B) Western blot analysis of Hif1 alpha expression in P5 testes (left) compared to extract of the adult brain sub-ventricular zone (SVZ) (right). Loading control ( beta-Actin) is shown below. (C) Section of adult (3 month old) testis showing Hif1 alpha expression in spermatogonia. Scale bar: 30μm. (D) Western blot analysis of whole adult testis. HEK293 cells treated with DFX were used as a positive control & intestinal tissue was used as a negative control. Loading control ( beta-Actin) is shown below. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27148974), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Roles of P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in the DFO-mediated up-regulate of HIF-1 alpha protein in APPsw cells. (A) APPsw were exposed to 100 μM Fe, 100 μM DFO, or both combined for 24 h. Whole cell lysates were prepared & subjected to analysis for P38 or GAPDH protein. (B) Western blot analysis revealed that strong phosphorylation of P38 MAPK was detected in the DFO-treated cells, whereas no significant changes were observed in cells treated Fe alone compared with control. There were not statistical changes in the levels of P38 MAPK among the groups. The data represent the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared with the control; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 with respect to the Fe treatment group. (C–E) APPsw cells were pretreated without or with SB203580 (10 μM) for 2 h & then treated without or with DFO for additional 22 h in the absence or presence of the inhibitor. Immunoblotting showed that DFO treatment significantly increased the levels of p-P38 MAPK compared with the control group, whereas the increase was significantly ameliorated by SB203580. Furthermore, the DFO-mediated up-regulation of HIF-1 alpha protein was greatly inhibited by SB203580. The data represent the mean ± S.E. (n = 3). **p < 0.01 compared with the control; ##p < 0.01 compared to the values of DFO treatment group (two-way ANOVA with Post hoc Fisher’s PLSD). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26082716), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) proteins after bilateral renal ischemia or sham ischemia. Immunoblots for HIF-1 alpha (A–C) & HIF-2 alpha (D–F) of tissue extracts from the cortex & outer & inner medulla of the left kidneys of rats 24 h & 5 days following recovery from either sham ischemia (○) or bilateral renal ischemia (●); n = 6 per group. G: typical image of the gel following electrophoresis. H: typical image of the nitrocellulose membrane following transfer. Values are expressed as medians (25th percentile, 75th percentile). Paired comparisons were performed using the Mann-Whitney U-test. Because paired comparisons were made at two time points, P values were conservatively adjusted using the Dunn-Sidak method with k = 2. PTr, PT, & PTr*T are the outcomes of two-way analysis of variance on ranking with the factors treatment (Tr) & time (T). AU, arbitrary unit; I1, 24 h after ischemia; I5, 5 days after ischemia; S1, 24 h after sham ischemia; S5, 5 days after sham ischemia. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30110566), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - DFO regulates the expression of HIF-1 alpha & HIF-1-related protein in the brains of APP/PS1 mice. (A) Western blots showing the expression levels of HIF-1 alpha protein in control & DFO-treated transgenic mice brains. (B) Immunoblot showed that DFO treatment significantly increased HIF-1 alpha protein levels, compared with controls. (C) The expression levels of HIF-1 alpha mRNA were detected by RT-PCR in the brains of APP/PS1 transgenic mice treated with DFO. (D) RT-PCR analysis showed that DFO treatment significantly increased the HIF-1 alpha mRNA levels in the transgenic mouse brain. GAPDH served as the internal control. (E) Immunohistochemically stains showed the distribution of HIF-1 alpha in the cortical & hippocampus sections of APP/PS1 mouse brain (Scale bar = 100 μm). (F) Western blots showing the expression levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), DMT1, & TFR proteins in APP/PS1 transgenic mice brains 3 months after DFO administration. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (G–J) DFO treatment led to a marked increase in the BDNF, DMT1 + IRE, & TFR protein levels in the brains of transgenic mice compared with the control. There was no significant change in the expression levels of DMT1-IRE protein between the groups, compared with the control. Data represent the mean ± S.E. of 6 independent experiments. **P < 0.01 vs. control group. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26082716), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Phagocyte infiltration contributes to the respiratory burst & consequent EPO signalling activation during inflammation resolution.ZymA (i.p., 1 mg per mouse) was applied to induce peritonitis in male WT mice. (a–c) Mice were treated with either 0.5 mg per mice i.p. of anti-Ly6G antibody or control (isotype control rat IgG2a) 1.5 day before zymA injection, & exudate leucocytes, peritoneum & peritoneal fluid were collected for analysis of ROS (a, n=3), hypoxia, HIF-1 alpha (b, n=3) & EPO (c, n=3) at 6 24 h. (d–f) Mice were treated with either anti-Ly6G antibody (0.5 mg per mice) plus clodronate liposomes (0.2 ml per 10 g) or control (isotype antibody+empty liposome) before zymA injection, & exudate leucocytes, peritoneum & peritoneal fluid were collected for analysis of ROS (d, n=3), hypoxia, HIF-1 alpha (e, n=3) & EPO (f, n=3) at 24 h. Representative data from two independent experiments are shown. For flow cytometry data, black numbers refer to the percentage of positive cells & red numbers refer to the mean fluorescent intensity. Error bars represent the s.e.m. *P<0.05, two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test. Full-size images for b & e are shown in Supplementary Fig. 12. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27397585), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - A “white-jade” muscle phenotype in EV-A71-infected mouse strain 129. aLeft panel: We coined a “white-jade” phenotype to describe the pathological changes in the color of the hindlimb muscle in EV-A71-infected mice (indicated by arrow). This phenotype showed characteristic muscle with locally whitened color in appearance & hardened tissue mass. In the saline control, tendons (not muscle) can be seen in white color. Right panel: An anatomical sketch of the hindlimb muscle. GM: gluteal muscle, QF: quadratus femoris muscle, BF: Biceps femoris muscle. b Both VP1 protein (upper) & myogenin protein (lower) were detected by IHC staining in the muscles, indicating EV-A71 infection, muscle injury & regeneration. The magnification is 200X. c Striking expression of HIF1A (hypoxia inducible factor 1-alpha) protein (brown color) was detected by IHC staining in the white-jaded tissue, but not in the non-white-jaded tissue from the same mouse. d Specific association between HIF1A expression & white-jaded muscle Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31711481), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Kidney-derived Sca-1+ cells produce Epo. (A) Epo protein levels in supernatants obtained from Sca-1+ cells cultured in normoxia or hypoxia (n = 3 biological replicates). (B) HIF-1 alpha & HIF-2 alpha protein levels in Sca-1+ kidney-derived cells after exposure to normoxia (20% O2) or hypoxia (1% O2). Numbers below the blots indicate the fold change of the ratio of HIF-1 alpha/Tubulin & HIF-2 alpha/Tubulin in 1% O2 to the respective 20% O2 control. (C) Epo RNA levels in Sca-1+ cells that were incubated either at 20% O2 of 1% O2 as indicated (n = 4 biological replicates). (D) Mesenchymal stem cell markers in renal Sca-1+ cells on day 21 of culture; reads per kilobase million (RPKM). (E) Volcano plot of 4592 significantly up- & 5376 significantly downregulated mRNAs in kidney-derived Sca-1+ cells on day 21 in culture compared to day 0. Mean values ± SEM are shown. * p < 0.05. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35203399), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hif1 alpha expression in neonatal & adult testis.(A) Section of testis from 5-day old (P5) male new born pups showing Hif1 alpha expression in MVH+ gonocytes within the seminiferous tubules (top) & negative control images without primary antibodies (bottom). Scale bar: 50μm. (B) Western blot analysis of Hif1 alpha expression in P5 testes (left) compared to extract of the adult brain sub-ventricular zone (SVZ) (right). Loading control ( beta-Actin) is shown below. (C) Section of adult (3 month old) testis showing Hif1 alpha expression in spermatogonia. Scale bar: 30μm. (D) Western blot analysis of whole adult testis. HEK293 cells treated with DFX were used as a positive control & intestinal tissue was used as a negative control. Loading control ( beta-Actin) is shown below. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27148974), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Evidence that hypoxia induces nuclear entry of FIH. (A) Protein levels of HIF1 alpha, HIF2 alpha, FIH & PHD2 in U2OS cells during hypoxia (1% O2) treatment at the indicated time points. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of FIH (green) in U2OS cells under hypoxic conditions (1% O2) at the indicated time points. TO-PRO-3 (blue) was used to stain nuclei. (C) Protein levels of FIH & HIF1 alpha from cytoplasmic or nuclear fractions in U2OS cells in normoxia or hypoxia (1% O2, 3 h). beta-tubulin & PARP were used as loading controls for the cytoplasmic & nuclear fractions, respectively. Figures beneath lanes 2 & 4 indicate relative intensities of nuclear FIH in normoxia & hypoxia. Note that different quantities of cytoplasmic & nuclear extracts were loaded. Scale bars: 20 µm. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30333145), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Respiratory burst contributes to the EPO signalling activation during inflammation resolution.ZymA (i.p., 1 mg per mouse) was applied to induce peritonitis in male WT mice or CGD mice. (a) Exudate leucocytes & peritoneum were collected at indicated intervals, & protein levels of HIF-1 alpha & HIF-2 alpha were measured by WB (n=3). (b) YC-1, 400083 or 400087 were intraperitoneally given to WT mice 3 h before zymA injection & the protein levels of related molecules were analysed by WB (n=2). (c) Mice were killed 1 h after injection of pimonidazole at indicated intervals & the protein adducts of reductively-activated pimonidazole were detected by WB with Hypoxiprobe-1-Mab-1 (HPI) (n=2). (d) Flow cytometry for ROS at indicated intervals (n=3). (e) Flow cytometry for cellular sources of ROS at indicated intervals (n=3). Representative data from at least two independent experiments are shown. For flow cytometry data from d, black numbers refer to the percentage of positive cells & red numbers refer to the mean fluorescent intensity. Error bars represent the s.e.m. *P<0.05, two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test. Full-size images for a–c are shown in Supplementary Figs 8–10, respectively. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27397585), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Effect of IKK2 inhibition on HUVEC, microvessel outgrowth from aortic rings, & VEGF-A expression. a Dose-dependent (10, 5 & 2.5 ng/ml) inhibitory effect of IMD0354 on HUVEC migration relative to control (DMSO 1 µl/ml). Living HUVEC were visualized with Calcein-AM (green). b Quantification of HUVEC migration distance (n = 8). One-way ANOVA test with Tukey multiple comparison was used to determine statistical significance. c HUVEC has grown on Geltrex to evaluate tube formation in the presence of IMD0354 compared to drug-free vehicle (DMSO). Vital HUVEC are stained with calcein-AM (green), & dead HUVEC are displayed in red (propidium iodide). Quantitative analysis of a number of junctions (d), & tubules (e) formed by HUVEC, & total tubule length (f) (n = 8). g Quantitative analysis of cell death induced by IMD0354 treatment (n = 8). h Effect of IMD0354 on cell proliferation in the aortic ring assay. Student t test was used to determine statistical significance. i Western blot analysis of VEGF-A expression in HUVEC treated with IMD0354 (10, 5, 2.5 ng/ml), with beta-actin as a loading control. j Western blot analysis of HIF-1 alpha expression in HUVEC treated with IMD0354 (10, 5, 2.5 ng/ml), with beta-actin as a loading control. k Immunofluorescent detection of VEGF-A (green) in HUVEC treated with IMD0354 (10, 5, 2.5 ng/ml). Cell nuclei visualized with DAPI staining (blue). n.s. p > 0.05; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10456-018-9594-9), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - The duration of enhanced radiosensitivity after normoxic pretreatment of cells undergoing Rapid Acute Hypoxia.(A) The RAH protocol is shown with variable delays to radiation after normoxic pretreatment. In this protocol all cells are transiently (25 min) exposed to normoxia for 25 min (+) & then returned to severe hypoxia (1% O2) for 1, 3, or 6 hours prior to radiation. Continuously normoxic cells (NOx) were irradiated as a positive control. (B) Results from anchorage-independent colony forming assays indicate that the decay of enhanced radiosensitivity for cells in the RAH protocol is generally more rapid than that observed for cells in the GCH protocol. To allow for ease of comparisons among cell types, raw values are expressed as a percentage of the corresponding cell type’s negative (non-irradiated) control & the means & SEMs are plotted. Each result represents at least three independent samples, plated in triplicate. Holm-Sidak comparisons for multiple groups were used for statistical comparisons of raw values (*p<0.05, **p<0.01). Also shown are Western blots of nuclear HIF-1 alpha at the time of irradiation for each cell line. Corresponding Western blots of lamin A/C are shown as a loading control. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25350400), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha overexpression rescues oxygen-induced radioresistance in RAH-treated cells, but not GCH-treated cells.Results are shown for the anchorage-independent colony forming assays for U87 cells transfected with either an empty vector or HIF-1 alpha expression vector & then exposed to GCH or RAH protocols without (–) or with (+) reoxygenation. Continuously normoxic cells (NOx) were irradiated as a positive control. To allow for ease of comparisons among conditions, raw values are presented as a percentage of that cell type’s negative (non-irradiated) control & the means & SEMs are plotted. Each result represents at least three independent samples, plated in triplicate. Holm-Sidak comparisons for multiple groups were used for statistical comparisons of raw values (*p<0.05, **p<0.01). Western blotting analysis of nuclear HIF-1 alpha at the time of irradiation is shown for each cell type below clonogenic results. Corresponding Western blots of lamin A/C are shown as a loading control & blots for hemagglutinin (HA) are shown below HIF-1 alpha overexpression vector results to demonstrate transfection efficacy. All lanes shown that are non-adjacent to the negative control (NOx) are denoted with a separating black line. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25350400), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - ONECUT2 modulates HIF1 alpha binding to chromatin in NE-like PC3 cells. a Western blot of HIF1 alpha & ONECUT2 in PC3 cells under normoxic & hypoxic conditions. Two different siRNAs targeting ONECUT2 were mixed together for knockdown experiments. b Left panel: heatmaps show HIF1 alpha ChIP-Seq signal in PC3 cells under hypoxic conditions with & without knockdown of ONECUT2; right panel: pileup of HIF1 alpha ChIP-Seq signals centered at HIF1 alpha ChIP-Seq peaks center. c Expression of ANGPTL4 & ADM, two hypoxia-regulated genes, with & without knockdown of ONECUT2 in PC3 cells. d Schematic illustration of the analysis identifying SMAD3 as an ONECUT2 regulated HIF1 alpha co-factor. Genes identified in motifs enriched in HIF1 alpha binding sites & ONECUT2 target genes were further filtered by HIF1 alpha interacting protein list from BioGRID. ONECUT2 target genes were defined as differentially expressed in ONECUT2 knockdown & control samples & with ONECUT2 binding sites nearby in PC3 cells under hypoxic conditions. e SMAD3 expression in response to ONECUT2 silencing in PC3 cells. f SMAD3 & HIF1 alpha binding sites with & without silencing of SMAD3. g The overlap of SMAD3 ChIP-Seq, HIF1 alpha ChIP-Seq & SMAD3-HIF1 alpha ChIP-re-ChIP-Seq peaks. h SMAD3 ChIP-Seq, HIF1 alpha ChIP-Seq & SMAD3-HIF1 alpha ChIP-re-ChIP-Seq signal near the promoter regions of hypoxia-induced genes ANGPTL4 & ADM. Error bars indicate s.d. from at least two technical replicates. P-value is calculated by one-way ANOVA. **: P < 0.01. Source data are provided as a Source Data file Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30655535), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - The duration of enhanced radiosensitivity after normoxic pretreatment differs among cell lines undergoing Graded Chronic Hypoxia.(A) The GCH protocol is shown with variable delays to radiation after normoxic pretreatment. After GCH, all cells are transiently (25 min) exposed to normoxia for 25 min (+) & are then returned to severe hypoxia (1% O2) for 1, 3, or 6 hours prior to radiation. Continuously normoxic cells (NOx) were irradiated as a positive control. (B) Results from anchorage-independent colony forming assays indicate that the decay of enhanced radiosensitivity differs among cell lines. To allow for ease of comparisons among cell types, raw values are expressed as a percentage of the corresponding cell type’s negative (non-irradiated) control & the means & SEMs are plotted. Each result represents at least three independent samples, plated in triplicate. Holm-Sidak comparisons for multiple groups were used for statistical comparisons of raw values (*p<0.05, **p<0.01). Also shown are Western blots of nuclear HIF-1 alpha at the time of irradiation for each cell line. Corresponding Western blots of lamin A/C are shown as a loading control. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25350400), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) proteins after bilateral renal ischemia or sham ischemia. Immunoblots for HIF-1 alpha (A–C) & HIF-2 alpha (D–F) of tissue extracts from the cortex & outer & inner medulla of the left kidneys of rats 24 h & 5 days following recovery from either sham ischemia (○) or bilateral renal ischemia (●); n = 6 per group. G: typical image of the gel following electrophoresis. H: typical image of the nitrocellulose membrane following transfer. Values are expressed as medians (25th percentile, 75th percentile). Paired comparisons were performed using the Mann-Whitney U-test. Because paired comparisons were made at two time points, P values were conservatively adjusted using the Dunn-Sidak method with k = 2. PTr, PT, & PTr*T are the outcomes of two-way analysis of variance on ranking with the factors treatment (Tr) & time (T). AU, arbitrary unit; I1, 24 h after ischemia; I5, 5 days after ischemia; S1, 24 h after sham ischemia; S5, 5 days after sham ischemia. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30110566), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Respiratory burst contributes to the EPO signalling activation during inflammation resolution.ZymA (i.p., 1 mg per mouse) was applied to induce peritonitis in male WT mice or CGD mice. (a) Exudate leucocytes & peritoneum were collected at indicated intervals, & protein levels of HIF-1 alpha & HIF-2 alpha were measured by WB (n=3). (b) YC-1, 400083 or 400087 were intraperitoneally given to WT mice 3 h before zymA injection & the protein levels of related molecules were analysed by WB (n=2). (c) Mice were killed 1 h after injection of pimonidazole at indicated intervals & the protein adducts of reductively-activated pimonidazole were detected by WB with Hypoxiprobe-1-Mab-1 (HPI) (n=2). (d) Flow cytometry for ROS at indicated intervals (n=3). (e) Flow cytometry for cellular sources of ROS at indicated intervals (n=3). Representative data from at least two independent experiments are shown. For flow cytometry data from d, black numbers refer to the percentage of positive cells & red numbers refer to the mean fluorescent intensity. Error bars represent the s.e.m. *P<0.05, two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test. Full-size images for a–c are shown in Supplementary Figs 8–10, respectively. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27397585), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - G9a inhibition reduces cell motility in breast cancer cell lines. G9a inhibition represses breast cancer cell motility in vitro. (A) Microarray analysis of differentially expressed genes comparing hypoxia-responsive genes from MCF7 cells expressing shNS & shG9a identifies a subset of 212 genes downregulated in hypoxia in a G9a-dependent manner. (B) Ingenuity Pathway Analysis results of the 212 G9a-dependent genes. (C) Evaluation of the migratory distance covered by MDA-MB-231 treated with UNC0642 (5 μM) or (D) transfected with either vector or shG9a. Results were evaluated through real-time imaging using the HoloMonitor M4, taking pictures every 10 minutes for 48 hours, in three independent experiments. An average of 20 cells per condition is shown for the representative circular displacement images. (E) Western blot analysis of G9a, H3K9me1 & H3K9me2 in MDA‑MB-231 transfected with vector or shG9a & incubated in hypoxia for 24 hours. HIF1 alpha was included as positive control for hypoxic conditions. H3 & Lamin A/C were used as loading control (F) Scratch wound assay for MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells treated with 5 μM UNC0642, under both normoxic (21% O2) & hypoxic (1% O2) conditions. Results were evaluated by real-time imaging performed by the IncuCyte Zoom every 24 hours & wound closure was quantified using ImageJ. Scale bar represents 500 μm. (G) Scratch wound assay of MCF7 breast cancer cells following G9a KD & G9a reconstitution. Scale bar represents 500 μm. (H) Western blot analysis of MCF7 cells transfected with shG9a & reconstituted with WT G9a. Data are represented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments (unpaired, non-parametric Student's t-test, **p<0.005, ****p<0.0001). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32292512), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hypoxia reduces inflammatory signaling pathways & NLRP3 expression & induces autophagy in IECs. a HT-29 cells were subjected to normoxia & hypoxia at the indicated times in the absence or presence of 10 µg/ml LPS. Autophagy was measured by variations in the ratio of LC3-II/LC3-I & the total amount of LC3 (LC3-I plus LC3-II) relative to beta-actin. Results are representative of two independent experiments. b, c & d HT-29 cells were subjected to normoxia & hypoxia for the indicated periods in the absence or presence of 10 µg/ml LPS, followed by transcript analysis. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-test. Results represent mean + s.e.m. of two independent experiments done in triplicate, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns not significant. e HT-29 cells were subjected to normoxia or hypoxia in the presence & absence of 10 µg/ml LPS & 20 µM of MG132. Results are representative of two independent experiments. f & g Putative binding sites for HIF-1 alpha & NF-kappa B were found in the p62 f & NLRP3 g promoters using Genomatix software tools. Numbers under the boxes indicate the distance from the transcription start site. HT-29 cells were subjected to normoxia (21% O2) or hypoxia (0.2% O2) for 6 h & 24 h. ChIP analysis was performed using antibodies against HIF-1 alpha & NF-kappa B for immunoprecipitation. PCR was performed using the promoter-specific primers for the p62 f & NLRP3 g promoter binding sites of HIF-1 alpha & NF-kappa B. Aliquots taken prior to immunoprecipitation were used as input control. PCR products were run on 2% agarose gel. The results are representative of three independent experiments. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28740109), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Deletion of Hif1 alpha decreases primary tumor growth. (A) Wild-type (WT) or knockout (KO) cells (n = 50,000) were transplanted into FVB/Nj mice. All tumors were harvested at day 56 to evaluate tumor weight, volume & burden (percentage tumor weight/total body weight, BW) (n = 10 recipients/genotype, P < 0.05, unpaired Student's t-test). (B) The growth rate of WT & KO tumors following transplant of 50,000 cells. Best-fit curves were established based on a polynomial fit algorithm using GraphPad Prism 4.0 software. Data in (A) & (B) are representative of seven independent experiments (> 60 recipients/genotype). (C) When 500 WT & KO cells were implanted into the mammary fat pad, the median time until 50% of recipients developed tumors > 500 mm3 was 64 days for WT mice & 127 days for KO mice (n = 14 recipients/genotype, P < 0.001, logrank test). (D) Western blot for HIF-1 alpha in three independent tumors (500 to 750 mm3) per genotype. WT & KO cells that were cultured for 6 hours under hypoxic conditions served as positive & negative controls, respectively. CRM, cross-reactive material. MTEC, mammary tumor epithelial cell. (E) Mean fold change ± SEM in expression of HIF-1 targets in KO tumors as determined by qRT-PCR (n = 5 tumors/genotype). Decreased gene expression in KO tumors is presented as a negative fold-change relative to WT tumors. (F) An increase in Ki67+ cells in KO tumors is balanced by an increase in caspase 3-positive cells (n = 5 tumors/genotype, *P < 0.05, Student's t-test). Representative immunostaining images are shown in Additional file 2 Figure S4. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (http://breast-cancer-research.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/bcr3087), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Effect of HIF-1 alpha silencing on alpha-MSH-induced apoptosis in B16-F10 melanoma cells during hypoxia.a Cells were transfected with shLacZ or shHIF-1 alpha plasmids for 48 h before harvest. HIF-1 alpha shRNA reduced the basal HIF-1 alpha mRNA & protein expression levels. b, c Relative mRNA expression levels were analyzed by real-time PCR. Data are expressed as fold change compared with control (means ± SD of triplicate experiments). d Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblot using the indicated antibodies. beta-Actin was used as an internal control for loading & transfer. e The population of apoptotic cells was analyzed by flow cytometry & qualified as mean ± SD from triplicate experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Knockdown of HIF-1 alpha diminished alpha-MSH-induced apoptosis in B16-F10 melanoma cells during hypoxia Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30062060), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hif1 alpha expression in neonatal & adult testis.(A) Section of testis from 5-day old (P5) male new born pups showing Hif1 alpha expression in MVH+ gonocytes within the seminiferous tubules (top) & negative control images without primary antibodies (bottom). Scale bar: 50μm. (B) Western blot analysis of Hif1 alpha expression in P5 testes (left) compared to extract of the adult brain sub-ventricular zone (SVZ) (right). Loading control ( beta-Actin) is shown below. (C) Section of adult (3 month old) testis showing Hif1 alpha expression in spermatogonia. Scale bar: 30μm. (D) Western blot analysis of whole adult testis. HEK293 cells treated with DFX were used as a positive control & intestinal tissue was used as a negative control. Loading control ( beta-Actin) is shown below. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27148974), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) proteins after bilateral renal ischemia or sham ischemia. Immunoblots for HIF-1 alpha (A–C) & HIF-2 alpha (D–F) of tissue extracts from the cortex & outer & inner medulla of the left kidneys of rats 24 h & 5 days following recovery from either sham ischemia (○) or bilateral renal ischemia (●); n = 6 per group. G: typical image of the gel following electrophoresis. H: typical image of the nitrocellulose membrane following transfer. Values are expressed as medians (25th percentile, 75th percentile). Paired comparisons were performed using the Mann-Whitney U-test. Because paired comparisons were made at two time points, P values were conservatively adjusted using the Dunn-Sidak method with k = 2. PTr, PT, & PTr*T are the outcomes of two-way analysis of variance on ranking with the factors treatment (Tr) & time (T). AU, arbitrary unit; I1, 24 h after ischemia; I5, 5 days after ischemia; S1, 24 h after sham ischemia; S5, 5 days after sham ischemia. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30110566), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Hypoxia reduces inflammatory signaling pathways & NLRP3 expression & induces autophagy in IECs. a HT-29 cells were subjected to normoxia & hypoxia at the indicated times in the absence or presence of 10 µg/ml LPS. Autophagy was measured by variations in the ratio of LC3-II/LC3-I & the total amount of LC3 (LC3-I plus LC3-II) relative to beta-actin. Results are representative of two independent experiments. b, c & d HT-29 cells were subjected to normoxia & hypoxia for the indicated periods in the absence or presence of 10 µg/ml LPS, followed by transcript analysis. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-test. Results represent mean + s.e.m. of two independent experiments done in triplicate, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns not significant. e HT-29 cells were subjected to normoxia or hypoxia in the presence & absence of 10 µg/ml LPS & 20 µM of MG132. Results are representative of two independent experiments. f & g Putative binding sites for HIF-1 alpha & NF-kappa B were found in the p62 f & NLRP3 g promoters using Genomatix software tools. Numbers under the boxes indicate the distance from the transcription start site. HT-29 cells were subjected to normoxia (21% O2) or hypoxia (0.2% O2) for 6 h & 24 h. ChIP analysis was performed using antibodies against HIF-1 alpha & NF-kappa B for immunoprecipitation. PCR was performed using the promoter-specific primers for the p62 f & NLRP3 g promoter binding sites of HIF-1 alpha & NF-kappa B. Aliquots taken prior to immunoprecipitation were used as input control. PCR products were run on 2% agarose gel. The results are representative of three independent experiments. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28740109), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - Transient hyperoxia does not sensitize normal human astrocytes to radiation.Results are shown for the colony forming assays for all previously assayed cell lines & a normal human astrocyte cell line (Astro). Cells were continuously maintained under normoxic conditions (NOx) or exposed to 25 min of hyperoxia (50% O2) & then returned to normoxic conditions for 25 min (HyperOx) before being treated with a 5 Gy dose of radiation. To allow for ease of comparisons among cell types, raw values are expressed as a percentage of the corresponding cells type’s negative (non-irradiated) control & the means & SEMs are plotted. Each result represents three independent samples, plated in triplicate (*p<0.05, Student’s t-test). Also shown are Western blots of nuclear HIF-1 alpha at the time of irradiation for each cell line. Corresponding Western blots of lamin A/C are shown as a loading control. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25350400), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] -
Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - YC-1 attenuates pro-inflammatory differentiation of macrophages. (a,b) qRT-PCR analyses, revealing mRNA expression of the pro-inflammatory M1-differentiation markers NOS2 (a) & IL-6 (b) in murine J774A.1 macrophages under normoxia (left bars) & hypoxia (right bars). LPS exposure was carried out to induce M1-polarization in presence of YC-1 or vehicle control (DMSO; **P ≤ 0.01, n = 9). (c,d) Western blots of nuclear extracts, revealing protein levels of HIF-1 alpha (c) & HIF-2 alpha (d) in J774.A1 macrophages treated with vehicle (DMSO) or YC-1 under normoxic (left) or hypoxic (right) culture conditions. Simultaneous LPS-treatment was performed to induce pro-inflammatory activation. Note LPS-induced stabilization of HIF-1 alpha- (c), but not HIF-2 alpha-levels (d), & reversal of LPS-induced HIF-1 alpha-stabilization by YC-1 (c). Histone H3 was used as a loading control. (e,f) qRT-PCR analyses, revealing mRNA expression of the pro-inflammatory M1-differentiation markers NOS2 (e) & IL-6 (f) in BMDMs under normoxia (left bars) & hypoxia (right bars). LPS exposure was carried out to induce M1-polarization in presence of YC-1 or vehicle control (DMSO; ***P ≤ 0.001, **P ≤ 0.01, n = 6). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-13638-z), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.

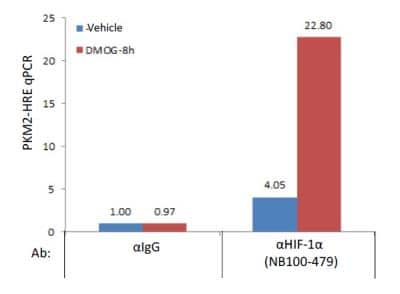
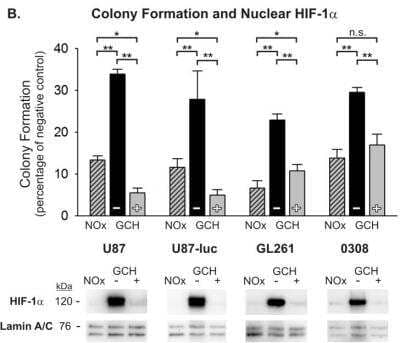
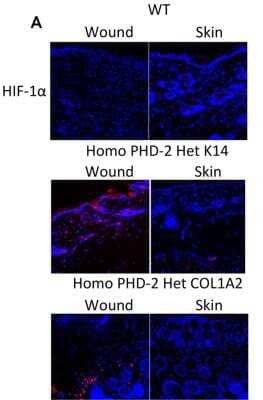
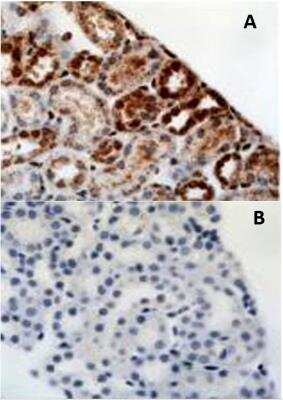
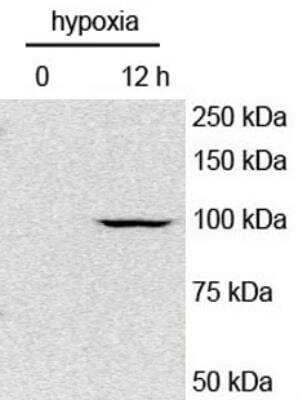

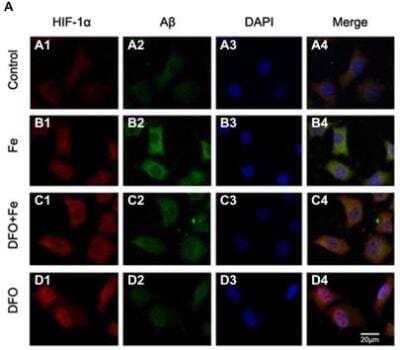
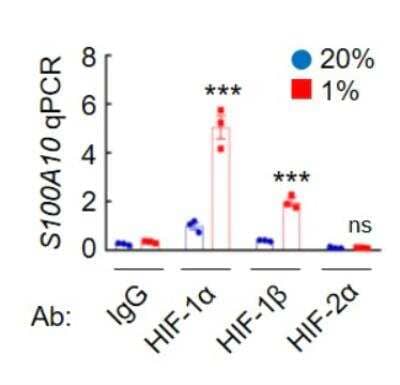
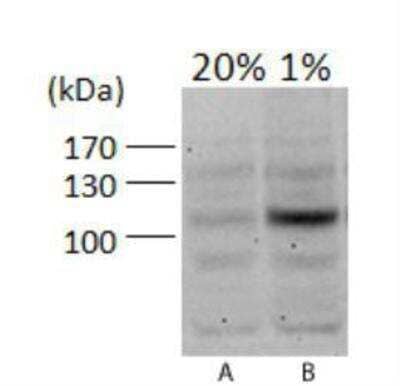
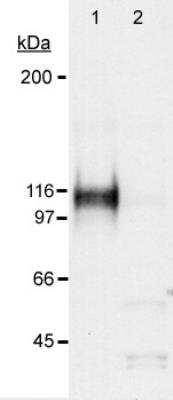


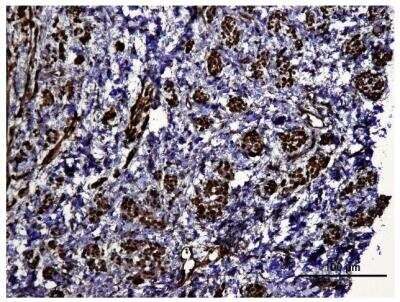
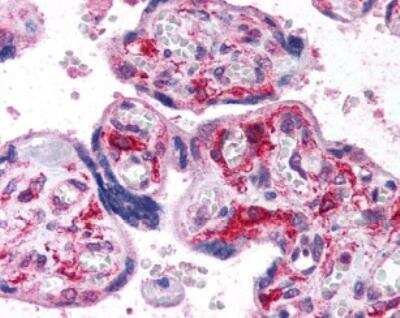
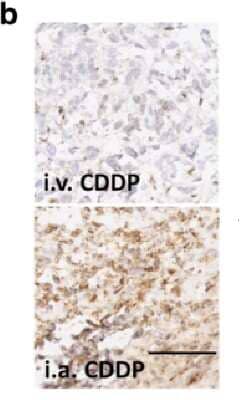
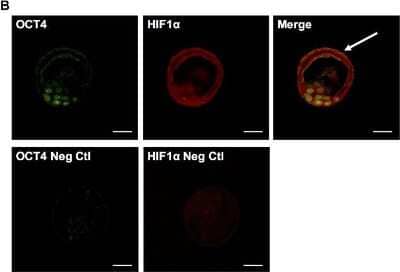
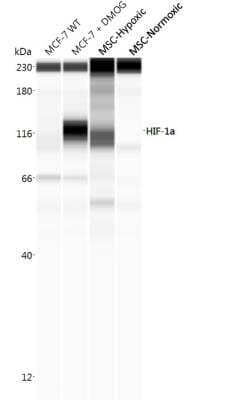
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-271220231253358.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415304234.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415291977.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241530424.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241539457.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241539597.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415394541.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415371998.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241535695.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415345325.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241529197.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415304264.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415371922.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241539258.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415304240.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415371924.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241534537.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241535617.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415371930.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415392531.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241534353.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241539711.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415175294.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415384126.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-3102024165722.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241553511.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-3102024161266.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-3102024155522.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415535187.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241554526.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415541984.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415532086.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241554549.jpg)
![Chromatin Immunoprecipitation: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415532065.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415533816.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415541997.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241554511.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415525223.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415535197.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415525279.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415535159.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415535179.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415533821.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241555237.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415535183.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415533826.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415533840.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415525237.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241554533.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241554523.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415532023.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415523915.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241612619.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241555246.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415535114.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241682112.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241612637.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415525245.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241553718.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415535138.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415541939.jpg)
![Chromatin Immunoprecipitation: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241554513.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415532013.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415532077.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-31020241682177.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415535154.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415541975.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415525255.jpg)
![Western Blot: HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-479] - HIF-1 alpha Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-479_rabbit-polyclonal-hif-1-alpha-antibody-310202415532080.jpg)