Human CD55/DAF Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF2009

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Asp35-Ser353
Accession # P08174
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human CD55/DAF Antibody
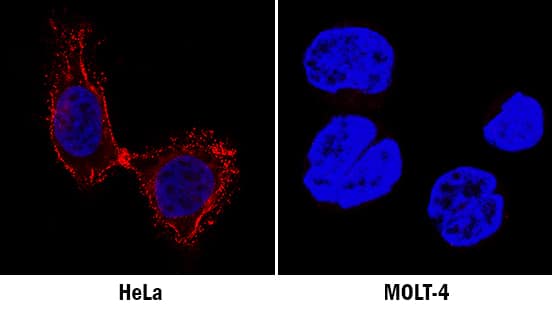
CD55/DAF in HeLa and MOLT-4 Human Cell Lines.
CD55/DAF was detected in immersion fixed HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cell line (left panel, positive staining) and MOLT-4 human acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line (right panel, negative staining) using Goat Anti-Human CD55/DAF Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2009) at 0.5 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to plasma membrane and cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.CD55/DAF in Human Colon Cancer Tissue.
CD55/DAF was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon cancer tissue using 15 µg/mL Goat Anti-Human CD55/DAF Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2009) overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained with the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.Applications for Human CD55/DAF Antibody
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cell line
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon cancer tissue
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: CD55/DAF
CD55, also known as DAF or decay-accelerating factor, is a 70‑75 kDa member of the RCA family of proteins. Human RCA (regulators of complement/C’ activation) proteins are products of chromosome 1 genes that are ubiquitously expressed on cells exposed to plasma complement proteins (1‑4). A hallmark of RCA proteins is the presence of four to 30 SCRs (short consensus repeats; also called CCPs for C’ control protein modules) in their plasma-exposed regions. SCRs are characterized by a 60‑65 amino acid (aa) module that contains a highly conserved Trp residue and two internal disulfide bonds that create a beta-barrel structure (1). Human CD55 is synthesized as a 381 aa precursor that contains a 34 aa signal sequence, a 319 aa mature region and a 28 aa C-terminal prosegment (5, 6). The mature region contains four SCR modules and a C-terminal O-glycosylated extension (7). Following cleavage of the prosegment, a serine is exposed that serves as an anchor for a GPI-linkage (8). Multiple polymorphisms are found in the molecule. Alternate splicing also exists. One form that may not be translated shows an intron insertion in the prosegment, resulting in a 79 aa substitution for the standard C-terminal 20 aas of the prosegment (6). Another form generates a truncated 199 aa precursor that cannot be membrane-bound and may not be secreted (9). Mature CD55 is 53% and 84% aa identical to mouse and monkey CD55, respectively. CD55 is known to bind CD97 via the first SCR (4). It also binds physiologically-generated C3 convertases with its second and third SCRs (7, 10). Binding results in an accelerated “decay”, or dissociation of active C3 convertases, thus blocking the development of C’ attack complexes on nonforeign cells (1, 2). Finally, viruses and bacteria are also known to utilize multiple SCR sites for infection (4).
References
- Herbert, A. et al. (2002) Biochem. Soc. Trans. 30:990.
- Miwa, T. and W-C. Song (2001) Int. Immunopharmacol. 1:445.
- Hourcade, D. et al. (2000) Immunopharmacology 49:103.
- Lea, S. (2002) Biochem. Soc. Trans. 30:1014.
- Medof, M.E. et al. (1987) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:2007.
- Caras, I.W. et al. (1987) Nature 325:545.
- Lukacik, P. et al. (2004) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:1279.
- Moran, P. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266:1250.
- Lublin, D.M. et al. (1994) Blood 84:1276.
- Williams, P. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:10691.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional CD55/DAF Products
Product Documents for Human CD55/DAF Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human CD55/DAF Antibody
For research use only
