Human Coagulation Factor VII Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB2338

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ala39-Pro444
Accession # NP_062562
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human Coagulation Factor VII Antibody
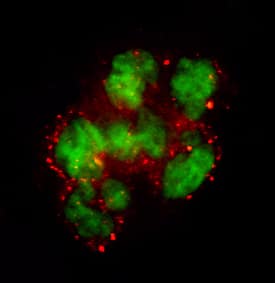
Coagulation Factor VII in Human PBMCs.
Coagulation Factor VII was detected in immersion fixed PHA-stimulated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) using 25 µg/mL Mouse Anti-Human Coagulation Factor VII Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB2338) for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained (red) and counterstained (green). View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.Applications for Human Coagulation Factor VII Antibody
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed PHA-stimulated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs)
Immunoprecipitation
Sample: Conditioned cell culture medium spiked with Recombinant Human Coagulation Factor VII (Catalog # 2338-SE), see our available Western blot detection antibodies
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Human Coagulation Factor VII (Catalog # 2338-SE)
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Coagulation Factor VII
Coagulation Factors VII and VIIa refer to the pro and active forms of the same protease, respectively (1). Factor VII is synthesized in the liver and circulates in the plasma where it binds to tissue factor (TF), an integral membrane protein found in a variety of cell types. Upon binding of TF, Factor VII is rapidly converted into VIIa. The resulting 1:1 complex of VIIa and TF initiates the coagulation pathway and has also important coagulation-independent functions such as angiognesis (2). The cleavage and activation of Coagulation Factors VII, IX and X by VIIa:TF is phospholipid-dependent whereas the cleavage of small peptide substrates is not (1). The predominant splicing variant of Factor VII in normal liver corresponds to the 444 amino acid precursor (3, 4). After a signal peptide (aa 1 to 38), the mature chain can be further processed into the light chain (aa 39 to 190) and the heavy chain (aa 191 to 444).
References
- Morrissey, J.H. (2004) in Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes, Barrett, A.J. et al. eds. p. 1659.
- Versteeg, H.H. et al. (2003) Carcinogenesis 24:1009.
- Hagen, F.S, et al. (1986) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:2412.
- O’Hara, P.J. et al. (1987) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:5158.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Coagulation Factor VII Products
Product Documents for Human Coagulation Factor VII Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human Coagulation Factor VII Antibody
For research use only