Human CRTAM APC-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB16951A

Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ser18-Ser286
Accession # O95727
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human CRTAM APC-conjugated Antibody
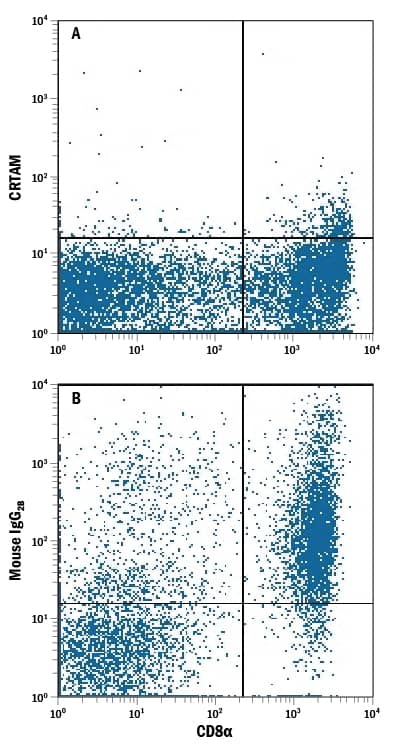
Detection of CRTAM in Human PBMCs by Flow Cytometry.
Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) either (A) untreated or (B) treated with PMA and Calcium Ionomycin for 24 hours were stained with Mouse Anti-Human CRTAM APC-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB16951A) and Mouse Anti-Human CD8a PE-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB1509P). Quadrant markers were set based on control antibody staining (Catalog # IC0041A). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Human CRTAM APC-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) treated with PMA and Calcium Ionomycin
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Background: CRTAM
CRTAM (Class I-restricted T cell-associated molecule) is a nectin family member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that is expressed by activated CD8+ and NK T cells (1‑4). NK activation receptor engagement, but not cytokines, also induce NK CRTAM expression (4, 5). CRTAM is found in spleen, thymus, small intestine, peripheral blood, and surprisingly, in brain where it is highly expressed by Purkinje cells of the cerebellum (1, 2). Human CRTAM is a 393 amino acid (aa), 80 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein with a 17 aa signal sequence, a 269 aa extracellular domain (ECD), a 21 aa transmembrane segment and an 84 aa cytoplasmic domain. The ECD has one V-type and one C1-type Ig-like domain, while the cytoplasmic region shows a potential class I PDZ domain (1‑5). Human CRTAM ECD shows 70%, 43% and 63% aa identity with mouse, rat and canine CRTAM ECD, respectively, but 73‑78% aa identity within the Ig-like domains. The V-type Ig-like domain mediates interaction with the corresponding domain on another nectin family member, IGSF4 (also called TSLC-1, Necl-2, Syncam or SgIGSF) (4, 5). CRTAM is a homodimer on the cell surface but does not show homotypic binding in trans (3‑5). The high affinity of CRTAM/IGSF4 adhesion allows CRTAM to disrupt IGSF4 homotypic interactions (3‑5). IGSF4 and T cell receptor co-engagement of CRTAM-expressing CD8+ cells induces increased IFN-gamma or IL-22 production (3, 4). A role in cancer surveillance through NK cell-mediated rejection of IGSF4-expressing tumors has been proposed (3‑5). IGSF4 is expressed broadly, including on epithelia, neurons, a subset of tonsillar B cells (4, 5), and a rare splenic T zone-restricted BCDA3+ dendritic cell population which interacts with CRTAM (3).
References
- Kennedy, J. et al. (2000) J. Leukoc. Biol. 67:725.
- Patino-Lopez, G. et al. (2006) J. Neuroimmunol. 171:145.
- Galibert, L. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:21955.
- Boles, K. S. et al. (2005) Blood 106:779.
- Arase, N. et al. (2005) Int. Immunol. 17:1227.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional CRTAM Products
Product Documents for Human CRTAM APC-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human CRTAM APC-conjugated Antibody
For research use only