Human DDR2 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF2538

Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Gln24-Arg399
Accession # Q16832
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human DDR2 Antibody
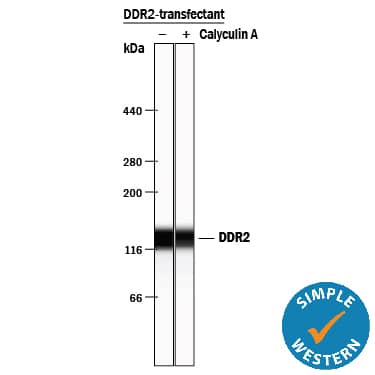
Detection of Human DDR2 by Simple WesternTM.
Simple Western lane view shows lysates of HEK293 human embryonic kidney cell line transfected with human DDR2 untreated (-) or treated (+) with Calyculin A for 10 minutes, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for DDR2 at approximately 139 kDa (as indicated) using 2.5 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human DDR2 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2538) followed by 1:50 dilution of HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF109). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230 kDa separation system.Detection of Human DDR2 by Knockdown Validated
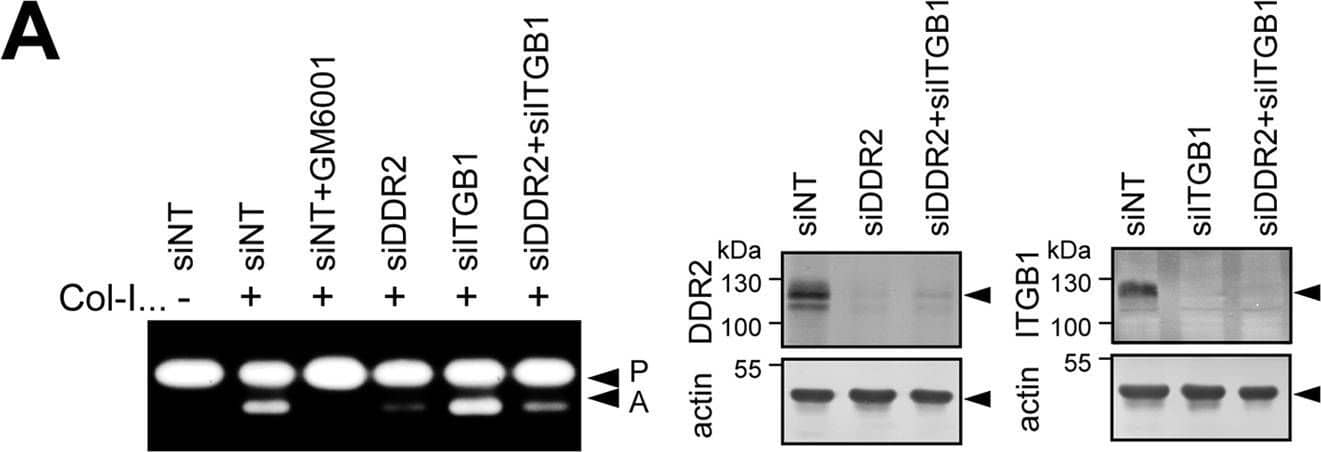
Role of DDR2 in MT1-MMP-dependent collagen film degradation and collagen invasion.A, human RASF or HDF transfected with siNT, siRNA for DDR2 (siDDR2), or siRNA for beta1 integrin (siITGB1) were subjected to collagen film degradation assay as described under “Experimental Procedures” (left panel). Conditioned media from this assay were analyzed by zymography. P, pro-MMP-2; A, active MMP-2. Scale bars, 270 μm. B, human RASF transfected with siNT, siRNA for DDR2, or siRNA for ITGB1 were subjected to Transwell collagen invasion assay as described under “Experimental Procedures” (upper panel). Levels of DDR2, ITGB1, and actin in transfected cells were analyzed by Western blotting (bottom panel). These are combined data of three independent experiments (n = 6 for each experiments). Error bars represent S.E. ***, p > 0.001; n.s., not significant. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0021925820365789), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Human DDR2 by Western Blot
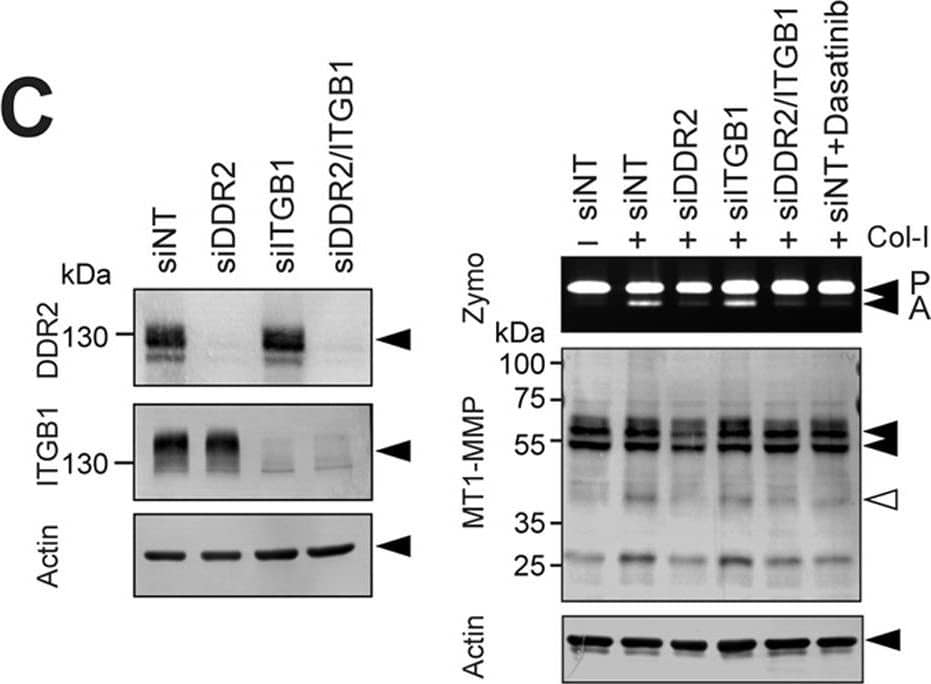
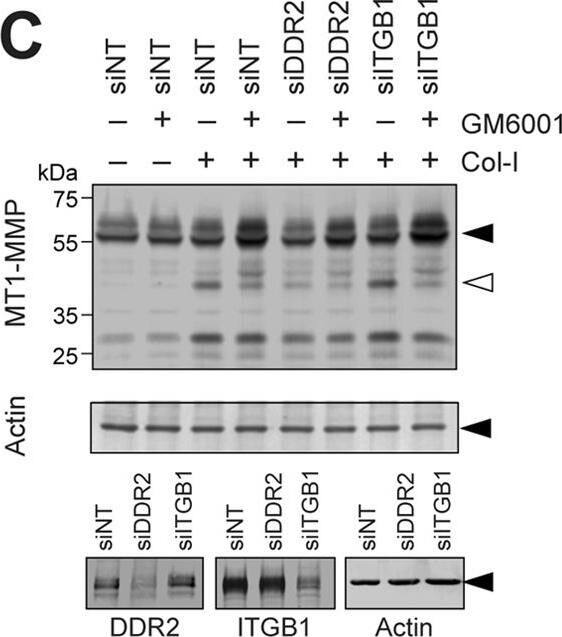
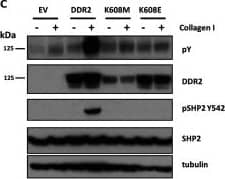
DDR2 but not integrins mediates collagen signaling to activate MT1-MMP functions in RASF.A, human RASF were stimulated with collagen I (Col-I) in the presence or absence of beta1 integrin-inhibitory antibody (6S6) or -activating antibody (P4G11) for 24 h in serum-free medium. Conditioned media and cell lysates were analyzed as in A. B, cell lysates from HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells, RASF, and HDF were analyzed for DDR1 and DDR2 expression by Western blotting. RASF and HDF express DDR2 but not DDR1, whereas HT1080 expresses both DDRs. C, RASF were transfected with siRNA for DDR2 (siDDR2), beta1 integrin (siITGB1), and/or siNT as indicated. 48 h later, cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting analyses for DDR2, ITGB1, and actin (left panel). 48 h after siRNA transfection, cells were also stimulated with collagen I (100 μg/ml) and cultured for a further 72 h. siNT-transfected cells were also treated with dasatinib (Dasa; 100 nm). Conditioned media and cell lysates were analyzed as in A (right panel). D, RASF transfected with siNT, siRNA for DDR2, or siRNA for ITGB1 were stimulated with collagen II (Col-II) of human origin (100 μg/ml) and bovine origin (100 μg/ml) for 48 h. Conditioned media and cell lysates were analyzed as in A. E, RASF transfected with siNT, siRNA for DDR2, or siRNA for ITGB1 were subjected to F-gelatin film degradation assay as in D. Scale bars, 270 μm. P, pro-MMP-2; A, active MMP-2; Zymo, zymography. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0021925820365789), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Human DDR2 Antibody
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human kidney and lung
Simple Western
Sample: HEK293 human embryonic kidney cell line transfected with human DDR2 treated with Calyculin A
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Human DDR2 (Catalog # 2538-DR)
Reviewed Applications
Read 3 reviews rated 4.7 using AF2538 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: DDR2
DDR2, also known as TYR010 and TKT, is a widely expressed 130 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the discoidin-like domain containing subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases (1). Mature human DDR2 consists of a 378 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ECD) that includes the discoidin-like domain, a 22 aa transmembrane segment, and a 434 aa cytoplasmic domain that includes the kinase domain (2). Within the ECD, human DDR2 shares 53% aa sequence identity with DDR1 and 97% aa sequence identity with mouse DDR2. The discoidin-like domain mediates DDR2 interactions with collagens I, III, and X (3-5). Collagens II and V are less efficacious ligands (3). DDR2 selectively recognizes the triple helical structure of collagen compared to monomeric or denatured collagen (3, 5, 6). Within collagen II, the D2 period is required for DDR2 binding, and the D1 period is additionally required to trigger DDR2 autophosphorylation (6). The ECD of DDR2 exists as a non-covalent dimer in solution, and dimerization of the receptor greatly enhances collagen binding (4, 7). DDR2 interaction with collagen I inhibits collagen fibrillogenesis and alters collagen fiber morphology (7). Ligand binding induces DDR2 autophosphorylation in the cytoplasmic domain (3, 5, 8), which promotes associations with Shc and Src (9). In addition to the above mechanism, DDR2 exhibits a distinct interaction with collagen X. A region other than the discoidin-like domain of DDR2 recognizes the non-helical NC1 domain of collagen X, and this interaction does not lead to receptor autophosphorylation (5). Activation of DDR2 by collagen induces upregulation of MMP-1, -2, and -13 as well as DDR2 itself (3, 8, 10). DDR2 is implicated in collagenous matrix destruction and cell invasiveness (8, 10). DDR2 is also upregulated in several pathological conditions, including hepatic fibrosis following injury, rheumatoid and osteoarthritis, and smooth muscle cell hyperplasia (8, 10-12).
References
- Vogel, W.F. et al. (2006) Cell. Signal. 18:1108.
- Karn, T. et al. (1993) Oncogene 8:3433.
- Vogel, W. et al. (1997) Mol. Cell 1:13.
- Leitinger, B. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:16761.
- Leitinger, B. and A.P.L Kwan (2006) Matrix Biol. 25:355.
- Leitinger, B. et al. (2004) J. Mol. Biol. 344:993.
- Mihai, C. et al. (2006) J. Mol. Biol. 361:864.
- Olaso, E. et al. (2001) J. Clin. Invest. 108:1369.
- Ikeda, K. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:19206.
- Xu, L. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:548.
- Wang, J. et al. (2002) J. Autoimmun. 19:161.
- Ferri, N. et al. (2004) Am. J. Pathol. 164:1575.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional DDR2 Products
Product Documents for Human DDR2 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human DDR2 Antibody
For research use only