Human Dermatopontin Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF4629

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Gln19-Val201
Accession # AAH33736
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human Dermatopontin Antibody
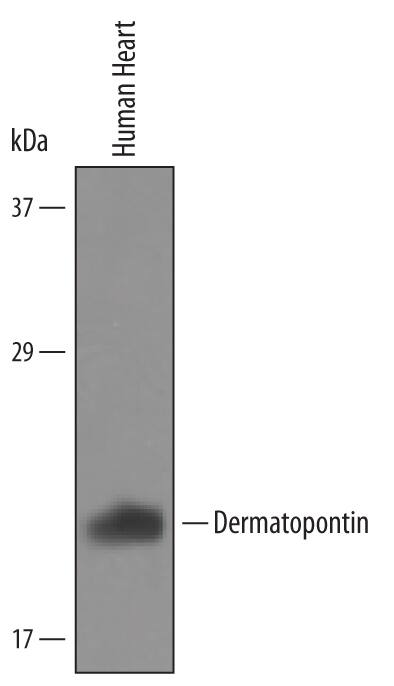
Detection of Human Dermatopontin by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of human heart tissue. PVDF Membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Human Dermatopontin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF4629) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF016). A specific band was detected for Dermatopontin at approximately 22 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 8.Applications for Human Dermatopontin Antibody
Western Blot
Sample: Human heart tissue
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Dermatopontin
Dermatopontin, also known as TRAMP (tyrosine rich acidic matrix protein), is a widely expressed noncollagenous protein component of the extracellular matrix (1, 2). Mature human Dermatopontin shares 96%, 92%, and 92% amino acid sequence identity with bovine, mouse, and rat Dermatopontin, respectively. It is a 22 kDa molecule that is tyrosine sulfated but not glycosylated (3, 4). Dermatopontin contains three disulfide bonded loop structures that enclose conserved hexapeptide motifs (5). It accelerates collagen fibril formation in vitro, and Dermatopontin deficient mice exhibit altered collagen matrix deposition and organization (6 - 8). Dermatopontin is downregulated in fibrotic growths such as leiomyoma and scar tissue (9, 10). It binds both TGF-beta and the proteoglycan decorin, interactions that can increase the bioavailability of TGF-beta (11, 12). Dermatopontin promotes bone mineralization under the control of the vitamin D receptor and inhibits BMP-2 effects on osteoblast precursors (13, 14).
References
- Okamoto, O. and S. Fujiwara (2006) Connect. Tissue Res. 47:177.
- Superti-Furga, A. et al. (1993) Genomics 17:463.
- Forbes, E.G. et al. (1994) FEBS Lett. 351:433.
- Cronshaw, A.D. et al. (1993) Matrix 13:255.
- Neame, P.J. et al. (1989) J. Biol. Chem. 264:5474.
- MacBeath, J.R.E. et al. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268:19826.
- Takeda, U. et al. (2002) J. Invest. Dermatol. 119:678.
- Cooper, L.J. et al. (2006) Invest. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 47:3303.
- Catherino, W.H. et al. (2004) Genes Chromosomes Cancer 40:204.
- Kuroda, K. et al. (1999) J. Invest. Dermatol. 112:706.
- Okamoto, O. et al. (1996) J. Biochem. 119:106.
- Okamoto, O. et al. (1999) Biochem. J. 337:537.
- Pochampally, R.R. et al. (2007) J. Bone Miner. Res. 22:1338.
- Behnam, K. et al. (2006) Connect. Tissue Res. 47:271.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Dermatopontin Products
Product Documents for Human Dermatopontin Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human Dermatopontin Antibody
For research use only