Human ECM1 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF3937

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ala20-Glu540
Accession # AAH23505
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human ECM1 Antibody
Detection of Human ECM‑1 by Western Blot.
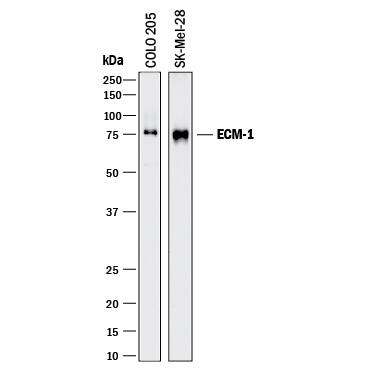
Western blot shows lysates of COLO 205 human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line and SK-Mel-28 human malignant melanoma cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Sheep Anti-Human ECM-1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3937) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF016). A specific band was detected for ECM-1 at approximately 75 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.ECM-1 in Human Colon Cancer Tissue.
ECM-1 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon cancer tissue using 15 µg/mL Sheep Anti-Human ECM-1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3937) overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained with the Anti-Sheep HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS019) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific labeling was localized to the plasma membrane of epithelial cells. Lower panel shows a lack of labeling if primary antibodies are omitted and tissue is stained only with secondary antibody followed by incubation with detection reagents. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.Detection of Human ECM‑1 by Simple WesternTM.
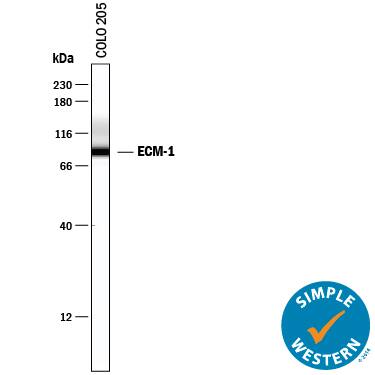
Simple Western lane view shows lysates of COLO 205 human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for ECM-1 at approximately 90 kDa (as indicated) using 10 µg/mL of Sheep Anti-Human ECM-1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3937) followed by 1:50 dilution of HRP-conjugated Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF016). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230 kDa separation system.Applications for Human ECM1 Antibody
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon cancer tissue
Simple Western
Sample: COLO 205 human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line
Western Blot
Sample: COLO 205 human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line and SK‑Mel‑28 human malignant melanoma cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: ECM1
Extracellular matrix protein-1 (ECM-1) is an 85 kDa, secreted glycoprotein important in connective tissue organization (1‑3). Of three identified splice variants the 540 amino acid (aa) form, ECM-1a, is the most widely expressed, with the highest expression in the placenta and heart (2). ECM-1b (415 aa) is found only in tonsil and associated with suprabasal keratinocytes (2, 4). Since ECM-1b expression is differentiation-dependent, a role in terminal keratinocyte differentiation has been suggested (4). ECM-1c (559 aa) accounts for approximately 15% of skin ECM-1 (5). Human ECM-1a contains a 19 aa signal peptide and a 521 aa secreted portion that includes an N-terminal proline-rich, cysteine-free region, two tandem repeat domains, and a C-terminal domain. There are six repeats of a CC(X7 ‑10)C motif (x = any aa) within the tandem repeat and C‑terminal domains. These motifs are involved in ligand binding to members of the albumin family, and are expected to form two (in ECM-1b) or three (in ECM-1a) “double loop” structures (2). Mature human ECM-1a shows 69%, 71%, 72%, and 76% aa identity with corresponding isoforms of mouse, rat, canine, and bovine ECM-1, respectively. ECM-1 is over-expressed in many malignant epithelial tumors and has demonstrated angiogenic activity (6, 7). A variety of ECM-1 mutations, mainly within the first tandem repeat, are considered causative of lipoid proteinosis, a condition showing thickened and irregular extracellular matrix within connective tissue (8). In the autoimmune condition lichen sclerosis, auto-antibodies mainly recognize the second tandem repeat or the C-terminus of ECM-1 (9). These domains also bind the extracellular matrix molecules fibulin-1 and perlecan (5, 10). The phenotypes of lipoid proteinosis and lichen sclerosis support a role for ECM-1 as a “biological glue” in the dermis (1).
References
- Chan, I. (2004) Exp. Dermatol. 29:52.
- Smits, P. et al. (1997) Genomics 45:487.
- Bhalerao, J. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem 270:16385.
- Smits, P. et al. (2000) J. Invest. Dermatol. 114:718.
- Mongiat, M. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:17491.
- Han, Z. et al. (2001) FASEB J. 15:988.
- Wang, L. et al. (2003) Cancer Lett. 200:57.
- Hamada, T. et al. (2003) J. Invest. Dermatol. 120:345.
- Oyama, N. et al. (2004) J. Clin. Invest. 113:1550.
- Fujimoto, N. et al. (2005) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 333:1327.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional ECM1 Products
Product Documents for Human ECM1 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human ECM1 Antibody
For research use only