Human FGF-BP Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB1593

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Val35-Cys234
Accession # Q14512
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human FGF-BP Antibody
Detection of Human FGF-BP by Western Blot
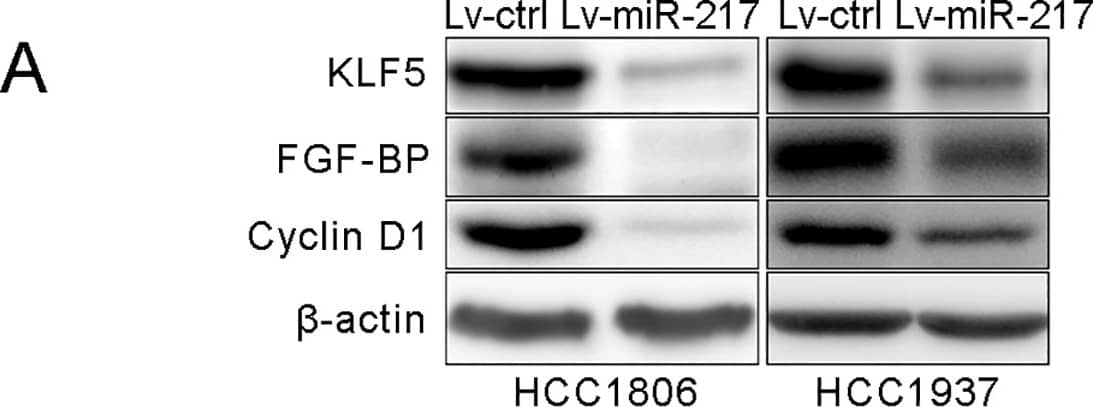
miR-217 targets KLF5 by binding to its 3’UTR.A. miR-217 decreased the KLF5, FGF-BP and Cyclin D1 protein levels in HCC1806 and HCC1937 TNBC cells. KLF5, FGF-BP and Cyclin D1 protein levels were detected by using WB. beta-actin was used as the loading control. B. The putative wild type binding sites of miR-217 on KLF5 3’UTR and its mutants. C. miR-217 mimics significantly inhibits the KLF5 3’UTR luciferase reporter activity through the second putative binding site. HEK293T cells were transfected with miR-217 mimics and pMIR-KLF5 3’-UTR or miR-217 binding sites mutated pMIR-KLF5 3’-UTR reporters (mut1, mut2 or mut1,2) together with the pCMV-Renilla control. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176395), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Mouse FGF-BP by Immunohistochemistry
mTORC1-STAT3-FGFBP1 pathway regulates angiogenesis in an OVA-induced chronic asthma model.A The timeline to establish OVA-induced chronic asthma models and therapeutic interventions (see the “Materials and methods” section for details). The mice were divided into three groups: the control group (Control), OVA-induced chronic asthma group (OVA), and rapamycin-treated group (Rapa). B The total number of leukocytes and eosinophil count in the BALF were counted using Wright–Giemsa staining. C Representative photographs of H&E staining (upper panels) and Masson’s staining (lower panels) of lung tissues (scale bar: 100 μm). D Inflammation score (left panels) and Wat/Pbm (right panels) of lung tissues. E Immunoblotting of the indicated proteins in lung tissues. F IHC analysis of the indicated proteins in lung tissues (scale bar: 100 μm). n = 8 mice per group. Results are shown as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. G Schematic illustration of activated mTORC1-STAT3-FGFBP1 signaling pathway promotes angiogenesis in airway epithelial cells. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34341336), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Mouse FGF-BP by Immunohistochemistry
PLA promotes angiogenesis through FGFBP1.A NCI-H292 cells, stably expressed shRNA targeting FGFBP1 (shFGFBP1) or a control shRNA (shSc), were treated with 20 μg/mL PLA for 24 h. Western blot (upper panel) and ELISA (lower panel) were performed to detect the protein levels of FGFBP1 in cell lysates and supernatants, respectively. B–E NCI-H292/shFGFBP1 and NCI-H292/shSc cells were treated with PLA (20 μg/mL) for 24 h and the cell-conditioned media were collected for tube formation assay (B, C) and CAM assay (D, E). B, D Representative micrographs of tube formation assay (B) and CAM assay (D). C, E Quantitations of total branching points of tube formation assay (C) and new vessels of CAM assay (E). F NCI-H292 cells infected with lentivirus harboring a vector encoding FGFBP1 (LvFGFBP1) or the empty vector (LvNC). Western blot (upper panel) and ELISA (lower panel) were performed to detect the protein levels of FGFBP1 in cell lysates and supernatants, respectively. (G–J) The cell-conditioned media of NCI-H292/LvFGFBP1 and NCI-H292/LvNC cells were collected for tube formation assay (G, H) and CAM assay (I, J). G, I Representative micrographs of tube formation assay (G) and CAM assay (I). H, J Quantitation of total branching points of tube formation assay (H) and new vessels of CAM assay (J). n = 6 chick embryos per group. Results are shown as mean ± SD. ***P < 0.001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34341336), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Human FGF-BP Antibody
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Human FGF-BP (Catalog # 1593-FB)
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: FGF-BP
Fibroblast growth factor binding protein (FGF‑BP), also known as HBp17, is a secreted glycoprotein that increases the bioavailability of FGFs (1). Mature FGF-BP is a 34 kDa, 211 amino acid (aa) O-glycosylated protein with five conserved intrachain disulfide bonds (2‑4). FGF-BP contains a heparin-binding domain (aa 110‑143) and a distinct FGF-binding region (aa 193‑243) (5). Mature human FGF‑BP shares 59% and 54% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat FGF-BP, respectively. FGF-BP is expressed throughout development and in adult squamous epithelium (2, 6). It is upregulated in injured skin, renal tubular epithelium, and spinal nerves as well as in carcinomas of the skin, colon, and pancreas (3, 7‑10). FGF-BP binds FGF-1, -2, -7, -10, and -22 which are secreted and sequestered in the extracellular matrix (ECM) (7, 11). The association of FGF-BP with heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG) weakens HSPG attachment of FGFs and promotes their release (2, 8, 12, 13). FGF‑BP enhances the mitogenic effects of FGFs, thereby contributing to epithelial, endothelial, and neuronal tissue repair, angiogenesis, and tumor growth (7‑9, 11, 14, 15).
References
- Abuharbeid, S. et al. (2006) Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 38:1463.
- Wu, D. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266:16778.
- Tassi, E. et al. (2006) Cancer Res. 66:1191.
- Lametsch, R. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:19469.
- Xie, B. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:1137.
- Aigner, A. et al. (2002) Histochem. Cell Biol. 117:1.
- Beer, H-D. et al. (2005) Oncogene 24:5269.
- Ray, P.E. et al. (2006) Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 290:R105.
- Tassi, E. et al. (2007) Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 293:R775.
- Kurtz, A. et al. (2004) Neoplasia 6:595.
- Tassi, E. et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:40247.
- Mongiat, M. et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:10263.
- Kurtz, A. et al. (1997) Oncogene 14:2671.
- Aigner, A. et al. (2001) Int. J. Cancer 92:510.
- Czubayko, F. et al. (1997) Nat. Med. 3:1137.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional FGF-BP Products
Product Documents for Human FGF-BP Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human FGF-BP Antibody
For research use only