Human IL-1 RI APC-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB269A

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human IL-1 RI APC-conjugated Antibody
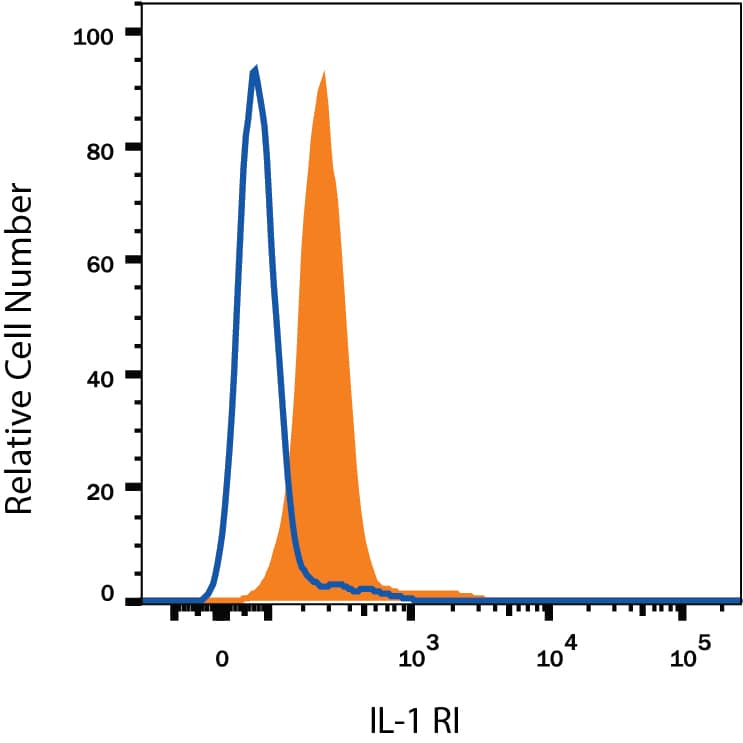
Detection of IL‑1 RI in HUVEC Human Cells by Flow Cytometry.
HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells were stained with Goat Anti-Human IL-1 RI APC-conjugated Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB269A, filled histogram) or control antibody (Catalog # IC108A, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Human IL-1 RI APC-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Background: IL-1 RI
Two distinct types of receptors that bind the pleiotropic cytokines IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta have been described. The IL-1 receptor Type I is an 80 kDa transmembrane protein that is expressed predominantly by T cells, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. IL-1 receptor Type II is a 68 kDa transmembrane protein found on B lymphocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, large granular leukocytes and endothelial cells. Both receptors are members of the immunoglobulin superfamily and show approximately 28% sequence identity in their extracellular domains. The two receptor types do not heterodimerize into a receptor complex.
An IL-1 receptor accessory protein that can heterodimerize with the Type I receptor in the presence of IL-1 alpha or IL-1 beta but not IL-1ra, was identified (1). This Type I receptor complex appears to mediate all the known IL-1 biological responses. The receptor Type II has a short cytoplasmic domain and does not transduce IL-1 signals. In addition to the membrane-bound form of IL-1 RII, a naturally-occurring soluble form of IL-1 RII has been described. It has been suggested that the Type II receptor, either as the membrane-bound or as the soluble form, serves as a decoy for IL-1 and inhibits IL-1 action by blocking the binding of IL-1 to the signaling Type I receptor complex. Recombinant IL-1 soluble receptor Type I is a potent antagonist of IL-1 action.
References
- Greenfeder, S. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:13757.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
Additional IL-1 RI Products
Product Documents for Human IL-1 RI APC-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human IL-1 RI APC-conjugated Antibody
For research use only