Human/Mouse Insulin R/CD220 APC-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB1544A

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
His28-Lys944
Accession # NP_001073285
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human/Mouse Insulin R/CD220 APC-conjugated Antibody
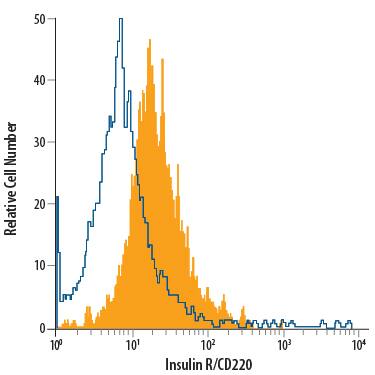
Detection of Insulin R/CD220 in Human Blood Monocytes by Flow Cytometry.
Human peripheral blood monocytes were stained with Goat Anti-Human/Mouse Insulin R/CD220 APC-conjugated Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB1544A, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC108A, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Detection of Insulin R/CD220 in Neuro‑2A Mouse Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
Neuro-2A mouse neuroblastoma cell line was stained with Goat Anti-Human/Mouse Insulin R/CD220 APC-conjugated Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB1544A, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC108A, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Human/Mouse Insulin R/CD220 APC-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: Human peripheral blood monocytes and Neuro‑2A mouse neuroblastoma cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Background: Insulin R/CD220
The Insulin Receptor (INS R) and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1 R) constitute a subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases (1‑4). The two receptors share structural similarity as well as overlapping intracellular signaling events, and are believed to have evolved through gene duplication from a common ancestral gene. INS R cDNA encodes a type I transmembrane single chain preproprotein with a putative 27 amino acid residues (aa) signal peptide. The large INS R extracellular domain is organized into two successive homologous globular domains, which are separated by a Cysteine-rich domain, followed by three fibronectin type III domains. The intracellular region contains the kinase domain sandwiched between the juxtamembrane domain used for docking insulin-receptor substrates (IRS), and the carboxy-terminal tail that contains two phosphotyrosine-binding sites. After synthesis, the single chain INS R precursor is glycosylated, dimerized and transported to the Golgi apparatus where it is processed at a furin-cleavage site within the middle fibronectin type III domain to generate the mature disulfide-linked alpha2 beta2 tetrameric receptor. The alpha subunit is localized extracellularly and mediates ligand binding while the transmembrane beta subunit contains the cytoplasmic kinase domain and mediates intracellular signaling. As a result of alternative splicing, two INS R isoforms (A and B) that differ by the absence or presence, respectively, of a 12 aa residue sequence in the carboxyl terminus of the alpha subunit exist. Whereas the A isoform is predominantly expressed in fetal tissues and cancer cells, the B isoform is primarily expressed in adult differentiated cells. Both the A and B isoforms bind insulin with high-affinity, but the A isoform has considerably higher affinity for IGF‑I and IGF‑II. Ligand binding induces a conformational change of the receptor, resulting in ATP binding, autophosphorylation, and subsequent downstream signaling. INS R signaling is important in metabolic regulation, but may also contribute to cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis. Mutations in the INS R gene have been linked to insulin-resistant diabetes mellitus, noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and leprechaunism, an extremely rare disorder characterized by abnormal resistance to insulin that results in a variety of distinguishing characteristics, including growth delays and abnormalities affecting the endocrine system. INS R is highly conserved between species, rat INS R shares 94% and 97% aa sequence homology with the human and mouse receptor, respectively.
References
- Nakae, J. et al. (2001) Endoc. Rev. 22:818.
- De Meyts, P. and J. Whittaker (2002) Nature Rev. Drug Disc. 1:769.
- Kim, J.J. and D. Accili (2002) Growth Hormone and IGF Res. 12:84.
- Sciacca, L. et al. (2003) Endocrinology 144:2650.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Insulin R/CD220 Products
Product Documents for Human/Mouse Insulin R/CD220 APC-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human/Mouse Insulin R/CD220 APC-conjugated Antibody
For research use only