Human/Mouse/Rat Thioredoxin-1 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB19701

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Val2-Val105
Accession # P10599
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human/Mouse/Rat Thioredoxin-1 Antibody
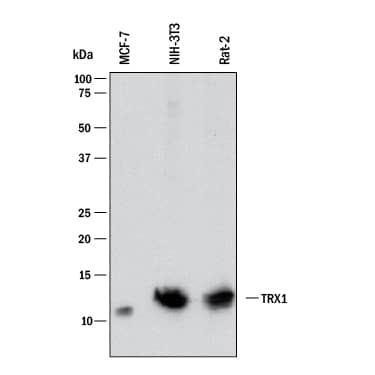
Detection of Human, Mouse, and Rat Thioredoxin‑1 by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line, NIH-3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line, and Rat-2 rat embryonic fibroblast cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat Thioredoxin-1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB19701) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF018). A specific band was detected for Thioredoxin-1 at approximately 12 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.Thioredoxin‑1 in HeLa Human Cell Line.
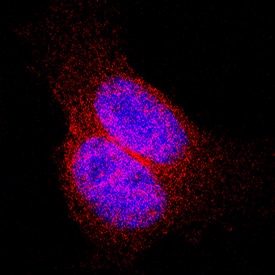
Thioredoxin-1 was detected in immersion fixed HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cell line using Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat Thioredoxin-1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB19701) at 8 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL007) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.Thioredoxin‑1 in Human Lung.
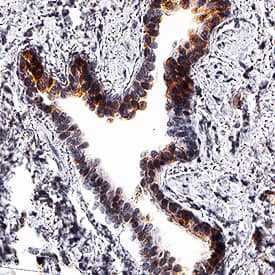
Thioredoxin-1 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human lung using Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat Thioredoxin-1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB19701) at 5 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC001). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm in alveolar cells. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Applications for Human/Mouse/Rat Thioredoxin-1 Antibody
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cell line
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human lung
Western Blot
Sample: MCF‑7 human breast cancer cell line, NIH‑3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line, and Rat‑2 rat embryonic fibroblast cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Thioredoxin-1
Thioredoxins (Trxs) are a group of small ubiquitous proteins in all living cells that are key regulators of cellular redox balance (1, 2). The mammalian Trx family has three members. The Trx-1, which is a secreted and cellular protein, the mitochondria-specific Trx-2, and the Trx-like cytosolic protein p32TrxL (3‑5). The active site of mammalian Trxs contains two cysteines in the conserved sequence -Y-C-G-P-C-K-. In Trx-1 the conserved cysteine residues are in positions 32 and 35, respectively. Trxs exist either in a reduced or in an oxidized state when the two cysteines at the active site form an intramolecular disulfide bridge. NADPH and the flavoprotein thioredoxin reductase can convert the oxidized Trx into the reduced Trx. Trx-1 is the only extracellular occurring thioredoxin, and is secreted by lymphocytes, hepatocytes, fibroblasts, and several tumor cells. Plasma concentrations of Trx-1 are up to 6 nM (6). In cells, Trx-1 is localized predominantly in the cytoplasm. Small amounts have been detected in the nucleus and in association with the outside surface of the cells. Expression of Trx-1 is increased under various stress conditions such as hypoxia, elevated hydrogen peroxide concentrations, photochemical oxidative stress, and viral and bacterial infections. Biological functions of Trx-1 include growth factor activity, antioxidant properties, a cofactor that provides reducing equivalents, and transcriptional regulation (1, 2). The synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis patients produces increased levels of Trx-1 under oxidative stress conditions, and a correlation exists between the plasma levels of Trx-1 and the severity of the disease, making Trx-1 a biomarker for this pathological condition (7, 8).
References
- Holmgren, A. (1985) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 54:237.
- Powis, G. and W.R. Monfort (2001) Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 41:269.
- Deiss, L.P. and A. Kimchi (1991) Science 252:117.
- Spyrou, G. et al. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272:2936.
- Miranda-Vizuete, A. et al. (1998) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 243:284.
- Nakamura, H. et al. (1997) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15:147.
- Mourice, M.M. et al. (1999) Arthritis Rheum. 42:2430.
- Jikimoto, T. et al. (2001) Mol. Immunol. 38:765.
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Thioredoxin-1 Products
Product Documents for Human/Mouse/Rat Thioredoxin-1 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human/Mouse/Rat Thioredoxin-1 Antibody
For research use only