Human PDGF-C Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB1560

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Val235-Gly345
Accession # Q9NRA1
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Human PDGF-C Antibody
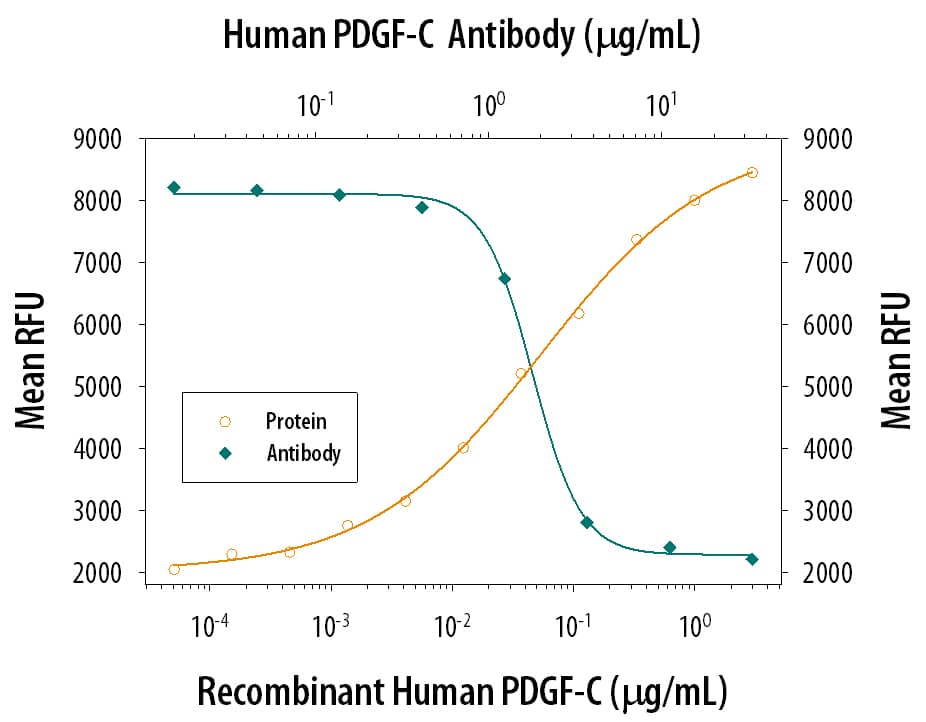
Proliferation Induced by PDGF‑CC and Neutralization by Human PDGF‑C Antibody.
Recombinant Human PDGF-CC (Catalog # 1687-CC) induces proliferation in the NR6R-3T3 mouse fibroblast cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line), as measured by Resazurin (Catalog # AR002). Proliferation elicited by Recombinant Human PDGF-CC (1 ug/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Mouse Anti-Human PDGF-C Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB1560). The ND50 is typically 0.6-3 ug/ml.Applications for Human PDGF-C Antibody
Neutralization
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: PDGF-C
The platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) family consists of proteins derived from four genes (PDGF-A, -B, -C, and -D) that form four disulfide-linked homodimers (PDGF-AA, -BB, -CC, and -DD) and one heterodimer (PDGF-AB) (1). These proteins regulate diverse cellular functions by binding to and inducing the homo- or hetero‑dimerization of two receptor tyrosine kinases (PDGF R alpha and R beta). Within the PDGF family, PDGF-C and PDGF-D constitute a subgroup that shares similar structural organization (2, 3). Both proteins are secreted as inactive homodimeric latent growth factors. Each monomer has two distinct protein domains: an N-terminal CUB domain; and a C-terminal PDGF/VEGF homology domain that shares 27‑35% sequence identity with the corresponding regions of other PDGF family members. An 80‑90 amino acid residue hinge region connects the two domains. Sequential removal of the CUB domains in the homodimeric latent growth factor by extracellular proteolytic cleavage at the hinge region is required to release the bioactive PDGF/VEGF homology domain(1). Twelve cysteine residues are found within the PDGF/VEGF homology domain of PDGF-C, including the characteristic eight invariant cysteine residues involved in inter- and intra-chains disulfide-bonds needed for the formation of the cysteine-knot structure. Bioactive PDGF-CC binds with high-affinity to PDGF R alpha but not PDGF R beta and activates PDGF R alpha homodimerization (1). PDGF-CC has also been shown to activate PDGF R alpha beta heterodimers (1). PDGF-CC is expressed in multiple embryonic and adult cell types and tissues. During embryonic development, PDGF-CC is involved in ductal morphogenesis (4). PDGF-CC is a potent angiogenic factor that stimulates vessel growth in the mouse cornea pocket assay and in the CAM assay (5). It stimulates coronary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation and may play an important role in cardiovascular development and function (6). PDGF-CC is also expressed in many tumors and tumor cell lines and has a causative role in tumorigenesis (7). Mature human and mouse PDGF-C share 93.7% amino acid sequence identity.
References
- Li, X. and U. Eriksson (2003) Cytokine &Growth Factor Rev. 14:91.
- LaRochells, W.J. et al. (2001) Nature Cell Biol. 3:517.
- Li, X. et al. (2000) Nature Cell Biol. 2:302.
- Aase, K. et al. (2002) Mech Dev. 110:187.
- Cao, R.H. et al. (2002) FASEB J. 16:1575.
- Gilbertson, D. et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:27406.
- Zwerner, J.P. and W.A. May (2001) Oncogene 20:626.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional PDGF-C Products
Product Documents for Human PDGF-C Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human PDGF-C Antibody
For research use only