Human/Primate Dopamine beta-Hydroxylase N-Terminus Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # PPS067

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human/Primate Dopamine beta-Hydroxylase N-Terminus Antibody
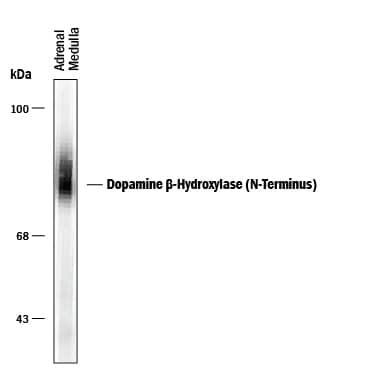
Detection of Dopamine beta‑Hydroxylase (N-Terminus).
Western blot of human adrenal medulla lysate showing specific immunolabeling of the ~75 kDa D betaH protein.Applications for Human/Primate Dopamine beta-Hydroxylase N-Terminus Antibody
Western Blot
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
Background: Dopamine beta-Hydroxylase
Dopamine beta-hydroxylase (D betaH; also dopamine beta-monooxygenase) is a 73-77 kDa member of the copper type II ascorbate-dependent monooxygenase family. It is both soluble (73 kDa) and membrane-bound (77 kDa) (anchored by an uncleaved signal sequence), and via hydroxylation, converts dopamine into norepinepherine. Human D betaH is a copper-containing disulfide-linked homodimer that is found in neurons and adrenal medullary cells. It is 603 amino acids (aa) in length and contains a 25 aa signal sequence followed by three domains. The first is an N-terminal 120 aa DOMON domain (dopamine beta-monooxygenase N-terminal) that may either bind D betaH to the cell membrane, or participate in tetramerization. This is followed by two 150 aa Cu+-type II ascorbate-dependent monooxygenase domains (aa 182-330 and 352-512). D betaH may be most active as a dimeric-dimer/tetramer, whose association status is dependent on local Cl- concentrations.
References
- Kreek, M.J. et al. (2005) Pharmacol. Rev. 57:1.
- Stewart, L. and J.P. Klinman (1999) FEBS Lett. 454:229.
- Houhou, L. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:12601.
- Timmers, H. et al. (2004) Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1018:520.
- Lamouroux, A. et al. (1987) EMBO J. 6:3931.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
Additional Dopamine beta-Hydroxylase Products
Product Documents for Human/Primate Dopamine beta-Hydroxylase N-Terminus Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human/Primate Dopamine beta-Hydroxylase N-Terminus Antibody
For research use only