Human Syndecan-1/CD138 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB2780

Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Gln18-Glu251
Accession # NP_002988
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human Syndecan-1/CD138 Antibody
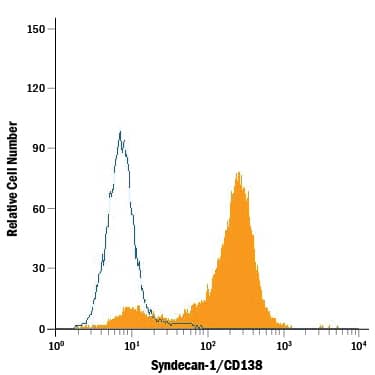
Detection of Syndecan-1/CD138 in RPMI 8226 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
RPMI 8226 human multiple myeloma cell line was stained with Rat Anti-Human Syndecan-1/CD138 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB2780, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB005, open histogram), followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Rat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0105B).Syndecan‑1/CD138 in U266 Human Cell Line.
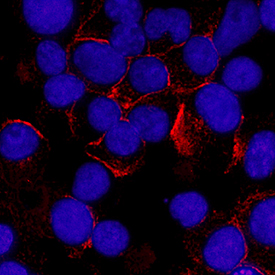
Syndecan-1/CD138 was detected in immersion fixed U266 human myeloma cell line using Rat Anti-Human Syndecan-1/CD138 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB2780) at 3 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Rat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL013) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to plasma membrane. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.Syndecan‑1/CD138 in Human Cervical Cancer Tissue.
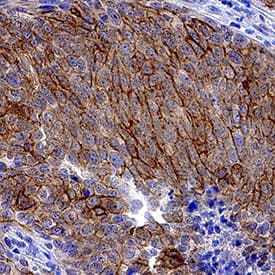
Syndecan-1/CD138 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human cervical cancer tissue using Rat Anti-Human Syndecan-1/CD138 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB2780) at 1.7 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Rat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS017) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to plasma membrane. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.Applications for Human Syndecan-1/CD138 Antibody
CyTOF-ready
Dual RNAscope ISH-IHC Compatible
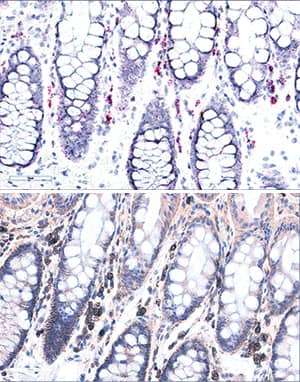
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections of human colon
Flow Cytometry
Sample: RPMI 8226 human multiple myeloma cell line
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed U266 human myeloma cell line
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human intestine, and immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human cervical cancer tissue
Reviewed Applications
Read 3 reviews rated 4.3 using MAB2780 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Syndecan-1/CD138
Syndecan-1, designated CD138, is a dimeric type I transmembrane (TM) protein that belongs to the syndecan family of Type 1 transmembrane proteins (1, 2). The four syndecan family members are major carriers of heparan sulfate (HS) and chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) that have different expression patterns and extracellular sequences. Syndecan-1 forms weak non-covalent homodimers, or heterodimers with Syndecan-2 or -3, through interactions of the transmembrane domain (3). It is synthesized as a 310 amino acid (aa) precursor with a 17 aa signal sequence, a 234 aa extracellular domain (ECD) that includes three closely-spaced consensus Ser-Gly HS attachment sites near the N-terminus, a 25 aa TM segment, and a 34 aa cytoplasmic region that includes a PDZ binding motif with a tyrosine phosphorylation site. The ECD is variably modified by GAGs, producing molecular weights of 120-200 kDa for native Syndecan-1. Soluble forms are shed via proteolytic cleavage. Human Syndecan-1 ECD shares 65-71% aa identity with the ECD of rat, mouse, canine, equine and bovine Syndecan-1. Syndecan-1 shows highest expression on epithelial cells such as keratinocytes, and terminally differentiated B cells such as plasma cells (4, 5). It aids wound healing in skin, cornea, and heart following myocardial infarction by promoting re-epithelialization, migration, and collagen deposition (4-8). It binds chemokines, creating chemotactic gradients when shed, but also binds and modulates integrins to control the influx of leukocytes (5, 7, 9). The net effect is to allow, but limit, inflammation. In myeloma and other cancers, shedding of Syndecan-1 can facilitate growth, angiogenesis and metastasis (10-12). Growth factors, such as FGFs and HGF, bind GAG chains and use Syndecan-1 as a coreceptor (12, 13). The GAG chains may also be used by a variety of viruses and bacteria for cell adhesion and uptake (4).
References
- Tkachenko, E. et al. (2005) Circ. Res. 96:488.
- Mali, M. et al. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265:6884.
- Dews, I.C. and K.R. MacKenzie (2007) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104:20782.
- Fears, C.Y. and A. Woods (2006) Matrix Biol. 25:443.
- Stepp, M.A. et al. (2002) J. Cell Sci. 115:4517.
- Ojeh, N. et al. (2008) J. Invest. Dermatol. 128:26.
- Stepp, M.A. et al. (2007) J. Cell Sci. 120:2851.
- Vanhoutte, D. et al. (2007) Circulation 115:475.
- Li, Q. et al. (2002) Cell 111:635.
- Beauvais, D.M. et al. (2009) J. Exp. Med. 206:691.
- Yang, Y. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:13326.
- Derksen, P.W.B. et al. (2002) Blood 99:1405.
- Su, G. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:14906.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Syndecan-1/CD138 Products
Product Documents for Human Syndecan-1/CD138 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human Syndecan-1/CD138 Antibody
For research use only