Human VCAM-1/CD106 Fluorescein-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # BBA22

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human VCAM-1/CD106 Fluorescein-conjugated Antibody
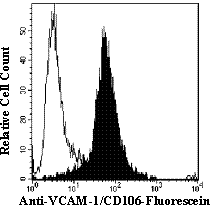
Detection of VCAM-1/CD106 in HUT-78 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
Applications for Human VCAM-1/CD106 Fluorescein-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
Background: VCAM-1/CD106
Human Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1/CD106) is a 100 - 110 kDa, 715 amino acid, type I transmembrane glycoprotein (1 - 3). A number of variants of human VCAM-1 occur as a result of alternate gene splicing (1). Moreover, a soluble form of VCAM-1 has been identified in culture supernatants (4), blood (5 - 7) and cerebrospinal fluid (7, 8). Various proteases, including MMPs, neutrophil elastase, and cathepsin B have been implicated in the shedding of transmembrane VCAM-1 (9, 10). VCAM-1 is expressed constitutively on non-vascular cells including: dendritic cells in lymphoid tissues and skin (11), macrophages (11), fibroblasts (12), melanoma cells (11), smooth muscle cells (13), adult satellite muscle cells (14), bone marrow stromal cells (15), chondrocytes (16), mesothelium (17), renal tubular epithelium and mesangium (18), embryonic myoblasts and myotubules (14), neurons (19) and choroid plexus epithelium (20). VCAM-1 expression on vascular endothelium can be induced by a number of inflammatory stimuli (11).
Functionally, VCAM-1 mediates cell adhesion and signal transduction by binding to its ligands/counter-receptors. Ligands for VCAM-1 are the integrins alpha41 (CD49d/CD29 or VLA4) and alpha47 (11, 21 - 24), alphaD2 (25, 26), and alpha91 (27). These VCAM-1 ligands are expressed on a variety of lymphoid cells. Accordingly, VCAM-1/VCAM-1 ligand interactions are key events in the rate and timing of leukocyte extravasation (11). Similarly, VCAM-1 mediates the adhesion of melanoma cells to endothelial cells and may play a role in metastasis (11). VCAM-1 expression on bone marrow stromal cells regulates T and B cell development as well as hematopoietic progenitor cell homing and trafficking (28 - 30). Other proposed roles for VCAM-1 include the regulation of osteoclastogenesis via a cell-to-cell contact mechanism (15), and the induction of sickle cell adherence to vascular endothelial cells during hypoxemia (31). Soluble VCAM-1 has been shown to mediate angiogenesis and is chemotactic for T lymphocytes and monocytes (11, 32).
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
Additional VCAM-1/CD106 Products
Product Documents for Human VCAM-1/CD106 Fluorescein-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human VCAM-1/CD106 Fluorescein-conjugated Antibody
For research use only