Human VEGF-C Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF752

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human VEGF-C Antibody
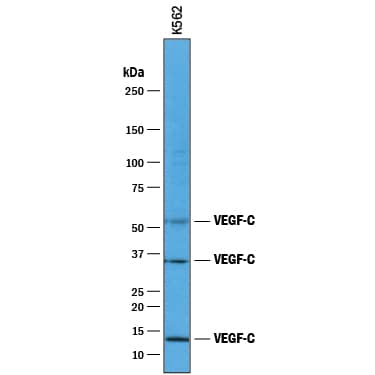
Detection of Human VEGF-C by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human VEGF-C Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF752) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF017). Specific bands were detected for VEGF-C at approximately 52 kDa, 34 kDa, and 13 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.VEGF-C in Human Colon Cancer Tissue.
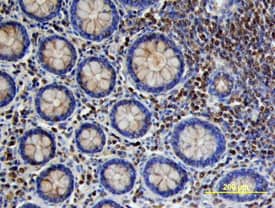
VEGF-C was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon cancer tissue using Goat Anti-Human VEGF-C Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF752) at 10 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific labeling was localized to stromal cells surrounding crypts in the colon mucosa (cross section across crypts). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.VEGF-C in Human Colon Cancer Tissue.
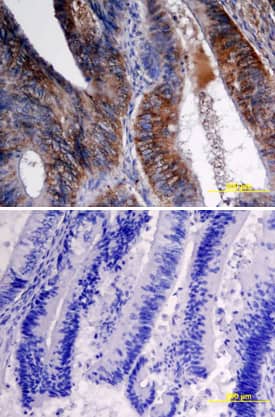
VEGF-C was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon cancer tissue using Goat Anti-Human VEGF-C Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF752) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific labeling was localized to epithelial cells in crypts of the colon mucusa (longitudinal section of crypts). Lower panel shows a lack of labeling if primary antibodies are omitted and tissue is stained only with secondary antibody followed by incubation with detection reagents. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.Applications for Human VEGF-C Antibody
ELISA
This antibody functions as an ELISA detection antibody when paired with Mouse Anti-Human VEGF‑C Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB752).
This product is intended for assay development on various assay platforms requiring antibody pairs. We recommend the Human VEGF-C DuoSet ELISA Kit (Catalog # DY752B) for convenient development of a sandwich ELISA or the Human VEGF-C Quantikine ELISA Kit (Catalog # DVEC00) for a complete optimized ELISA.
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon and human colon cancer tissue
Western Blot
Sample: K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line
Reviewed Applications
Read 2 reviews rated 4.5 using AF752 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: VEGF-C
Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) and VEGF-D constitute a VEGF sub-family that share the conserved VEGF homology domain (VHD) with other VEGF family members but are distinguished by their preferential formation of non-covalent homodimers. Both VEGF-C and -D have long N- and C-terminal propeptide extensions. The VEGF-C propeptide undergoes stepwise proteolytic processing to generate ligands with increasing affinity for VEGF-R3. However, only the fully processed VEGF-C containing just the VHD can bind VEGF-R2. None of the VEGF-C forms have appreciable affinity for VEGF-R1. VEGF-C is expressed in multiple adult human tissues, most prominently in lymph nodes, heart, placenta, ovary, and small intestine. Traces of VEGF-C are also detected in brain, liver, thymus, skeletal muscles, spleen, prostate, testis and colon. Unlike other VEGF family members, VEGF-C expression is not regulated by hypoxia. VEGF-C is a lymphangiogenic growth factor and the VEGF-C/VEGF-R3 signaling pathway has been shown to be crucial for lymphangiogenesis. VEGF-C and VEGF-R3 are usually co-expressed at sites with lymphatic vessel sprouting, in the embryo, and in various pathological conditions. VEGF-C stimulates lymphangiogenesis in the avian chorioallantoic membrane model. Over-expression of VEGF-C in breast cancer cells has been shown to increase intratumoral lymphangiogenesis, resulting in enhanced metastasis to regional lymph nodes and to the lungs. Mouse tumors expressing elevated levels of VEGF-C have increased lymphatic metastasis and increased lymphatic surface area in the tumor margin. VEGF-C is also associated with lymph node metastasis of colorectal carcinoma. Besides lymphangiogenesis, VEGF-C can have potent effects on physiological angiogenesis through its interaction with VEGF R2. The protein can stimulate migration and proliferation of endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo and has been shown to stimulate angiogenesis in the mouse cornea and in rabbit hind limb ischaemia.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
Additional VEGF-C Products
Product Documents for Human VEGF-C Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human VEGF-C Antibody
For research use only