Mouse Clusterin Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF2747


Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Glu22-Glu448
Accession # Q06890
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse Clusterin Antibody
Clusterin in Mouse Liver.
Clusterin was detected in perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse liver using Goat Anti-Mouse Clusterin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2747) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Lower panel shows a lack of labeling if primary antibodies are omitted and tissue is stained only with secondary antibody followed by incubation with detection reagents. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.Clusterin in Mouse Intestine.
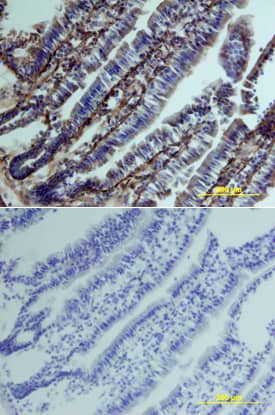
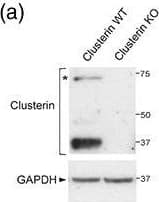
Clusterin was detected in perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse intestine using Goat Anti-Mouse Clusterin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2747) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Lower panel shows a lack of labeling if primary antibodies are omitted and tissue is stained only with secondary antibody followed by incubation with detection reagents. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.Detection of Human Clusterin/APOJ by Western Blot
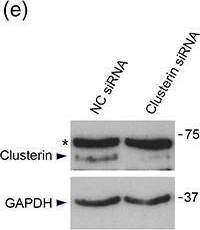
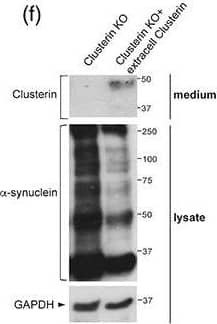
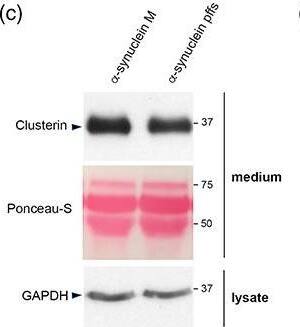
Conservation of clusterin‐dependent alpha‐synuclein preformed fibrils (pffs) uptake from mouse to human astrocytes. (a) Representative image of hiAstrocytes (27 days of differentiation) treated with * alpha‐synuclein pffs for 48 hr. Scale bar 10 μm. (b) Cell lysates from hiAstrocytes (27 days of differentiation) treated with alpha‐synuclein pffs, or monomeric alpha‐synuclein (m), for 48 hr were subjected to immunoblotting using alpha‐synuclein and GAPDH antibodies. Asterisks in the alpha‐synuclein immunoblot indicate alpha‐synuclein nonspecific bands. (c) Medium from hiAstrocytes (27 days of differentiation) treated with alpha‐synuclein pffs, or monomeric alpha‐synuclein (M), for 48 hr were subjected to immunoblotting using clusterin antibody. Ponceau‐S staining was used as loading control. (d) Quantification of clusterin is normalized to GAPDH protein of cell lysates. Data are representative of three independent experiments and are expressed as the mean ± SD. Data were analyzed using unpaired t test; *p = .0446. (e) Cell lysates from hiAstrocytes (31 days of differentiation) transfected with negative control (NC) or clusterin siRNA for 24 hr were subjected to immunoblotting using clusterin and GAPDH antibodies. Asterisk in the clusterin immunoblot indicates clusterin nonspecific band. (f) Quantification of clusterin precursor is normalized to GAPDH. Data are representative of three independent experiments and are expressed as the mean ± SD. Data were analyzed using unpaired t test; *p = .0165. (g) Representative images of hiAstrocytes (35 days of differentiation) transfected with NC or clusterin siRNA and treated with * alpha‐synuclein pffs for 24 hr. Scale bar 10 μm. (h) Quantification of * alpha‐synuclein pffs is shown as mean of fluorescence intensity from three independent experiments (~50 cells per experiment). Quantification of * alpha‐synuclein pffs is calculated as fluorescence intensity divided by the cell area (μm2). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. Data were analyzed using unpaired t test; *p = .0178. Individual points of the graphs represent each single experiment [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com] Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33045109), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse Clusterin Antibody
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse embryo (E15), intestine, and liver
Immunoprecipitation
Sample: Conditioned cell culture medium spiked with Recombinant Mouse Clusterin (Catalog # 2747‑HS), see our available Western blot detection antibodies
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Mouse Clusterin (Catalog # 2747-HS)
Mouse Clusterin Sandwich Immunoassay
Reviewed Applications
Read 2 reviews rated 5 using AF2747 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Clusterin
Clusterin, also known as Apolipoprotein J, Sulfated Glycoprotein 2 (SGP-2), TRPM-2, and SP-40,40, is a secreted multifunctional protein that was named for its ability to induce cellular clustering. It binds a wide range of molecules and may function as a chaperone of misfolded extracellular proteins. It also participates in the control of cell proliferation, apoptosis, and carcinogenesis (1, 2). Clusterin is predominantly expressed in adult testis, ovary, adrenal gland, liver, heart, and brain and in many epithelial tissues during embryonic development (3). Mouse Clusterin is synthesized as a precursor that contains two coiled coil domains, two nuclear localization signals (NLS), and one heparin binding domain (3-6). Intracellular cleavages of the precursor remove the signal peptide and generate comparably sized alpha and beta chains which are secreted as an 80 kDa N-glycosylated disulfide-linked heterodimer (7, 8). Mature mouse Clusterin shares 77% and 93% amino acid sequence identity with human and rat Clusterin, respectively. High μg/mL concentrations of Clusterin circulate predominantly as a component of high density lipoprotein particles, and these are internalized and degraded through interactions with LRP-2/Megalin (9, 10). In human, an alternately spliced 50 kDa isoform of Clusterin (nCLU) lacks the signal peptide and remains intracellular (5, 11). This molecule is neither glycosylated nor cleaved into alpha and beta chains (11). In the cytoplasm, nCLU destabilizes the actin cytoskeleton and inhibits NF kappaB activation (12, 13). Cellular exposure to ionizing radiation promotes the translocation of nCLU to the nucleus where it interacts with Ku70 and promotes apoptosis (5, 11). This function contrasts with the cytoprotective effect of secreted Clusterin (14). During colon cancer tumor progression there is a downregulation of the intracellular form and an upregulation of the glycosylated secreted form (11).
References
- Carver, J.A. et al. (2003) IUBMB Life 55:661.
- Shannan, B. et al. (2006) Cell Death Differ. 13:12.
- French, L.E. et al. (1993) J. Cell Biol. 122:1119.
- Lee, K.H. et al. (1993) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 194:1175.
- Leskov, K.S. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:11590.
- Pankhurst, G.J. et al. (1998) Biochemistry 37:4823.
- Burkey, B.F. et al. (1991) J. Lipid. Res. 32:1039.
- de Silva, H.V. et al. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265:14292.
- Jenne, D.E. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266:11030.
- Kounnas, M.Z. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:13070.
- Pucci, S. et al. (2004) Oncogene 23:2298.
- Moretti, R. M. et al. (2007) Cancer Res. 67:10325.
- Santilli, G. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:38214.
- Trougakos, I.P. et al. (2004) Cancer Res. 64:1834.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Clusterin Products
Product Documents for Mouse Clusterin Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse Clusterin Antibody
For research use only