Mouse GITR/TNFRSF18 APC-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB5241A

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Met1-His153
Accession # O35714
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse GITR/TNFRSF18 APC-conjugated Antibody
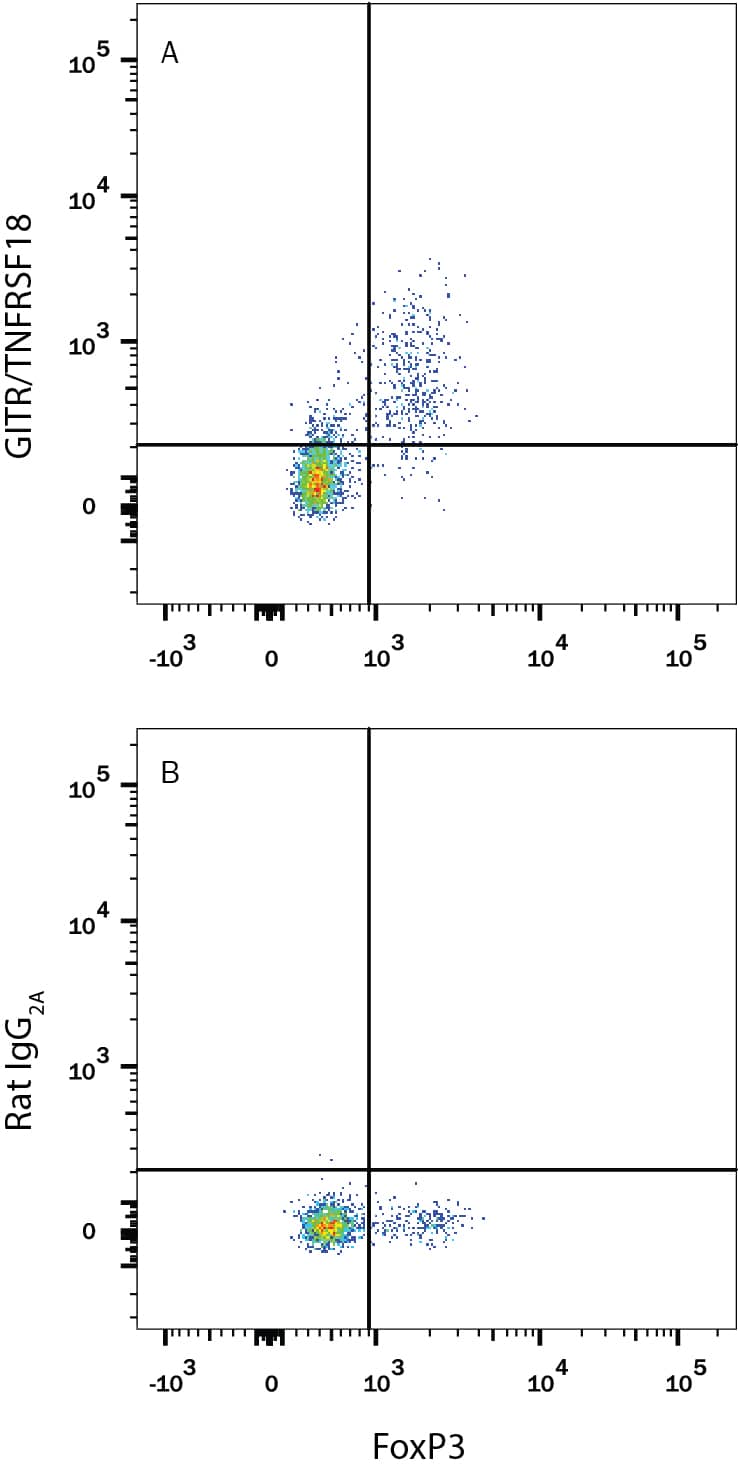
Detection of GITR/TNFRSF18 in Mouse Splenocytes Stimulated to Induce Tregs by Flow Cytometry.
Mouse splenocytes stimulated to induce Regulatory T Cells (Tregs) were stained with Rabbit Anti-Human/Mouse FoxP3 Alexa Fluor® 488-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # IC8214G) and either (A) Rat Anti-Mouse GITR/TNFRSF18 APC-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB5241A) or (B) Rat IgG2AAllophycocyanin Isotype Control (Catalog # IC006A). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Mouse GITR/TNFRSF18 APC-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: Mouse splenocytes stimulated to induce Regulatory T Cells (Tregs)
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
Background: GITR/TNFRSF18
GITR (Glucocorticoid-induced Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor), also known as AITR and CD357, is a 39-40 kDa member of the co‑stimulatory subset of the TNF receptor superfamily (1, 2). In mouse, the GITR gene is composed of five exons and encodes multiple length isoforms that arise from alternative splicing. The "standard", or first reported isoform is a type I transmembrane protein, 228 amino acids (aa) in length that contains a 19 aa signal sequence, a 134 aa extracellular region, a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 54 aa cytoplasmic domain. The extracellular region contains four potential N-linked glycosylation sites plus three cysteine-rich pseudorepeats of about 40 aa each (3, 4). The cytoplasmic domain has a P-x-Q/E-E motif that is known to associate with TRAF2. This is a common characteristic of TNFRSF members with co‑stimulatory functions (1). There is a naturally-occurring soluble form. Given its membership in the TNFRSF, it likely functions as a trimer on the cell surface (2). However, its ligand GITRL appears to act as a dimer, and this may affect stoichiometry of a functional GITR complex (5). In mouse, GITR is expressed by multiple cell types. These include keratinocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, NK cells, NKT cells, macrophages, and CD138+ plasma cells (6-8). It has been studied most extensively on T cells, where it appears on multiple subsets of T cells, including gamma delta CD25+ Tregs, and CD4+ GITR+ CD45RBlo effector cells,thymus-derived Tregs (CD4+ CD25+ CD83+ and CD4+ CD25+ CD103+ ), Tr1 (IL-10+ FoxP3- ) cells, CD8+ CD25+ FoxP3+ IL-10+ Tregs, and CD4- CD8- FoxP3- PD-1++ DN Tregs (9). GITR would appear to have both stimulatory and inhibitory activity, depending on the context (1). Notably, seemingly analogous interactions between the human and rodent systems can produce nonequivalent outcomes. For example, the GITR:GITRL interaction between NK cells and tumor cells results in decreased IFN-gamma secretion and and cytotoxicity by human NK cells, but the opposite effect in mouse NK cells (7). Over aa 21-153, mouse GITR shares 84% and 53% aa sequence identity with rat and human GITR, respectively.
References
- Hehlgans, T. and K. Pfeffer (2006) Immunology 115:1.
- Croft, M. (2003) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3:609.
- Nocentini, G. et al. (1997) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:6216.
- Nocentini, G. et al. (2000) Cell Death Differ. 7:408.
- Zhou, Z. et al. (2008) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105:641.
- Wang, J. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:37725.
- Placke, T. et al. (2010) Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2010:239083.
- Clouthier, D.L. and T.H. Watts (2014) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 25:91.
- Ronchetti, S. et al. (2015) J. Immunol. Res. 2015:171520.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional GITR/TNFRSF18 Products
Product Documents for Mouse GITR/TNFRSF18 APC-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse GITR/TNFRSF18 APC-conjugated Antibody
For research use only