Mouse Nogo Receptor/NgR Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF1440

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Cys27-Ser447
Accession # Q99PI8
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse Nogo Receptor/NgR Antibody
Detection of Mouse Nogo Receptor/NgR by Western Blot
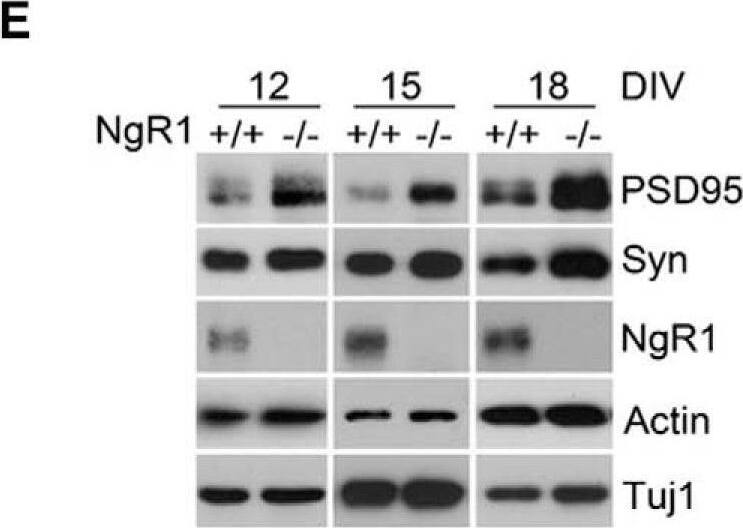
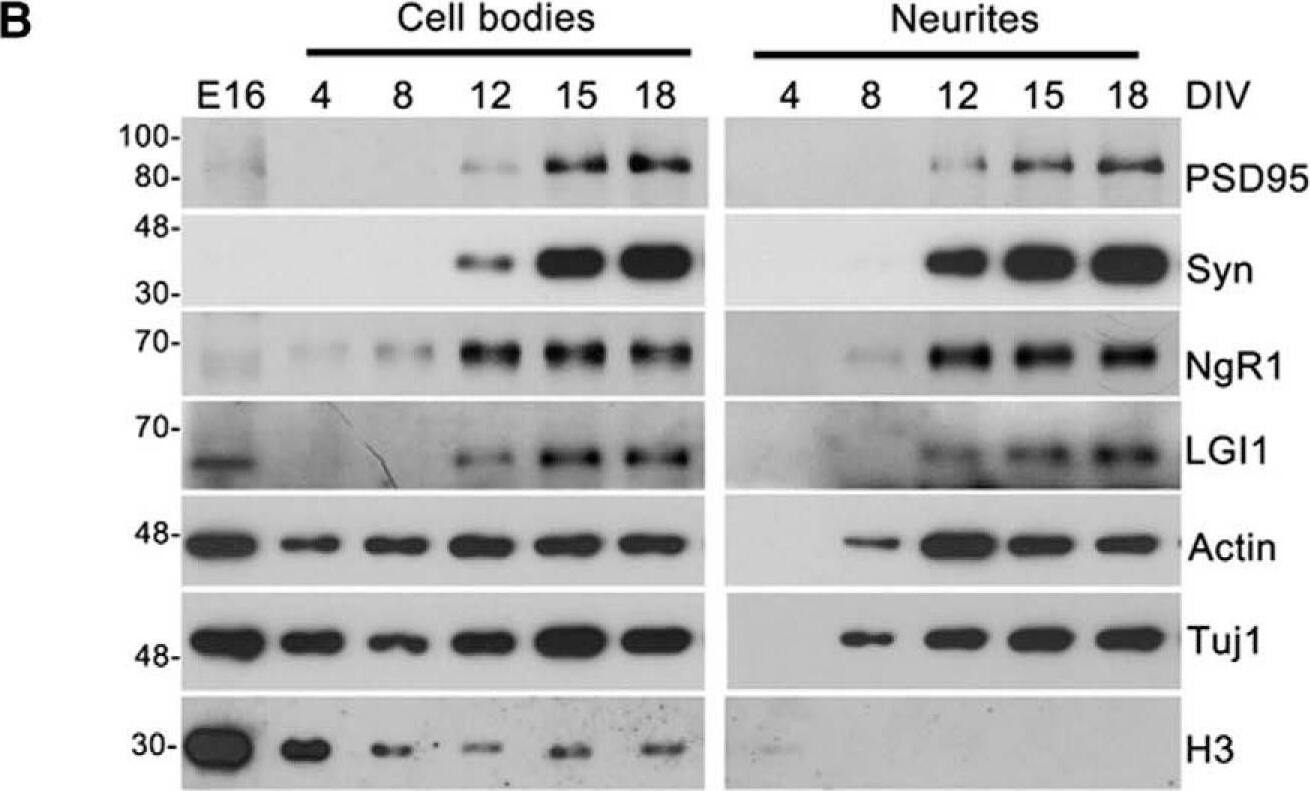
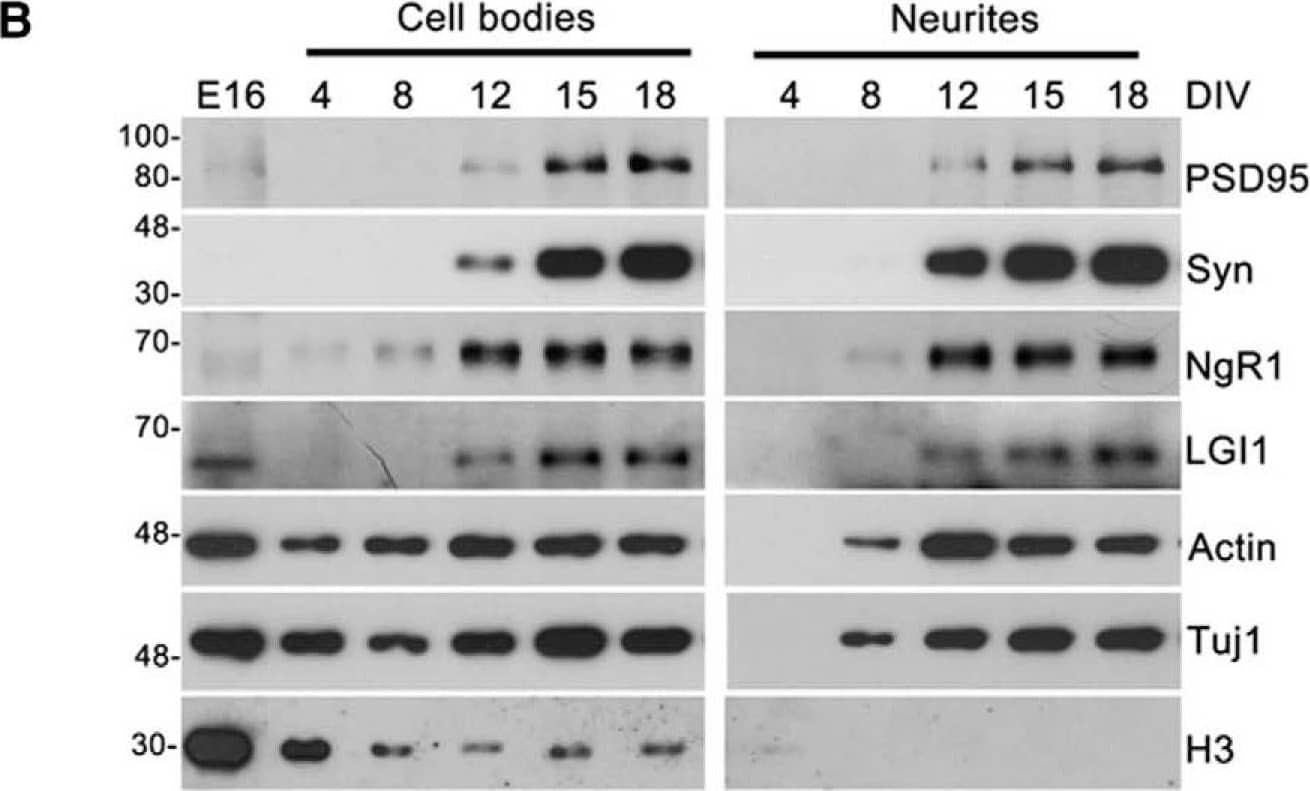
NgR1 and LGI1 regulate synaptic proteins in cortical neurons in vitro.A, Twiss filter schematic showing culture system to coculture hippocampal neurons with astrocytes and separate neuronal processes from cell bodies. Hippocampal neurons seeded on filters with a pore size 1 µm that cell bodies will not pass through. Axons and dendrites grow on the filter tops and extend down onto the filter bottom. Astrocytes are seeded on the bottom of the well to provide growth factors. B, Time course of lysates from hippocampal neurons grown on filters suspended over an astrocyte feeder layer for the times indicated. The first lane in the left panel labeled E16 is a sample of hippocampal neurons lysed directly after dissociated before plating. Lysates from filter tops including cell bodies and processes are on the left. Lysates of the filter bottoms containing axons and dendrites but no cell bodies are on the right. Antibodies used to probe the lysates are indicated on the right. Histone-3 (H3), a structural protein found in chromatin and present only in the nucleus is detected only in the cell body lysates. C, Lysates from filter bottoms containing axons and dendrite but not cell bodies from LGI1+/+ and LGI1-/- littermates of cortical cultures grown for the indicated number of DIV. D, Quantification of PSD95 levels relative to actin levels and normalized to WT controls in LGI1 samples at 12, 15, and 18 DIV, n = 3 separate experiments. E, Western blottings of lysates from filter bottoms of NgR1+/+ and NgR1-/- cortical cultures harvested at 12, 15, or 18 DIV synaptic markers, Syn and PSD95. Actin and Tuj1 are loading controls. F, Quantification of PSD95 relative to actin levels and normalized to WT controls in NgR1, n = 4 separate experiments. Significant differences are indicated on the graphs analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc tests, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30225353), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Mouse Nogo Receptor/NgR by Western Blot
NgR1 and LGI1 regulate synaptic proteins in cortical neurons in vitro.A, Twiss filter schematic showing culture system to coculture hippocampal neurons with astrocytes and separate neuronal processes from cell bodies. Hippocampal neurons seeded on filters with a pore size 1 µm that cell bodies will not pass through. Axons and dendrites grow on the filter tops and extend down onto the filter bottom. Astrocytes are seeded on the bottom of the well to provide growth factors. B, Time course of lysates from hippocampal neurons grown on filters suspended over an astrocyte feeder layer for the times indicated. The first lane in the left panel labeled E16 is a sample of hippocampal neurons lysed directly after dissociated before plating. Lysates from filter tops including cell bodies and processes are on the left. Lysates of the filter bottoms containing axons and dendrites but no cell bodies are on the right. Antibodies used to probe the lysates are indicated on the right. Histone-3 (H3), a structural protein found in chromatin and present only in the nucleus is detected only in the cell body lysates. C, Lysates from filter bottoms containing axons and dendrite but not cell bodies from LGI1+/+ and LGI1-/- littermates of cortical cultures grown for the indicated number of DIV. D, Quantification of PSD95 levels relative to actin levels and normalized to WT controls in LGI1 samples at 12, 15, and 18 DIV, n = 3 separate experiments. E, Western blottings of lysates from filter bottoms of NgR1+/+ and NgR1-/- cortical cultures harvested at 12, 15, or 18 DIV synaptic markers, Syn and PSD95. Actin and Tuj1 are loading controls. F, Quantification of PSD95 relative to actin levels and normalized to WT controls in NgR1, n = 4 separate experiments. Significant differences are indicated on the graphs analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc tests, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30225353), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Mouse Nogo Receptor/NgR by Western Blot
NgR1 and LGI1 regulate synaptic proteins in cortical neurons in vitro.A, Twiss filter schematic showing culture system to coculture hippocampal neurons with astrocytes and separate neuronal processes from cell bodies. Hippocampal neurons seeded on filters with a pore size 1 µm that cell bodies will not pass through. Axons and dendrites grow on the filter tops and extend down onto the filter bottom. Astrocytes are seeded on the bottom of the well to provide growth factors. B, Time course of lysates from hippocampal neurons grown on filters suspended over an astrocyte feeder layer for the times indicated. The first lane in the left panel labeled E16 is a sample of hippocampal neurons lysed directly after dissociated before plating. Lysates from filter tops including cell bodies and processes are on the left. Lysates of the filter bottoms containing axons and dendrites but no cell bodies are on the right. Antibodies used to probe the lysates are indicated on the right. Histone-3 (H3), a structural protein found in chromatin and present only in the nucleus is detected only in the cell body lysates. C, Lysates from filter bottoms containing axons and dendrite but not cell bodies from LGI1+/+ and LGI1-/- littermates of cortical cultures grown for the indicated number of DIV. D, Quantification of PSD95 levels relative to actin levels and normalized to WT controls in LGI1 samples at 12, 15, and 18 DIV, n = 3 separate experiments. E, Western blottings of lysates from filter bottoms of NgR1+/+ and NgR1-/- cortical cultures harvested at 12, 15, or 18 DIV synaptic markers, Syn and PSD95. Actin and Tuj1 are loading controls. F, Quantification of PSD95 relative to actin levels and normalized to WT controls in NgR1, n = 4 separate experiments. Significant differences are indicated on the graphs analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc tests, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30225353), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse Nogo Receptor/NgR Antibody
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Mouse Nogo Receptor/NgR Fc Chimera (Catalog # 1440-NG)
Reviewed Applications
Read 2 reviews rated 3.5 using AF1440 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Nogo Receptor/NgR
Nogo Receptor (NgR), also named reticulon 4 receptor, is a glycosylphosphoinositol (GPI)-anchored protein that belongs to the family of leucine-rich repeat (LRR) proteins (1). It is expressed predominantly in the central nervous systems in neurons and their axons. NgR plays an essential role in mediating axon growth inhibition induced by the structurally distinct myelin-derived proteins Nogo, myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG), and myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (Omgp) (2, 3). Human NgR cDNA encodes a 473 amino acid (aa) residue precursor with a 26 aa putative signal peptide, an LRR-type N-terminal region, eight LRR repeats, a cysteine-rich LRR-type C-terminal region, a GPI linkage domain and a 26 aa C-terminal propeptide that is removed in the mature form (1). All of the LRR domains within NgR are required for ligand binding and receptor oligomerization (4). NgR mediates its inhibitory actions by interacting with the p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR), a tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TNFRSF) member also known for modulating the activities of the Trk family of receptor tyrosine kinases, and for inducing apoptosis in neurons and oligodendrocytes (5). Upon ligand binding, NgR binds to and activates the p75NTR. The activated p75NTR then sequesters the Rho guanine dissociation inhibitor (Rho-GDI) away from Rho and allows Rho to change into the active GTP-bound state which can interact with signaling proteins to suppress axonal growth and regeneration (4). The truncated extracellular domain of NgR has been shown to bind the myelin-derived inhibitors and block inhibition of axon growth by myelin (6).
References
- Fournier, A.E. et al. (2001) Nature 409:341.
- GrandPre, T. et al. (2002) Nature 417:547.
- Wang, K.C. et al. (2002) Nature 420:74.
- Barton, W.A. et al. (2003) EMBO Journal 22:3291.
- Yamashita, T. and M. Tohyama (2003) Nature Neuroscience 6:461.
- Fournier, A.S. et al. (2002) J. Neurosci. 22:8876.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Nogo Receptor/NgR Products
Product Documents for Mouse Nogo Receptor/NgR Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse Nogo Receptor/NgR Antibody
For research use only