Mouse/Rat DLL1 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF5026

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ser22-Gln516
Accession # Q61483
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse/Rat DLL1 Antibody
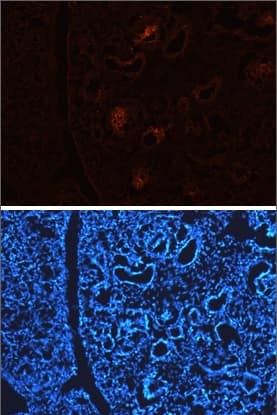
DLL1 in Embryonic Mouse Kidney.
DLL1 was detected in immersion fixed frozen sections of embryonic mouse kidney (E13.5) using 10 µg/mL Sheep Anti-Mouse/Rat DLL1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF5026) overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained with the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (red, upper panel; Catalog # NL010) and counterstained with DAPI (blue, lower panel). View our protocol for Fluorescent IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.Detection of Mouse DLL1 by Immunohistochemistry
Dll1 and Dll4 are expressed in distinct patterns in the mice gastrointestinal epithelium.Immunohistochemistry of Dll1 and Dll4 were performed using mice small intestinal (A, B) and colonic tissues (D, E). Within the small intestinal epithelium, staining by anti-Dll1 antibody showed positive cells exclusively within the crypt (A, B), whereas staining by anti-Dll4 antibody showed positive cells both in the crypt and in the villi. Quantification of Dll1+ve and Dll4+ve intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) showed that Dll1+ve IECs are predominantly found within the crypt, whereas Dll4+ve IECs are found mostly in the villi (C). In the colonic epithelium, staining by anti-Dll1 antibody showed positive cells exclusively within the lower part of the crypt (D, E), whereas staining by anti-Dll4 antibody showed positive cells both in the lower- and upper part of the crypt, including the surface epithelium. Quantification of Dll1+ve and Dll4+ve IECs showed that Dll1+ve IECs are found exclusively within the lower half of the crypt, whereas Dll4+ve IECs are found both in the lower and upper region of the crypt at a comparable frequency (F). Negative staining of non-immunized isotype antibodies (Control Ab) confirmed the specific staining of Dll1 (A) and Dll4 (D). Scale bar represents 20 µm. Quantitative data are shown as mean ∓ SD of triplicate experiments (n = 3). ∗ indicates P < 0.05 as determined by Welch’s t-test. N.S. indicates not significant. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24860699), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Mouse DLL1 by Immunohistochemistry
Dll1+ve or Dll4+ve IECs constitute the intestinal stem cell niche.Double immunostaining of Dll1 or Dll4 with a stem-cell niche cell marker, Lysozyme or c-kit, was performed in the mice small intestine and in the colon, respectively. (A) Immunostaining of Dll4 (green) with Lysozyme (red) shows that Dll4 is expressed in Paneth cells of the small intestine (yellow arrowhead). Scale bar represents 20 µm. (B) Double immunostaining of Dll1 (green) and c-kit (red) shows that Dll1+ve colonic IECs mostly co-express c-kit (yellow arrowhead). Also, double immunostaining of Dll4 (green) and c-kit (red) showed that a distinct population of Dll4+ve cells co-express c-kit (yellow arrowhead). Scale bar represents 20 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24860699), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse/Rat DLL1 Antibody
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed frozen sections of embryonic mouse kidney (E13.5)
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Mouse DLL1 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 5026-DL)
Recombinant Rat DLL1 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 3970-DL)
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 5 using AF5026 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: DLL1
Delta-like protein 1 (DLL1) is a 90‑100 kDa type I transmembrane protein in the Delta/Serrate/Lag-2 (DSL) family of Notch ligands. Mature mouse DLL1 consists of a 528 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ECD) with one DSL domain and eight EGF-like repeats, a 23 aa transmembrane segment, and a 154 aa cytoplasmic domain (1). Within the ECD, mouse DLL1 shares 91% and 95% aa sequence identity with human and rat DLL1, respectively. It shares 26%, 35%, and 51% aa sequence identity with DLL2, 3, and 4, respectively. A 60 kDa ECD fragment, released by ADAM9, 12, or 17 mediated proteolysis, promotes the proliferation of hematopoietic progenitor cells (2, 3). The residual membrane-bound portion of DLL1 can be cleaved by presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase, enabling the cytoplasmic domain to migrate to the nucleus (4). DLL1 localizes to adherens junctions on neuronal processes through its association with the scaffolding protein MAGI1 (5). DLL1 is widely expressed, and it plays an important role in embryonic somite formation, cochlear hair cell differentiation, lymphocyte differentiation, and the maintenance of neural and myogenic progenitor cells (6‑12). The upregulation of DLL1 in arterial endothelial cells following injury or angiogenic stimulation is central to postnatal arteriogenesis (13). DLL1 is also overexpressed in cervical carcinoma and glioma and contributes to tumor progression (14‑15).
References
- Bettenhausen, B. et al. (1995) Development 121:2407.
- Dyczynska, E. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:436.
- Karanu, F.N. et al. (2001) Blood 97:1960.
- Ikeuchi, T. and S.S. Sisodia (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:7751.
- Mizuhara, E. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:26499.
- Takahashi, Y. et al. (2003) Development 130:4259.
- Teppner, I. et al. (2007) BMC Dev. Biol. 7:68.
- Kiernan, A.E. et al. (2005) Development 132:4353.
- Schmitt, T.M. and J.C. Zuniga-Pflucker (2002) Immunity 17:749.
- Hozumi, K. et al. (2004) Nat. Immunol. 5:638.
- Shimojo, H. et al. (2008) Neuron 58:52.
- Schuster-Gossler, K. et al. (2007) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 104:537.
- Limbourg, A. et al. (2007) Circ. Res. 100:363.
- Purow, B.W. et al. (2005) Cancer Res. 65:2353.
- Gray, G.E. et al. (1999) Am. J. Pathol. 154:785.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional DLL1 Products
Product Documents for Mouse/Rat DLL1 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse/Rat DLL1 Antibody
For research use only