Recombinant Human CD44v6 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 11175-CD

Key Product Details
Source
CHO
Accession #
Structure / Form
Disulfide-linked homodimer
Conjugate
Unconjugated
Applications
Bioactivity
Product Specifications
Source
Chinese Hamster Ovary cell line, CHO-derived human CD44 protein
| Human CD44v6 (Gln21-Thr222) (IQATPSSTTEETATQKEQWFGNRWHEGYRQTPKEDSHSTTGTAG)(Asp224-Trp269) Accession # NP_001001391.1 |
GGIEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
| N-terminus | C-terminus |
Purity
>95%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Gln21
Predicted Molecular Mass
59 kDa
SDS-PAGE
105-120 kDa, under reducing conditions.
Activity
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA.
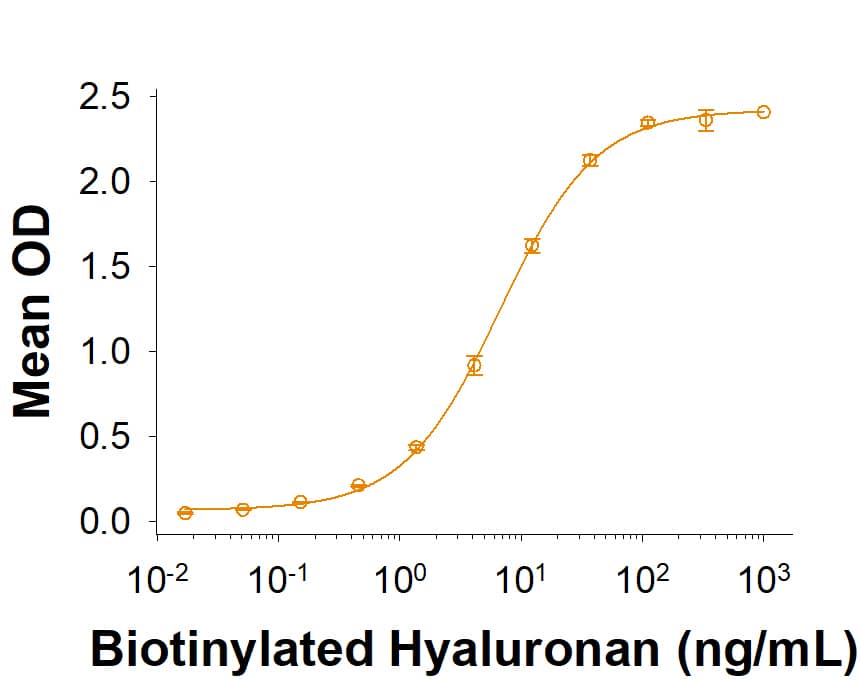
When Recombinant Human CD44v6 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 11175-CD) is immobilized at 1 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Biotinylated Hyaluronan binds with an ED50 of 4.00-40.0 ng/mL.
When Recombinant Human CD44v6 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 11175-CD) is immobilized at 1 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Biotinylated Hyaluronan binds with an ED50 of 4.00-40.0 ng/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human CD44v6 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
Recombinant Human CD44v6 Fc Chimera Protein Binding Activity.
When Recombinant Human CD44v6 Fc Chimera Protein (Catalog # 11175-CD) is immobilized at 1 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Biotinylated Hyaluronan binds with an ED50 of 4.00-40.0 ng/mL.Recombinant Human CD44v6 Fc Chimera Protein SDS-PAGE.
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human CD44v6 Fc Chimera Protein (Catalog # 11175-CD) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 105-120 kDa and 210-240 kDa, respectively.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
11175-CD
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: CD44
References
- Ponta, H. et al. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4:33.
- Screaton, G.R. et al. (1992) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:12160.
- Screaton, G.R. et al. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268:12235.
- Lynch, K.W. (2004) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:931.
- Todaro, M. et al. (2014) Cell stem cell 14:342.
- Vizoso, F.J. et al. (2004) J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 130:679.
- Ma, L. et al. (2019) Cell Death Dis. 10:30.
- Yu, Q. and B.P. Toole (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:20603.
- Nagano, O. and H. Saya (2004) Cancer Sci. 95:930.
- Nakamura, H. et al. (2004) Cancer Res. 64:876.
- Murakami, D. et al. (2003) Oncogene 22:1511.
- Lammich, S. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:44754.
Alternate Names
CD44, ECMR-III, HCAM, HCELL, LHR, MDU2, MDU3, MIC4, MUTCH-I, Pgp1
Gene Symbol
CD44
UniProt
Additional CD44 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human CD44v6 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human CD44v6 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...