Recombinant Human CTLA-4 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AVI7268

Key Product Details
Source
Accession #
Structure / Form
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
Source
| Human CTLA-4 (Ala37-Phe162) Accession # P16410.3 |
IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
Avi-tag |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | ||
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
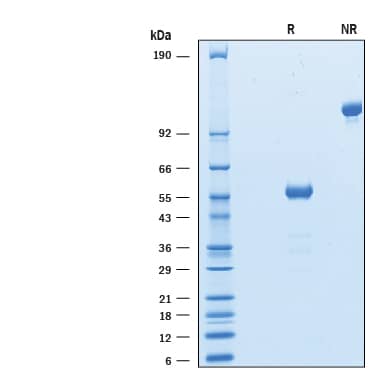
SDS-PAGE
Activity
When Recombinant Human B7‑1/CD80Fc Chimera (Catalog # 10133-B1) is immobilized at 0.5 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Biotinylated Recombinant Human CTLA-4 Fc Chimera Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI7268) binds with an ED50 of 0.4-2.4 ng/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human CTLA-4 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF
Recombinant Human CTLA-4 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein Binding Activity
When Recombinant Human B7-1/CD80 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 10133-B1) is immobilized at 0.5 µg/mL, Biotinylated Recombinant Human CTLA-4 Fc Chimera Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI7268) binds with an ED50 of 0.4-2.4 ng/mL.Recombinant Human CTLA-4 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein SDS-PAGE
2 μg/lane of Biotinylated Recombinant Human CTLA-4 Fc Chimera Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI7268) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 53-61 kDa and 110-120 kDa, respectively.Binding of Human B7-1/CD80 to CTLA-4 Fc Avi-tag Protein by surface plasmon resonance (SPR).
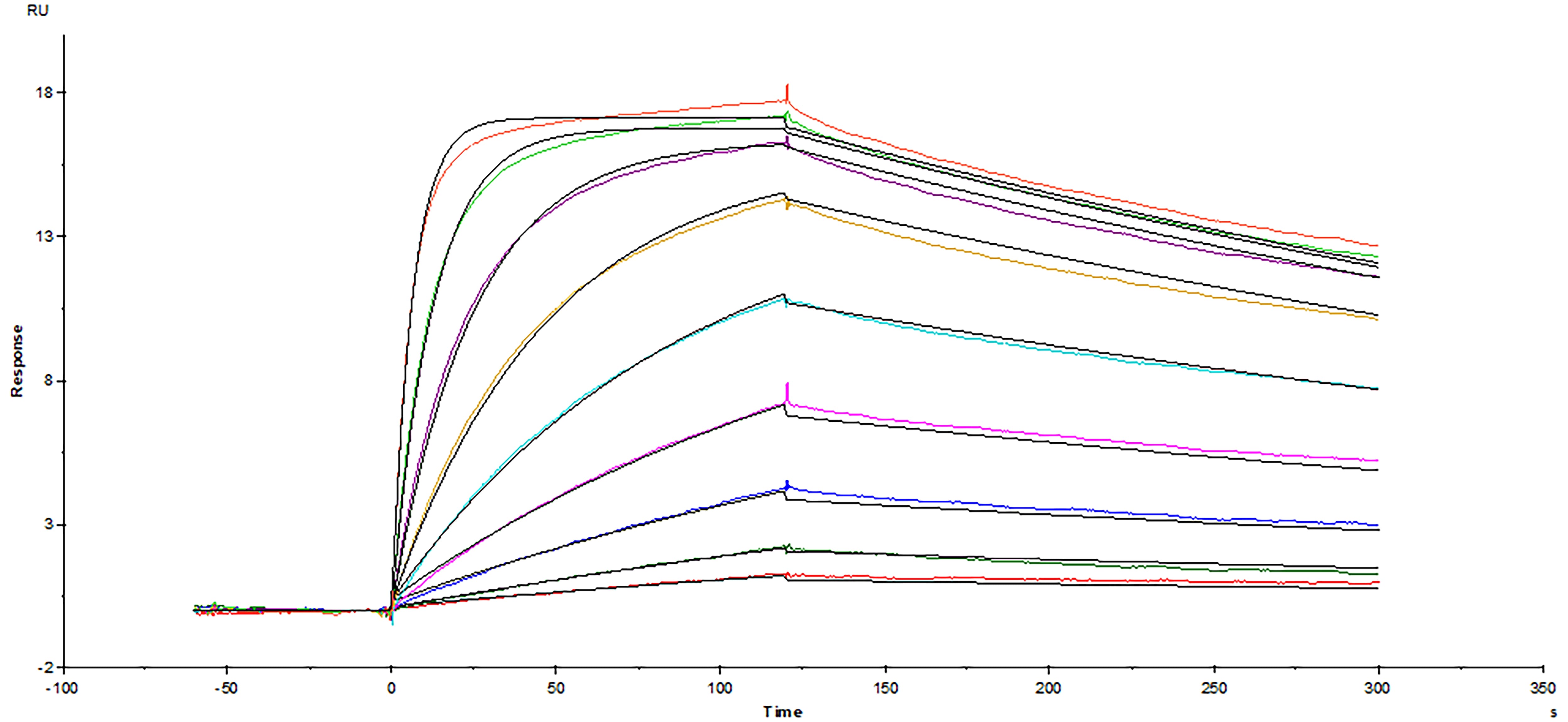
Avi-tag Biotinylated Recombinant Human CTLA-4 Fc protein (Catalog # AVI7268) was immobilized on a Biacore Sensor Chip CM5 via the Avi-tag biotin, and binding to Recombinant Human B7-1/CD80 Fc protein (10133-B1) was measured at a concentration range between 82 pM and 21 nM. The double-referenced sensorgram was fit to a 1:1 binding model to determine the binding kinetics and affinity, with an affinity constant of KD=0.2511 nM.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
AVI7268
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: CTLA-4
CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein‑4, designated CD152), is a type I transmembrane T cell inhibitory molecule that is a member of the Ig superfamily (1, 2). Human or mouse CTLA-4 cDNA encodes 223 amino acids (aa) including a 35 aa signal sequence, a 126 aa extracellular domain (ECD) with one Ig-like V-type domain, a 21 aa transmembrane (TM) sequence, and a 41 aa cytoplasmic sequence. It is found as a covalent homodimer of 41-43 kDa (2) Within the ECD, human CTLA-4 shares 68%, 71% and 83‑86% aa sequence identity with mouse, rat and porcine/bovine/rabbit/feline/canine CTLA-4, respectively. A 174 aa form that lacks TM and cytoplasmic sequences (sCTLA-4) is possibly secreted (3-5). Isoforms of 56-79 aa that mainly contain parts of the cytoplasmic domain are reported. In mouse, an isoform lacking the Ig-like domain has ligand-independent inhibitory activity and is termed liCTLA-4 (6). CD28, which is structurally related to CTLA-4, is constitutively expressed on naïve T cells and promotes T cell activation when engaged by B7-2 on antigen-presenting cells (APC) within the immunological synapse (IS) (1, 7, 8). In contrast, CTLA-4 is recruited from intracellular vesicles to the IS beginning 1-2 days after T cell activation (2, 7, 8). It forms a linear lattice with B7-1 on APC, inducing negative regulatory signals and ending T cell activation (9). Abatacept, a therapeutic human CTLA-4-Ig fusion protein (trade name Orencia), competes with CD28 for B7-1 and B7-2 binding and has been used to antagonize T cell activation in autoimmune conditions and to enhance transplant survival (10). Mice deleted for CTLA-4 show no abnormalities until after birth, but then develop lethal autoimmune reactions due to continued T cell activation and poor control by regulatory T cells, which constitutively express CTLA-4 in wild-type mice and humans (11-13).
References
- Harper, K. et al. (1991) J. Immunol. 147:1037.
- Teft, W.A. et al. (2006) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 24:65.
- Magistrelli, G. et al. (1999) Eur. J. Immunol. 29:3596.
- Tector, M. et al. (2009) BMC Immunol. 10:51.
- Oaks, M.K. and K.M. Hallett (2000) J. Immunol. 164:5015.
- Vijayakrishnan, L. et al. (2004) Immunity 20:563.
- Pentcheva-Hoang, T. et al. (2004) Immunity 21:401.
- Jansson, A. et al. (2005) J. Immunol 175:1575.
- Darlington, P.J. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 175:996.
- Platt, A.M. et al. (2010) J. Immunol. 185:1558.
- Wing, K. et al. (2008) Science 322:271.
- Friedline, R.H. et al. (2009) J. Exp. Med. 206:421.
- Jain, N. et al. (2010) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107:1524.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional CTLA-4 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human CTLA-4 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human CTLA-4 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF
For research use only