Recombinant Human D-Amino Acid Oxidase His-tag Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 10116-DO

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
E. coli-derived human D-Amino Acid Oxidase protein
Arg2-Leu347
with N-terminal Met and 6-His tag
Arg2-Leu347
with N-terminal Met and 6-His tag
Purity
>90%, by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions and visualized by silver stain.
Endotoxin Level
<1.0 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Met
Predicted Molecular Mass
40 kDa
SDS-PAGE
39 kDa, under reducing conditions
Activity
Measured by its ability to produce hydrogen peroxide during the oxidative deamination of D-amino acids.
The specific activity is >1000 pmol/min/μg, as measured under the described conditions.
The specific activity is >1000 pmol/min/μg, as measured under the described conditions.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human D-Amino Acid Oxidase His-tag Protein, CF
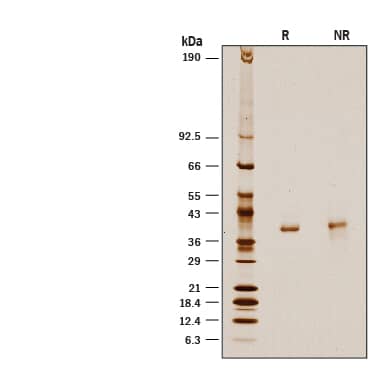
Recombinant Human D-Amino Acid Oxidase His-tag Protein SDS-PAGE
1 μg/lane of Recombinant Human D-Amino Acid Oxidase His-tag (Catalog # 10116-DO) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by silver staining, showing a band at 39 kDa.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
10116-DO
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Tris, NaCl and Glycerol. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with dry ice or equivalent. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: D-Amino Acid Oxidase
References
- Molla, G. et al. (2006) FEBS Lett. 580:2358.
- Kawazoe, T. et al. (2006) Protein Sci. 15:2708.
- Sacchi, S. et al. (2018) Front. Mol. Biosci. 5:55.
- Sacchi, S. et al. (2008) J. Biol. Chem. 283:22244.
- Kawazoe, T. et al. (2007) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 355:385.
- Mitchell, J. et al. (2010) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107:7556.
- Cirulli, E.T. et al. (2015) Science 347:1436.
- Lin, C. H. et al. (2017) J. Alzhemier's Dis. 56:959.
- Lin, C.H. et al. (2014) Curr. Pharm. Des. 20:5169.
- Heresco-Levy, U. et al. (2005) Biol. Psychiatry 57:577.
- Zhou, W.J. et al. (2010) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 332:248.
- Gong, N. et al. (2011) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 336:282.
- Szilagyi, B. et al. (2018) Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 13:973.
- Khangura, R.K. et al. (2019) Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 23:1.
Long Name
D-Amino Acid Oxidase
Alternate Names
DAAO, DAMOX, DAO, OXDA
Gene Symbol
DAO
UniProt
Additional D-Amino Acid Oxidase Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human D-Amino Acid Oxidase His-tag Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human D-Amino Acid Oxidase His-tag Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...