Recombinant Human EpCAM/TROP1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AVI960
Biotinylated

Key Product Details
Learn more about Avi-tag Biotinylated Proteins
Source
HEK293
Accession #
Structure / Form
Disulfide-linked homodimer, biotinylated via Avi-tag
Conjugate
Biotin
Applications
Bioactivity
Product Specifications
Source
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human EpCAM/TROP1 protein
Human EpCAM/TROP-1 |
IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
Avi-tag |
Purity
>95%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Gln24, inferred from deblocking reaction revealing Glu25.
Predicted Molecular Mass
56 kDa
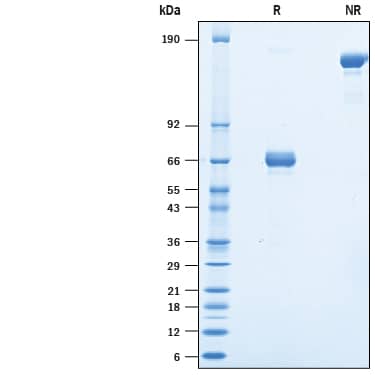
SDS-PAGE
55-75 kDa, under reducing conditions
Activity
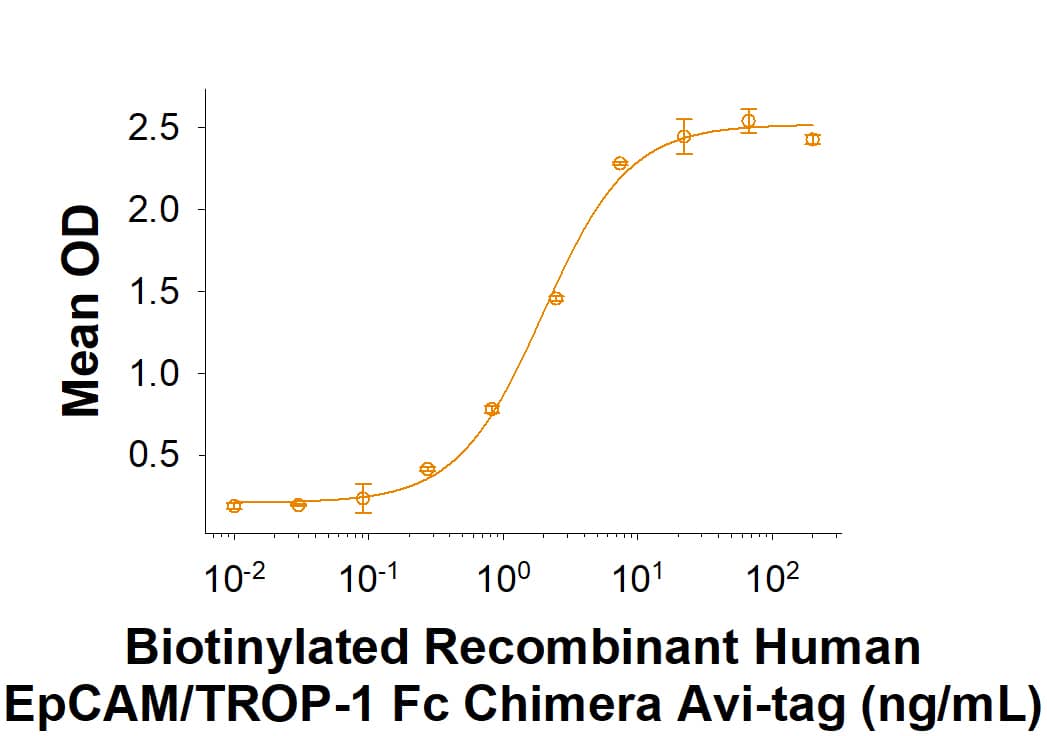
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA.
When Human EpCAM/TROP1 Affinity Purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF960) is immobilized at 0.25 µg/mL (100 µL/well), it binds to Biotinylated Recombinant Human EpCAM/TROP‑1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag with an ED50 of 1-6 ng/mL.
Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of the L Cells mouse fibroblast cell line.
The ED50 for this effect is 0.7-2.8 μg/mL.
When Human EpCAM/TROP1 Affinity Purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF960) is immobilized at 0.25 µg/mL (100 µL/well), it binds to Biotinylated Recombinant Human EpCAM/TROP‑1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag with an ED50 of 1-6 ng/mL.
Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of the L Cells mouse fibroblast cell line.
The ED50 for this effect is 0.7-2.8 μg/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human EpCAM/TROP1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF
Recombinant Human EpCAM/TROP1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein Binding Activity
When Human EpCAM/TROP1 Affinity Purified Polyclonal Ab (Catalog # AF960) is immobilized at 0.25 µg/mL (100 µg/well), Biotinylated Recombinant Human EpCAM/TROP-1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI960) binds with an ED50 of 1-6 ng/mL.Recombinant Human EpCAM/TROP1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein SDS-PAGE
2 μg/lane of Biotinylated Recombinant Human EpCAM/TROP-1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI960) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 55-75 kDa and 110-150 kDa, respectively.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
AVI960
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: EpCAM/TROP1
References
- Kloudova, K. et al. (2016) Oncotarget. 7:46120.
- Huang, L. et al. (2018) Int. J. Mol. Med. 42:1771.
- Munz, M. et al. (2009). J. Cancer Res. 69:5627.
- Khosla, R. et al. (2017). Stem Cells Trans. Med. 6:807.
- Balzar, M. et al. (2001) Mol. Cell. Biol. 21:2570.
- Balzar, M. et al. (1998) Mol. Cell. Biol. 18:4388.
Long Name
Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule
Alternate Names
17-1A, CD326, GA733-2, gp40, KS1/4, M4S1, TACSTD1, TROP1
Gene Symbol
EPCAM
UniProt
Additional EpCAM/TROP1 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human EpCAM/TROP1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human EpCAM/TROP1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...