Recombinant Human HGF (NK1), Animal-Free Protein
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # Qk013

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
E. coli-derived human HGF protein
Purity
Single species with expected mass
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
Predicted Molecular Mass
20 kDa
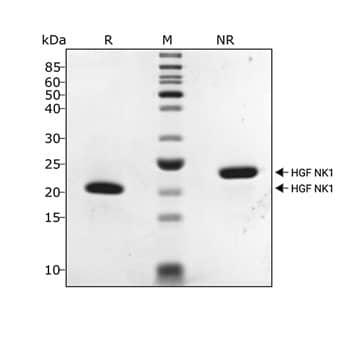
SDS-PAGE
Monomeric HGF (NK1) protein only
Activity
No significant difference between EC50 of reference and test lots
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human HGF (NK1), Animal-Free Protein
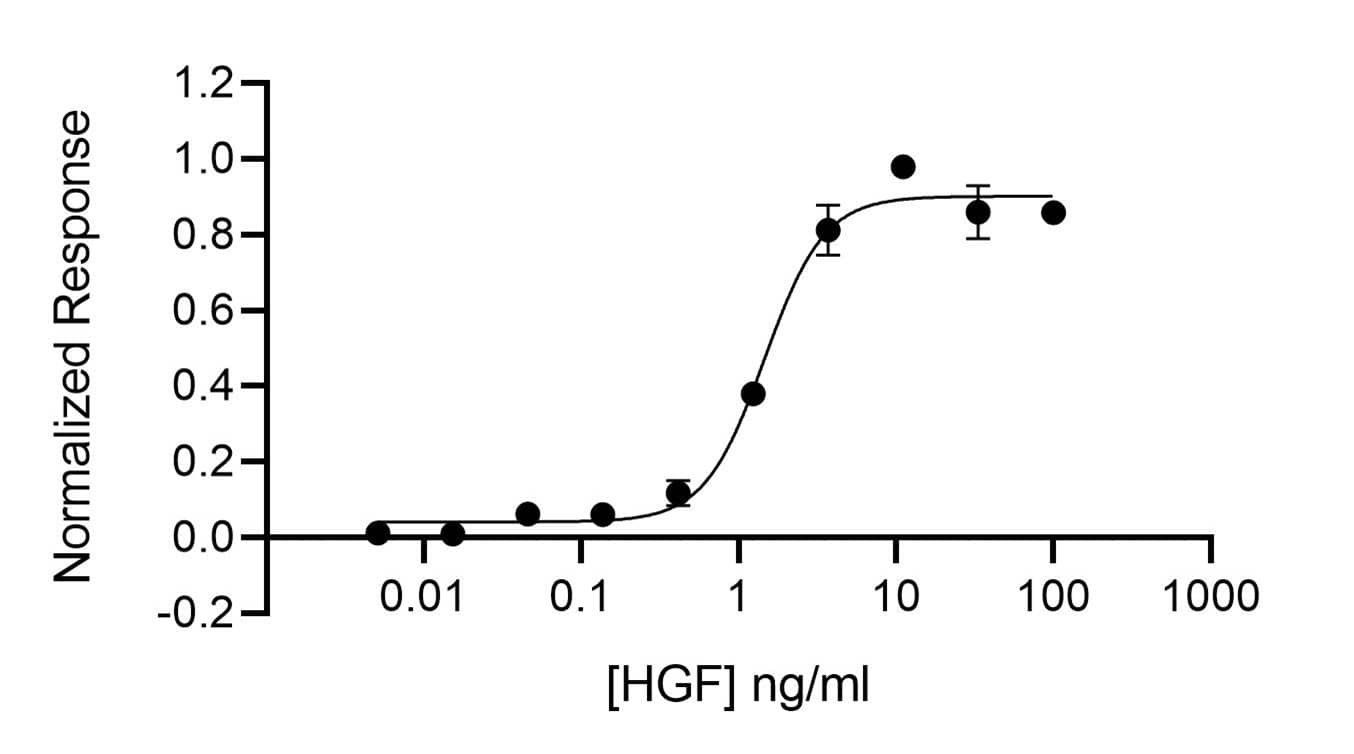
Recombinant Human HGF (NK1), Animal-Free Protein Bioactivity
HGF NK1 activity is determined using the Promega serum response element luciferase reporter assay (*) in transfected HEK293T cells. Cells were treated in duplicate with a serial dilution of HGF for 6 hours. Firefly luciferase activity is measured and normalized to the control Renilla luciferase activity. EC50 = 1.5 ng/ml (72.9 pM).*Promega pGL4.33[luc2P/SRE/Hygro] #E1340Recombinant Human HGF (NK1), Animal-Free Protein SDS-PAGE
HGF NK1 migrates as major band at 20 kDa in non-reducing conditions and 18 kDa upon reduction.Purified recombinant protein (7 µg) was resolved using 15% w/v SDS-PAGE in reduced (+DTT, R) and non-reduced conditions (NR) and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250. NB reduced samples were not boiled as the protein is sensitive to high temperatures, which causes degradation.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
Qk013
| Formulation | Lyophilized from acetonitrile/TFA |
| Reconstitution | Resuspend in 10mM HCl at >100 µg/ml, prepare single use aliquots, add carrier protein if desired. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped lyophilized at ambient temperture, on ice blocks or dry ice. Shipping at ambient temperture does not affect the bioactivity or stability of the protein. Upon reciept, store immediately at the conditions stated below. |
| Stability & Storage | Store lyophilized protein between -20 and -80 °C until the date of expiry. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. |
Background: HGF
References
- Karihaloo, A. et al. (2005) Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 100:e40.
- Hammond, D.E. et al. (2004) Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 286:21.
- Rosario, M. and Birchmeier, W. (2004) Dev. Cell 7:3.
- Lesk, A.M. and Fordham, W.D. (1996) J. Mol. Biol. 258:501.
- Nakamura, T. et al. (1989) Nature 342:440.
- Mizuno, K., et al. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269:1131.
- Gheradi, E. et al. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 100:12039.
- Corso, S. et al. (2005) Trends Mol. Med. 11:284.
- Maeshima, A. et al. (2000) Kid. Int. 58:1511.
- Montesano, R. et al. (1991) Cell 67:901.
- Chiu, S-J. et al. (2002) J. Biomed. Sci. 9:261.
- Saelman, E.U.M. et al. (1995) J. Cell Sci. 108:3531.
- 13. Tanaka, Y. et al. (2002) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 299:472.
- 14. Mineo, R. et al. (1994) Endocrinology 145:4355.
- 15. Urbanek, K. et al. (2005) Circ. Res. 97:663.
Long Name
Hepatocyte Growth Factor
Alternate Names
DFNB39, F-TCF, Hepatopoietin A, HGFB, HPTA, SF
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
HGF
UniProt
Additional HGF Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human HGF (NK1), Animal-Free Protein
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human HGF (NK1), Animal-Free Protein
The above product was manufactured, tested and released by R&D System's contract manufacturer, Qkine Ltd, at 1 Murdoch House, Cambridge, UK, CB5 8HW. The product is for research use only and not for the diagnostic or theraputic use.
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...