Recombinant Human M-CSF Protein Best Seller
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 216-MC

Key Product Details
Source
Accession #
Structure / Form
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
Source
Glu33-Ser190, with an N-terminal Met
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
Activity
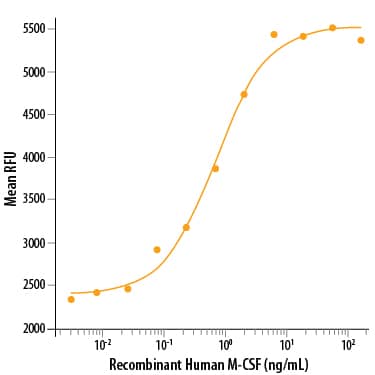
The ED50 for this effect is 0.5-1.5 ng/mL.
Reviewed Applications
Read 15 reviews rated 4.9 using 216-MC in the following applications:
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human M-CSF Protein
Recombinant Human M‑CSF Protein SEC-MALS.
Recombinant human M-CSF (Catalog # 216-MC) has a molecular weight (MW) of 39.2 kDa as analyzed by SEC-MALS, suggesting that this protein is a homodimer. MW may differ from predicted MW due to post-translational modifications (PTMs) present (i.e. Glycosylation).Recombinant Human M-CSF Protein Bioactivity
Recombinant Human M-CSF (Catalog # 216-MC) stimulates cell proliferation of the M‑NFS‑60 mouse myelogenous leukemia lymphoblast cell line in a dose-dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is 0.5-1.5 ng/mL.Recombinant Human M-CSF Protein SDS-PAGE
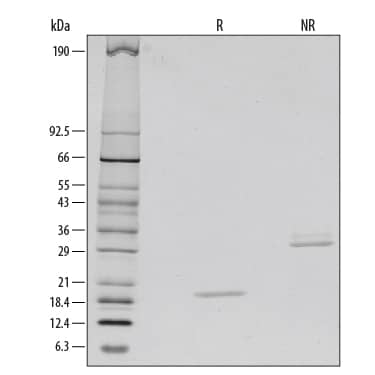
1 μg/lane of Recombinant Human M-CSF was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by silver staining, showing bands at 19 kDa and 35 kDa, respectively.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
Carrier Free
What does CF mean?CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
What formulation is right for me?In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
Carrier: 216-MC
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 50-500 μg/mL in sterile PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Carrier Free: 216-MC/CF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 50-500 μg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: M-CSF
M‑CSF that lacks cleavage and PG sites and produces an N-glycosylated 68 kDa TM dimer and a slowly produced 44 kDa secreted dimer (7). Although forms may vary in activity and half-life, all contain the N‑terminal 150 aa portion that is necessary and sufficient for interaction with the M-CSF receptor (10, 11). The first 223 aa of mature human M-CSF shares 88%, 86%, 81% and 74% aa identity with corresponding regions of dog, cow, mouse and rat M‑CSF, respectively (12, 13). Human M-CSF is active in the mouse, but mouse M-CSF is reported to be species-specific.
References
- Pixley, F.J. and E.R. Stanley (2004) Trends Cell Biol. 14:628.
- Chitu, V. and E.R. Stanley (2006) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 18:39.
- Fixe, P. and V. Praloran (1997) Eur. Cytokine Netw. 8:125.
- Ryan, G.R. et al. (2001) Blood 98:74.
- Makrigiannakis, A. et al. (2006) Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 17:178.
- Nandi, S. et al. (2006) Blood 107:786.
- Rettenmier, C.W. and M.F. Roussel (1988) Mol. Cell Biol. 8:5026.
- Suzu, S. et al. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267:16812.
- Manos, M.M. (1988) Mol. Cell. Biol. 8:5035.
- Koths, K. (1997) Mol. Reprod. Dev. 46:31.
- Jang, M-H. et al. (2006) J. Immunol. 177:4055.
- Kawasaki, E.S. et al. (1985) Science 230: 291.
- Wong, G.G. et al. (1987) Science 235:1504.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional M-CSF Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human M-CSF Protein
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human M-CSF Protein
For research use only