Recombinant Human Nectin-1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AVI10697

Key Product Details
Source
Accession #
Structure / Form
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
Source
| Human Nectin-1 (Gln31-Gly346) Accession # Q15223.3 |
IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
Avi-tag |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | ||
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
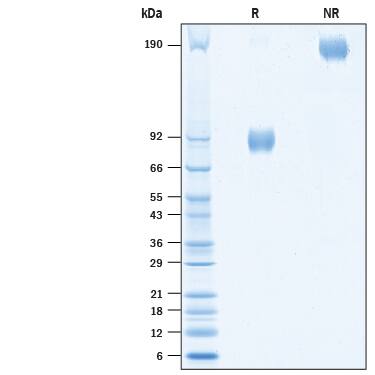
SDS-PAGE
Activity
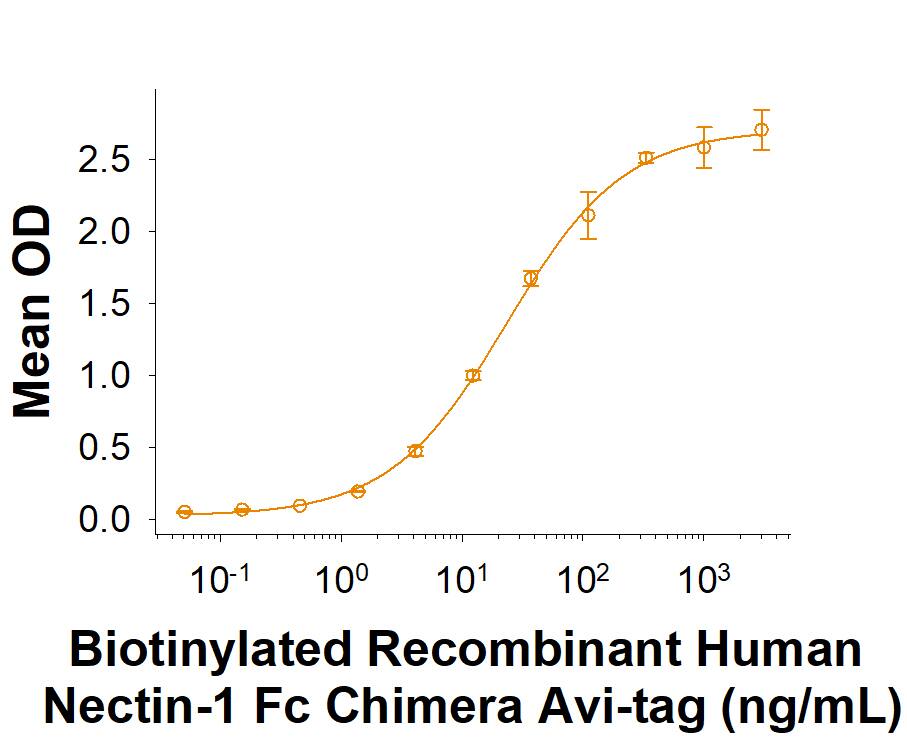
When Recombinant Human Nectin-3 Protein (Catalog # 3064-N3) is immobilized at 0.5 μg/mL, 100 μL/well, the concentration of Biotinylated Recombinant Human Nectin‑1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI10697) that produces 50% of the optimal binding response is approximately 6.0-40 ng/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human Nectin-1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF
Biotinylated Recombinant Human Nectin-1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein Binding Activity.
When Recombinant Human Nectin-3 Protein (3064-N3) is immobilized at 0.5 μg/mL, 100 μL/well, the concentration of Biotinylated Recombinant Human Nectin‑1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI10697) that produces 50% of the optimal binding response is approximately 6.0-40 ng/mL.Recombinant Human Nectin-1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein SDS-PAGE.
2 μg/lane of Biotinylated Human Nectin-1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI10697) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 85-96 kDa and 160-190 kDa.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
AVI10697
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: Nectin-1
Nectin-1 (designated CD111), also called PRR-1 (poliovirus receptor-related protein 1) or HVEC (herpesvirus entry mediator C), is a widely expressed 110 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein important in formation of adherens junctions and synapses. It is a member of the nectin family within the Ig superfamily (1, 2). The Latin word necto means "to connect", indicating the role of nectins in Ca2+-independent cell-cell adhesion (2). Nectin-1 forms homodimers in cis, followed by interactions in trans with Nectin-1, -3 or -4 (2). The 517 amino acid (aa) human Nectin-1 isoform 1 contains a 30 aa signal sequence, a 325 aa extracellular domain (ECD), a 21 aa transmembrane segment (TM), and a 141 aa cytoplasmic region. Nectin ECDs contain three Ig-like domains: an N-terminal V-type that mediates ligand binding, and two C2-type (3). Nectin-1, like other nectins, has a splice form (isoform 2 or HigR, 458 aa) with alternate TM and cytoplasmic sequences. Another, isoform 3, is a 352 aa secreted protein (4). The common region of mature human Nectin-1 (aa 31-334) shares 93%, 94%, 96% and 96% aa identity with mouse, rat, bovine and porcine Nectin-1, respectively. Nectin-1 binds viral glycoprotein D to mediate herpesvirus (but not poxvirus) entry into vaginal mucosa, sensory neurons and fibroblasts (4-7). In forming adherens junctions and synapses, nectins 1 and 3 initiate cell-cell interactions, recruiting alphav beta3 integrin extracellularly and cadherins intracellularly through afadin and other junctional proteins (2, 8-11). These interactions organize the cytoskeleton, strengthen attachment to basement membrane and promote further cell-cell connections. Nectin-1 also recognizes CD96 on NK cells (12). Deficiency of Nectin-1 can result in cleft lip/palate ectodermal dysplasia (13). Nectin-1 down-regulation in epithelial cancers, mediated in part by ectodomain shedding, may contribute to invasiveness (14). Our Avi-tag Biotinylated Human Nectin-1 features biotinylation at a single site contained within the Avi-tag, a unique 15 amino acid peptide. Protein orientation will be uniform when bound to streptavidin-coated surface due to the precise control of biotinylation and the rest of the protein is uncharged so there is no interference in the protein's bioactivity.
References
- Lopez, M. et al. (1995) Gene 155:261.
- Takai, Y. et al. (2008) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9:603.
- Fabre, S. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:27006.
- Lopez, M. et al. (2001) J. Virol. 75:5684.
- Cocchi, F. et al. (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:15700.
- Linehan, M. M. et al. (2004) J. Virol. 78:2530.
- Simpson, S. A. et al. (2005) J. Neurovirol. 11:208.
- Mizoguchi, A. et al. (2002) J. Cell Biol. 156:555.
- Togashi, H. et al. (2006) J. Cell Biol. 174:141.
- Tachibana, K. et al. (2000) J. Cell Biol. 150:1161.
- Takai, Y. and H. Nakanishi (2003) J. Cell Science 116:17.
- Seth, S. et al. (2007) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 364:959.
- Suzuki, K. et al. (2000) Nat. Genet. 25:427.
- Tanaka, Y. et al. (2002) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 299:472.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Nectin-1 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human Nectin-1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human Nectin-1 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF
For research use only