Recombinant Human SCF Protein, CF Best Seller
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 11010-SC
HEK293-expressed

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human SCF/c-kit Ligand protein
Glu26-Ala189
Glu26-Ala189
Purity
>95%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Glu26
Predicted Molecular Mass
18 kDa
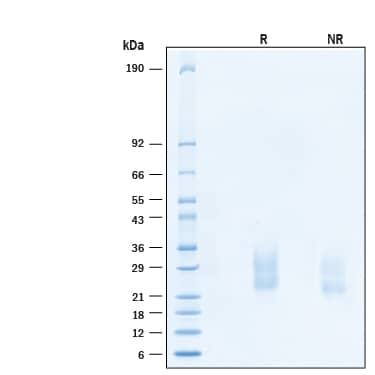
SDS-PAGE
22-31 kDa, under reducing conditions.
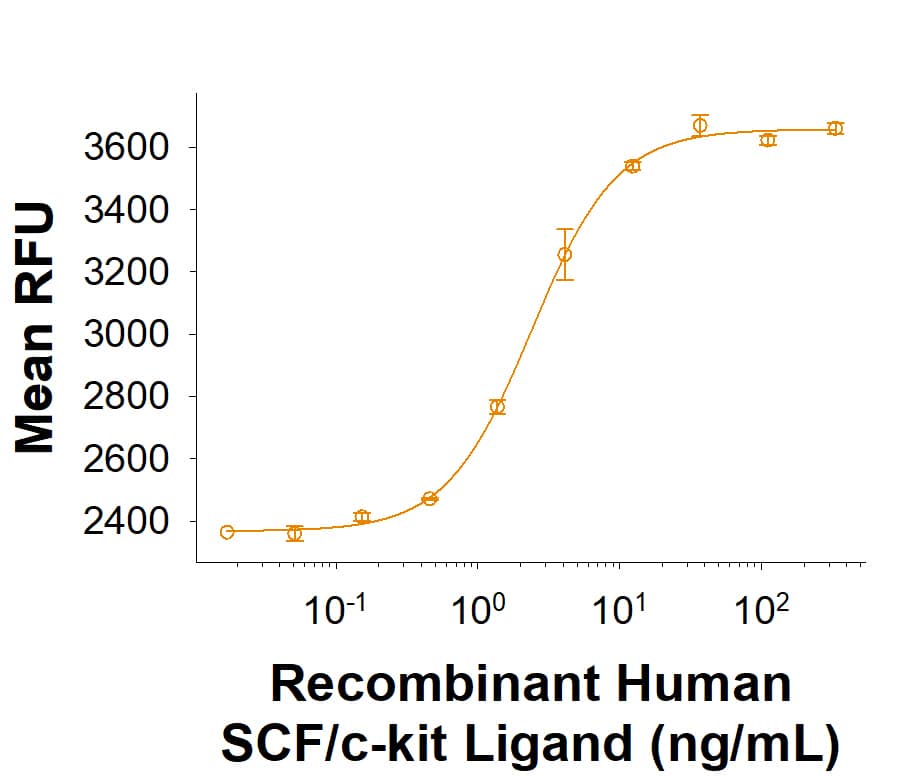
Activity
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells. Kitamura, T. et al. (1989) J. Cell Physiol. 140:323.
The ED50 for this effect is 1.00-5.00 ng/mL.
The ED50 for this effect is 1.00-5.00 ng/mL.
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 5 using 11010-SC in the following applications:
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human SCF Protein, CF
Recombinant Human SCF/c‑kit Ligand Protein Bioactivity.
Recombinant Human SCF/c‑kit Ligand Protein (Catalog # 11010-SC) induces proliferation of TF‑1 human erythroleukemic cells. The ED50 for this effect is 1.00-5.00 ng/mL.Recombinant Human SCF/c‑kit Ligand Protein SDS-PAGE.
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human SCF/c‑kit Ligand Protein (Catalog # 11010-SC) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 22-32 kDa.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
11010-SC
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100-500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: SCF/c-kit Ligand
Mature stem cell factor consists of a 189 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ECD), a 23 aa transmembrane domain, and a 36 aa cytoplasmic tail (10). The ECD shows both N linked and O-linked glycosylation (11). SCF protein exists in two forms, a membrane-bound form and a proteolytically processed soluble form that lacks the transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic tail. The soluble form is created by proteolytic cleavage at two alternate sites in the extracellular juxtamembrane region releasing a 25 kDa soluble SCF protein which is comparable to the only form produced by Steel-dickie mutant mice (12, 13). There is also an alternately spliced isoform of human SCF that lacks 28 amino acids that encompasses the primary proteolytic recognition site (14). This form cannot be cleaved and is only membrane bound. SCF binds to C-kit (CD117). C-kit is expressed on many different cell types including HSCs, mast cells, germ cells, and melanocytes. Binding of SCF to C-kit induces receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation of tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic domain (15). Tyrosine phosphorylation initiates multiple signaling pathways including RAS, PI3 kinase, Src, and JAK/STAT. Stem cell factor is highly conserved among mammals. Human SCF protein shares 79% 87% aa sequence identity with dog, cat, mouse, and rat SCF. Rat SCF is active on mouse and human cells, but human SCF is only weakly active on mouse cells (10).
SCF is a versatile factor in the differentiation
of many specific cell types like spermatogonial stem cells (16) and megakaryocyte
progenitors (17). Apart from differentiation, SCF also can maintain stemness in
cells. This is the case for human bone marrow mesenchymal cells, which require
SCF and hepatocyte growth factor for maintenance (18). Hematopoietic stem cells
similarly require SCF from surrounding cells in their niche to maintain their
stemness and their progenitors (19). SCF has also improved protocols for
continuous generation of cells in culture systems, like granulocytes and
macrophages (20).
For
treatment of graft versus host disease, SCF is used in combination with other
cytokines to generate myeloid-derived suppressor cells from human umbilical
cord blood (21). SCF is also used to generate T cells for cell-based therapies,
drug screening and disease modeling (22). In regenerative studies, SCF is applied
in wound healing hydrogel as a means of increasing its adhesion strength and
tissue regeneration (23).
References
- Ashman, L.K. (1999) Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 31:1037.
- Sette, C. et al. (2000) Int. J. Dev. Biol. 44:599.
- Yoshida, H. et al. (2001) J. Invest. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 6:1.
- Erlandsson, A. et al. (2004) Exp. Cell Res. 301:201.
- Kapur, R. et al. (2002) Blood 100:1287.
- Wang, C.H. et al. (2007) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27:540.
- Bashamboo, A. et al. (2006) J. Cell Sci. 119:3039.
- Reber, L. et al. (2006) Eur. J. Pharmacol. 533:327.
- Kanellakis, P. et al. (2006) Cardiovasc. Res. 70:117.
- Martin, F.H. et al. (1990) Cell 63:203.
- Arakawa, T. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266:18942.
- Majumdar, M.K. et al. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269:1237.
- Brannan, C.I. et al. (1991) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 88:4671.
- Anderson, D.M. et al. (1991) Cell Growth Differ. 2:373.
- Lemmon, M.A. et al. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272:6311.
- Nasimi, M. et al. (2021) Reprod Sci. 28:963.
- Krisch, L. et al. (2021) Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:8224.
- Cao, Z. et al. (2020) Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:1.
- Comazzetto, S. et al. (2019) Cell Stem Cell. 24:477.
- Bernecker, C. et al. (2019) Stem Cells Dev. 28:1540.
- Park, M.Y. et al. (2019) Front Immunol. 10:1.
- Netsrithong, R. et al. (2020) Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:1.
- Zhang, Li. et al. (2021) Journal Mater Chem B. 29:5887.
Long Name
Stem Cell Factor
Alternate Names
c-kit Ligand, DCUA, DFNA69, FPH2, FPHH, KITLG, KL-1, MGF, SHEP7, SLF
Gene Symbol
KITLG
UniProt
Additional SCF/c-kit Ligand Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human SCF Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human SCF Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...