Recombinant Human Universal Type I IFN Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 11020-IF
IFN-alpha-2A/IFN-alpha-1B

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human IFN-alpha protein
| Human IFNA-2A (Cys24-Gln85) Accession # P01563.1 |
Human IFNA-1B (Ile87-Glu189) Accession # CAA23799.1 |
| N-terminus | C-terminus |
Purity
>95%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Cys24
Predicted Molecular Mass
19 kDa
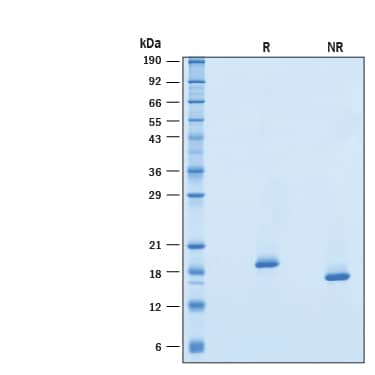
SDS-PAGE
16-22 kDa, under reducing conditions.
Activity
Measured in anti-viral assays using HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cells infected with encephalomyocarditis (EMC) virus. Meager, A. (1987) in Lymphokines and Interferons, a Practical Approach. Clemens, M.J. et al. (eds): IRL Press. 129.
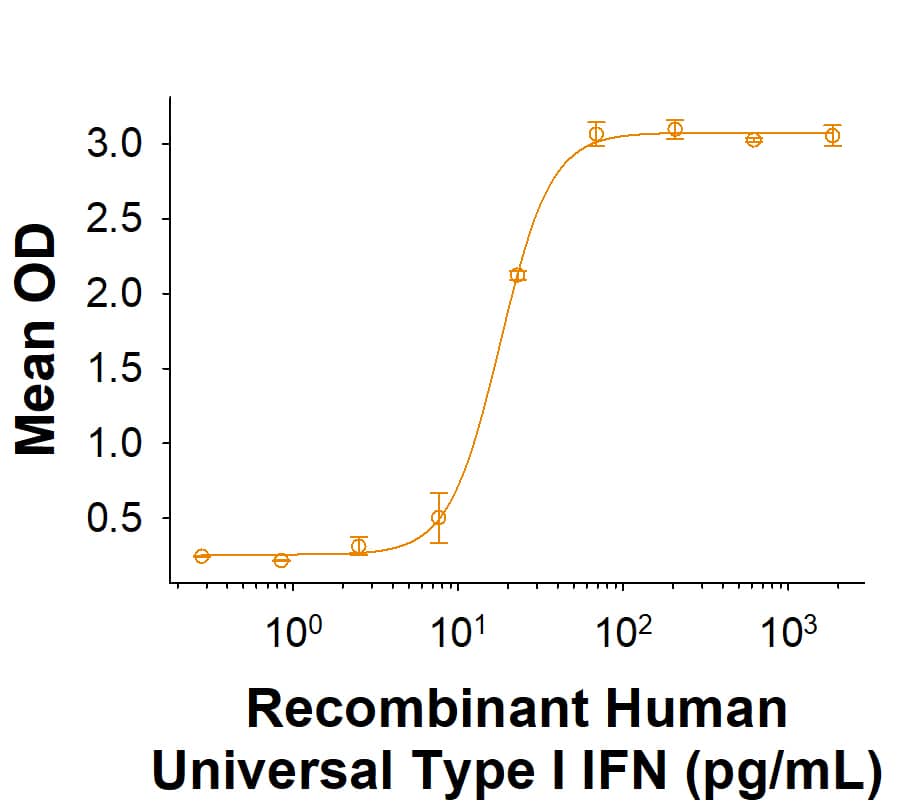
The ED50 for this effect is 6.00-60.0 pg/mL.
The ED50 for this effect is 6.00-60.0 pg/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human Universal Type I IFN Protein, CF
Recombinant Human Universal Type I IFN Protein Bioactivity.
Recombinant Human Universal Type I IFN (Catalog # 11020-IF) demonstrates anti-viral activity in HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cells infected with encephalomyocarditis (EMC) virus. The ED50 for this effect is 6.00-60.0 pg/mLRecombinant Human Universal Type I IFN Protein SDS-PAGE.
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human Universal Type I IFN Protein (Catalog # 11020-IF) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 16-22 kDa.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
11020-IF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: IFN-alpha
References
- Pestka, S. et al. (1987) Annu Rev Biochem. 56:727.
- Goeddel, D.V. et al. (1980) Nature 287:411.
- Matsumiya, T. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 179:4542.
- Schreiber, G. and J. Piehler (2015) Trends Immunol. 36:139.
- Wittling, M.C. et al. (2021) Front Immunol. 11:605673.
- van Pesch, V. et al. (2004) J. Virol. 78:8219.
- James, C.M. et al. (2007) Vaccine. 25(10):1856.
- Moll, H.P. et al. (2011) Cytokine. 53:52.
- Horisberger, M.A. and de Staritzky, K. (1987) J Gen Virol. 68:945.
- Hu, R. et al. (1999) J Immunol. 163:854.
- Horisberger, M.A. and Di Marco, S. (1995) Pharmacol Ther. 66:507.
- Rubinstein, M. et al. (1978) Science. 202:1289.
- Harper, M.S. et al. (2015) PLOS Pathogens 11:e1005254.
- George, J. and Mattapallil, J.J. (2018) Front Immunol. 9:299.
Long Name
Interferon alpha
Alternate Names
IFNalpha, LeIF D
Entrez Gene IDs
3440 (Human)
Gene Symbol
IFNA2
UniProt
Additional IFN-alpha Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human Universal Type I IFN Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human Universal Type I IFN Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...