Recombinant Human VLDLR Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 8444-VL

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human VLDL R protein
Thr25-Ser797, with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Thr25-Ser797, with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Purity
>95%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Thr25
Predicted Molecular Mass
86 kDa
SDS-PAGE
116-142 kDa, reducing conditions
Activity
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA.
When Recombinant Human LRPAP is coated at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well), the concentration of Recombinant Human VLDL R hat produces 50% of the optimal binding response is found to be approximately 5-30 ng/mL.
When Recombinant Human LRPAP is coated at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well), the concentration of Recombinant Human VLDL R hat produces 50% of the optimal binding response is found to be approximately 5-30 ng/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human VLDLR Protein, CF
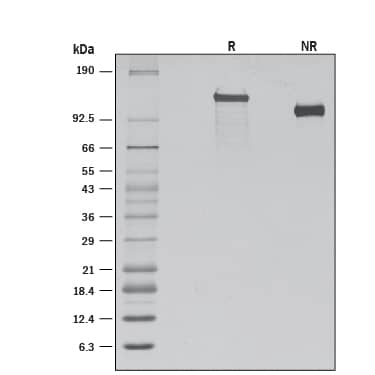
Recombinant Human VLDLR Protein SDS-PAGE
1 μg/lane of Recombinant Human VLDL R (Catalog # 8444-VL) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by silver staining, showing bands at 129 and 107 kDa, respectively.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
8444-VL
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution |
Reconstitute at 250 μg/mL in sterile PBS.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: VLDLR
References
- May, P. et al. (2005) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 62:2325.
- Sakai, J. et al. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269:2173.
- Iijima, H. et al. (1998) J. Biochem. 124:747.
- Ruiz, J. et al. (2005) J. Lipid Res. 46:1721.
- Wyne, K.L. et al. (1996) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 16:407.
- Hauser, P.S. et al. (2011) Prog. Lipid Res. 50:62.
- Argraves, K.M. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:26550.
- Obunike, J.C. et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:8934.
- Yagyu, H. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:10037.
- Webb, D.J. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:7412.
- van Eck, M. et al. (2005) Atherosclerosis 183:230.
- Hiesberger, T. et al. (1999) Neuron 24:481.
- Trommsdorff, M. et al. (1999) Cell 97:689.
- Weeber, E.J. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:39944.
Long Name
Very Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor
Alternate Names
CHRMQ1, VLDL R, VLDLRCH
Gene Symbol
VLDLR
UniProt
Additional VLDLR Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human VLDLR Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human VLDLR Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...