Recombinant Mouse CD6 His Tagged Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 9946-CD

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Mouse myeloma cell line, NS0-derived mouse CD6 protein
Leu18-Gly396, with a C-Terminal 6-His tag
Leu18-Gly396, with a C-Terminal 6-His tag
Purity
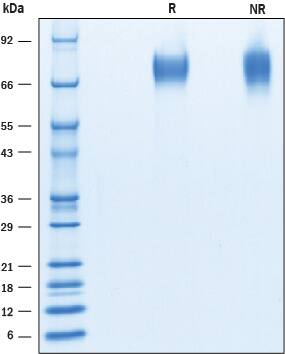
>95%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Leu18
Predicted Molecular Mass
42 kDa
SDS-PAGE
70-80 kDa, reducing conditions
Activity
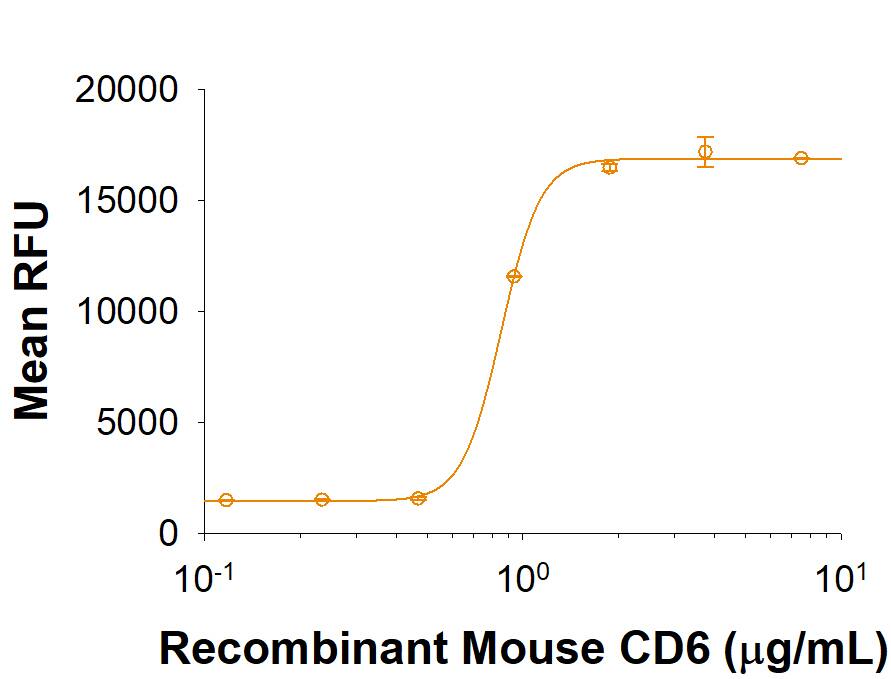
Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of HuT 78 human cutaneous T cell lymphoma cells.
The ED50 for this effect is 0.4-2.4 μg/mL.
The ED50 for this effect is 0.4-2.4 μg/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Mouse CD6 His Tagged Protein, CF
Recombinant Mouse CD6 His Tagged Protein Bioactivity
Immobilized Recombinant Mouse CD6 (Catalog # 9946-CD) supports the adhesion of HuT 78 human cutaneous T cell lymphoma cells. The ED50 for this effect is 0.4-2.4 μg/mL.Recombinant Mouse CD6 His Tagged Protein SDS-PAGE
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Mouse CD6 was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® blue staining, showing bands at 70 - 80 kDa.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
9946-CD
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage |
|
Background: CD6
References
- Sarrias, M. et al. (2007) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 104:11724.
- Chappell, P. et al. (2015) Structure. 23:1426.
- Whitney, G.S. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:18187.
- Mayer, B. et al. (1990) J. Neuroimmunol. 29:193.
- Robinson, W.H. et al. (1995) J. Immunol. 155:4739.
- Aruffo, A. et al. (1997) Immunol. Today 18:498.
- Gangemi, R. et al. (1989) J. Immunol. 143:2439.
- Swack, J.A. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266:7137.
- Starling, G.C. et al. (1996) Eur. J. Immunol. 26:738.
- Swack, J.A. et al. (1989) Mol. Immunol. 26:1037.
- Pawelec, G. and H.J. Buhring (1991) Human Immunol. 31:165.
- Singer, N.G. et al. (1996) Immunology 88:537.
- Degen, W.G. et al. (1998) Am. J. Pathol. 152:805.
- Osorio, L.M. et al. (1995) Cell Immunol. 166:44.
- Robinson, W.H. et al. (1995) Eur. J. Immunol. 25:2765.
- Whitney, G. et al. (1995) Mol. Immunol. 32:89.
Alternate Names
CD6
Gene Symbol
CD6
UniProt
Additional CD6 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Mouse CD6 His Tagged Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Mouse CD6 His Tagged Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...