Recombinant Mouse IL-7 Protein Best Seller
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 407-ML

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Glu26-Ile154, with an N-terminal Met
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
Activity
The ED50 for this effect is 0.15-0.3 ng/mL.
Reviewed Applications
Read 3 reviews rated 3.7 using 407-ML in the following applications:
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Mouse IL-7 Protein
Recombinant Mouse IL-7 Protein Bioactivity
Recombinant Mouse IL-7 (Catalog # 407-ML) stimulates cell proliferation of PHA-activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes. The ED50 for this effect is 0.15-0.3 ng/mL.Recombinant Mouse IL-7 Protein SDS-PAGE
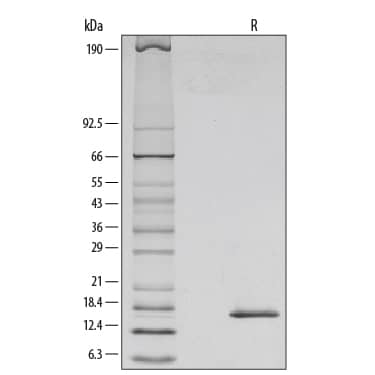
1 μg/lane of Recombinant Mouse IL-7 was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) conditions and visualized by silver staining, showing a single band at 17 kDa.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
Carrier Free
What does CF mean?CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
What formulation is right for me?In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
Carrier: 407-ML
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 50 μg/mL in sterile PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Carrier Free: 407-ML/CF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute 5 µg vials at 50 µg/mL in sterile PBS. Reconstitute 25 µg or larger vials at 100 µg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: IL-7
IL-7 (interleukin-7) is a 25 kDa cytokine of the hemopoietin family that plays important roles in lymphocyte differentiation, proliferation, and survival (1-4). Mouse IL-7 cDNA encodes 154 amino acids (aa) that include a 25 aa signal peptide (4). Mouse IL-7 shares approximately 88% aa sequence identity with rat IL-7 and 58-60% with human, equine, bovine, ovine, porcine, feline and canine IL-7. Human and mouse IL-7 exhibit cross-species activity (2, 3). IL-7 is produced by a wide variety of cells in primary and secondary lymphoid tissues, including stromal epithelial cells of the thymus, bone marrow, and intestines (1, 2, 5). Circulating IL-7 is limiting in healthy animals, but increases during lymphopenia (1, 6). IL-7 signals through a complex of the IL-7 Receptor alpha subunit (IL-7 R alpha, also known as CD127) with the common gamma chain ( gammac) (1). The gammac is also a subunit of the receptors for IL-2, -4, -9, -15, and -21 (1). IL-7 R alpha is expressed on double negative (CD4-CD8-) and CD4+ or CD8+ single positive naïve and memory T cells, but undergoes IL-7-mediated down‑regulation and shedding during antigen-driven T cell proliferation, and is absent on regulatory T cells (1, 2, 6-11). IL-7 contributes to the maintenance of all naïve and memory T cells, mainly by promoting expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 (9-11). It is required for optimal T cell-dendritic cell interaction (6). IL-7 is expressed early in B cell development prior to the appearance of surface IgM (1, 5, 9). In mouse, IL-7 activation of IL-7 R alpha is critical for both T cell and B cell lineage development, while in humans, it is required for T cell but not for B cell development (4, 9, 12, 13). However, IL-7 functions in both mouse and human pro-B cells to suppress premature Ig light chain recombination during proliferative growth (14, 15).
References
- Sasson, S.C. et al. (2006) Curr. Drug Targets 7:1571.
- Barata, J.T. et al. (2006) Exp. Hematol. 34:1133.
- Goodwin, R.G. et al. (1990) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:302.
- Namen, A.E. et al. (1988) Nature 333:571.
- Shalapour, S. et al. (2012) PLoS ONE 7: e31939.
- Saini, M. et al. (2009) Blood 113:5793.
- Park, J.H. et al. (2004) Immunity 21:289.
- Vranjkovic, A. et al. (2007) Int. Immunol. 19:1329.
- Sudo, T. et al. (1993) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 90:9125.
- Seddon, B. et al. (2003) Nat. Immunol. 4:680.
- Schluns, K.S. et al. (2000) Nat. Immunol. 5:426.
- Peschon, J.J. et al. (1994) J. Exp. Med. 180:1955.
- Pribyl, J.A. and T.W. LeBien (1996) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 93:10348.
- Johnson, K. et al. (2012) J. Immunol. 188:6084.
- Nodland, S.E. et al. (2011) Blood 118:2116.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional IL-7 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Mouse IL-7 Protein
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Mouse IL-7 Protein
For research use only