Mouse Pure-Blot anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody (eB182) [DyLight 680]
Novus Biologicals, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # NBP3-11667

Conjugate
Catalog #
Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Rabbit
Applications
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence, Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot
Label
DyLight 680 (Excitation = 692 nm, Emission = 712 nm)
Antibody Source
Monoclonal Mouse IgG Clone # eB182
Concentration
LYOPH mg/ml
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Rabbit IgG
Clonality
Monoclonal
Host
Mouse
Isotype
IgG
Description
This secondary antibody was prepared from tissue culture supernatant by Protein G affinity chromatography. Assay by Immunoelectrophoresis resulted in a single precipitin arc against Anti-Rabbit Serum.
Store vial at 4C prior to restoration. For extended storage aliquot contents and freeze at -20C or below. Avoid cycles of freezing and thawing. Centrifuge product if not completely clear after standing at room temperature. This product is stable for several weeks at 4C as an undiluted liquid. Dilute only prior to immediate use.
Store vial at 4C prior to restoration. For extended storage aliquot contents and freeze at -20C or below. Avoid cycles of freezing and thawing. Centrifuge product if not completely clear after standing at room temperature. This product is stable for several weeks at 4C as an undiluted liquid. Dilute only prior to immediate use.
Scientific Data Images
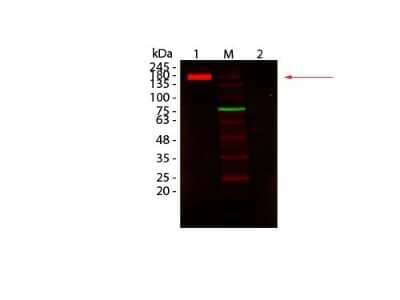
Western Blot: Mouse Pure-Blot anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody (eB182) [DyLight 680] [NBP3-11667] - Lane 1: Rabbit IgG, Non-denatured. Lane 2: Rabbit IgG, Denatured. Load: 50 ng per lane. Primary antibody: none. Secondary antibody: Mouse Pure-Blot anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary antibody (eB182) [DyLight 680] at 1:1,000 for 60 min at RT. Block for 30 min at RT. Predicted: 160 kDa for non-denatured; observed: 170-180 kDa for non-denatured. Band migrates at slightly higher molecular weight.
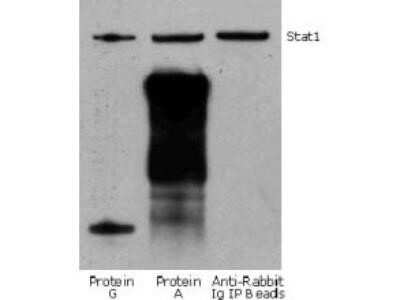
Western Blot: Mouse Pure-Blot anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody (eB182) [DyLight 680] [NBP3-11667] - Jurkat cell lysate (0.5 ml of 1x10e7 cells/ml) was incubated with rabbit anti-human Stat1 and immunoprecipitated using Protein G, Protein A and Anti-Rabbit Ig IP Beads. Precipitate from 5x10e5 cells was subjected to electrophoresis, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and Western blotted with anti-Stat1 using Mouse Pure-Blot anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary antibody (eB182) [DyLight 680].
Mouse Pure-Blot anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody (eB182) [DyLight 680]
Western Blot of Fluorescent TrueBlot(R): Anti-Rabbit IgG DyLight 680 Conjugated. Lane 1: Rabbit IgG, Non-denatured. Lane 2: Rabbit IgG, Denatured. Load: 50 ng per lane. Primary antibody: none. Secondary antibody: Mouse Pure-Blot anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody (eB182) [DyLight 680]antibody at 1:1,000 for 60 min at RT. Block for 30 min at RT. Predicted: 160 kDa for non-denatured; observed: 170-180 kDa for non-denatured. Band migrates at slightly higher molecular weight.Applications
Application
Recommended Usage
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence
1:500 - 1:2500
Western Blot
1:1000
Application Notes
This secondary antibody has been tested in western blot and immunoprecipitation and may also be used for detection in immunoassays that do not employ immunoprecipitation. This secondary antibody is provided as a lyophilized powder. To conserve reagent, we recommend incubating the blots from minigels in sealed bags (removing as much air as possible) with minimal volume (2-3 mLs). If used conservatively at 2.5mLs/blot will yield enough reagent for 40 blots. Note that there are three key procedural considerations: 1. Protein A or G should not be used for the immunoprecipitation. Use of protein A or G beads with the rabbit Pure-Blot will result in contaminating bands. For immunoprecipitation, anti-rat IgG beads, or anti-rabbit IgG beads should be used for rat or rabbit immunoprecipitating antibodies, respectively. 2. Immunoprecipitate should be completely reduced. 3. blocking buffer for Fluorescent Western Blotting should be used as the blocking protein for the immunoblot. All recommended dilutions for listed applications are intended as an initial recommendation, specific conditions for each protein and antibody combination should be specifically optimized by the end user.
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Protein G purified
Reconstitution
Reconstitute with 100 ul deionized water (or equivalent).
Formulation
Lyophilized from 0.02 M Potassium Phosphate, 0.15 M Sodium Chloride, pH 7.2, 10 mg/ml Polyethylene Glycol (PEG-8000)
Preservative
0.01% Sodium Azide
Concentration
LYOPH mg/ml
Shipping
The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below.
Stability & Storage
Store lyophilized antibody at 4C. Aliquot reconstituted liquid and store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
Background: IgG (H+L)
The 4 IgG subclasses, sharing 95% amino acid identity, include IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4 for humans and IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, and IgG3 for mice. The relative abundance of each human subclass is 60% for IgG1, 32% for IgG2, 4% for IgG3, and 4% for IgG4. In an IgG deficiency, there may be a shortage of one or more subclasses (4).
References
1. Painter RH. (1998) Encyclopedia of Immunology (Second Edition). Elsevier. 1208-1211
2. Chapter 9 - Antibodies. (2012) Immunology for Pharmacy. Mosby 70-78
3. Schroeder H, Cavacini, L. (2010) Structure and Function of Immunoglobulins. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 125(2 0 2): S41-S52. PMID: 20176268
4. Vidarsson G, Dekkers G, Rispens T. (2014) IgG subclasses and allotypes: from structure to effector functions. Front Immunol. 5:520. PMID: 25368619
Alternate Names
IP Detection Reagent
Additional IgG (H+L) Products
Product Specific Notices
DyLight (R) is a trademark of Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. and its subsidiaries.
This product is for research use only and is not approved for use in humans or in clinical diagnosis. Secondary Antibodies are guaranteed for 1 year from date of receipt.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
![Mouse Pure-Blot anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody (eB182) [DyLight 680] Mouse Pure-Blot anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody (eB182) [DyLight 680]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp3-11667_mouse-monoclonal-mouse-pure-blot-anti-rabbit-igg-h-l-secondary-antibody-eb182-dylight-680-245202310564640.jpg)
![Mouse Pure-Blot anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody (eB182) [DyLight 680] Mouse Pure-Blot anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody (eB182) [DyLight 680]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp3-11667_mouse-monoclonal-mouse-pure-blot-anti-rabbit-igg-h-l-secondary-antibody-eb182-dylight-680-255202313135150.jpg)