Rabbit anti-Sheep IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [Alkaline Phosphatase]
Novus Biologicals, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # NB120-7112

Conjugate
Catalog #
Forumulation
Catalog #
Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Sheep
Applications
Dot Blot, ELISA, Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot
Label
Alkaline Phosphatase
Antibody Source
Polyclonal Rabbit IgG
Concentration
Please see the vial label for concentration. If unlisted please contact technical services.
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Rabbit anti-Sheep IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [Alkaline Phosphatase] was produced by repeated immunization with Sheep IgG whole molecule in rabbit.
Clonality
Polyclonal
Host
Rabbit
Isotype
IgG
Description
Store vial at 4C before opening. DO NOT FREEZE. This product is stable at 4C as an undiluted liquid. Dilute only prior to immediate use. Freezing alkaline phosphatase conjugates will result in a substantial loss of enzymatic activity.
This product was prepared from monospecific antiserum by immunoaffinity chromatography using Sheep IgG coupled to agarose beads followed by solid phase adsorption(s) to remove any unwanted reactivities. Assay by immunoelectrophoresis resulted in a single precipitin arc against anti-Alkaline Phosphatase (calf intestine), anti-Rabbit Serum, Sheep IgG and Sheep Serum.
This product was prepared from monospecific antiserum by immunoaffinity chromatography using Sheep IgG coupled to agarose beads followed by solid phase adsorption(s) to remove any unwanted reactivities. Assay by immunoelectrophoresis resulted in a single precipitin arc against anti-Alkaline Phosphatase (calf intestine), anti-Rabbit Serum, Sheep IgG and Sheep Serum.
Scientific Data Images for Rabbit anti-Sheep IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [Alkaline Phosphatase]
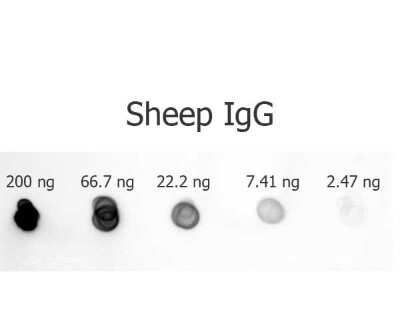
Dot Blot: Rabbit anti-Sheep IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [Alkaline Phosphatase] [NB120-7112] - Dot Blot of Rabbit anti-Sheep IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [Alkaline Phosphatase].
Antigen: Sheep IgG.
Load: 200 ng, 66.7 ng, 22.2 ng, 7.41 ng or 2.47 ng as indicated.
Primary antibody: N/A.
Secondary antibody: Rabbit anti-Sheep IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [Alkaline Phosphatase]
Block: Blocking Buffer for Fluorescent Western Blotting at RT for 1 hour.
Antigen: Sheep IgG.
Load: 200 ng, 66.7 ng, 22.2 ng, 7.41 ng or 2.47 ng as indicated.
Primary antibody: N/A.
Secondary antibody: Rabbit anti-Sheep IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [Alkaline Phosphatase]
Block: Blocking Buffer for Fluorescent Western Blotting at RT for 1 hour.
Applications for Rabbit anti-Sheep IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [Alkaline Phosphatase]
Application
Recommended Usage
ELISA
1:5000
Immunohistochemistry
1:200 - 1:1000
Western Blot
1:500 - 1:2000
Application Notes
This product has been tested by ELISA and dot blot and is suitable for use in immunoelectrophoresis, western-blot, competitive western-blot, ELISA and competitive ELISA assays. Specific conditions for reactivity and signal detection should be optimized by the end user.
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Multi-step
Formulation
0.05 M Tris Chloride, 0.15 M Sodium Chloride, 0.001 M Magnesium Chloride, 0.0001 M Zinc Chloride, 50% (v/v) Glycerol; pH 8.0, 10 mg/mL Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) - Immunoglobulin and Protease free
Preservative
0.1% Sodium Azide
Concentration
Please see the vial label for concentration. If unlisted please contact technical services.
Shipping
The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below.
Stability & Storage
Store at 4C. Do not freeze.
Background: IgG (H+L)
The 4 IgG subclasses, sharing 95% amino acid identity, include IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4 for humans and IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, and IgG3 for mice. The relative abundance of each human subclass is 60% for IgG1, 32% for IgG2, 4% for IgG3, and 4% for IgG4. In an IgG deficiency, there may be a shortage of one or more subclasses (4).
References
1. Painter RH. (1998) Encyclopedia of Immunology (Second Edition). Elsevier. 1208-1211
2. Chapter 9 - Antibodies. (2012) Immunology for Pharmacy. Mosby 70-78
3. Schroeder H, Cavacini, L. (2010) Structure and Function of Immunoglobulins. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 125(2 0 2): S41-S52. PMID: 20176268
4. Vidarsson G, Dekkers G, Rispens T. (2014) IgG subclasses and allotypes: from structure to effector functions. Front Immunol. 5:520. PMID: 25368619
Additional IgG (H+L) Products
Product Documents for Rabbit anti-Sheep IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [Alkaline Phosphatase]
Product Specific Notices for Rabbit anti-Sheep IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [Alkaline Phosphatase]
This product is for research use only and is not approved for use in humans or in clinical diagnosis. Secondary Antibodies are guaranteed for 1 year from date of receipt.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...