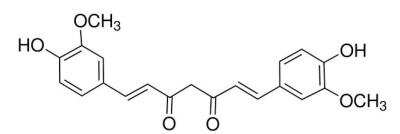
Curcumin
Novus Biologicals, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # NBP2-26243

Key Product Details
Species
Human
Product Specifications
Application Notes
1.Inhibition of NF-kB signaling. This includes inhibition of NF-kB activity induced by Toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands, TNF-phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA), and hydrogen peroxide. 2. Inhibition of other cell signaling molecules including c-Jun/AP-1, Protein kinase C, MAPK, Bcl-2, COX-2, EGFR, and mTOR pathways. Additionally, curcumin can directly inhibit homodimerization of TLR4. 3. Curcumin activates certain signaling molecules including sucBax and Bcl-XS. 4. Researchers are encouraged to consult the literature regarding additional information on curcumin applications.
Scientific Data Images for Curcumin
Curcumin [NBP2-26243] - inhibition of PMA and TNF-a activated NF-kB signaling. NF-kB/SEAPorterTM HEK 293 (NBP2-26260) cells were plated in 12-well plates (0.5 x 10^6 cells/well) for 16 h. Cells were preincubated with different concentrations of DMSO-solubilized curcumin for 2 h or a DMSO vehicle (V) control. Cell were then stimulated with 10 ng/ml phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA) [A] or 10 ng/ml TNF-a [B] for 24 h. The SEAPorter Assay Kit was used to measure SEAP, the readout assay for measuring NF-kB activation in TLR5/NF-kB cells. The results showed that the cells had basal level of NF-kB activity which was increased by PMA or TNF-a . They also show that curcumin decreased PMA and TNF-a activated NF-kB signaling in a dose-dependent manner
Ligand Activation: Curcumin [NBP2-26243]
Ligand Activation: Curcumin [NBP2-26243] - Curcumin inhibition of ligand activated TLR/NF-kB signaling. TLR5/NF-kB/SEAPorterTM HEK 293 (NBP2-26277) cells were plated in 12-well plates (0.5 x 106 cells/well) for 16 h. Cells were preincubated with increasing concentrations of DMSO-solubilized curcumin (IMG-2010) for 2 h or a DMS0 vehicle (V) control. Cell were stimulated with the TLR5 ligand Flagellin (10 ng/ml: NBP2-25289 for 24 h. The SEAPorter Assay Kit was used to measure SEAP, the readout assay for measuring NF-kB activation in TLR5/NF-kB cells. The results showed that the cells had a minimal basal level of NF-kB activity which was dramatically increased by Flagellin. They also, shown that curcumin decreased Flagellin-activated NF-kB signaling in a dose-dependent manner.
Curcumin [NBP2-26243]
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Concentration
Please see the protocols for proper use of this product. If no protocol is available, contact technical services for assistance.
Reconstitution Instructions
Reconstitute with DMSO to bring curcumin to a final concentration of 11 mg/ml.
Shipping
The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below.
Storage
Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
Background: Curcumin
Alternate Names
(E,E)-1,7-bis(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione, Curcuma longa, Curcuma longa (Turmeric), Diferuloylmethane, Diferulylmethane, Natural Yellow 3
Additional Curcumin Products
Product Documents for Curcumin
Product Specific Notices for Curcumin
This product is for research use only and is not approved for use in humans or in clinical diagnosis. Support products are guaranteed for 6 months from date of receipt.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
![Ligand Activation: Curcumin [NBP2-26243] Ligand Activation: Curcumin [NBP2-26243]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Curcumin-Ligand-Activation-NBP2-26243-img0007.jpg)