B7-H6 可促进自然杀伤细胞的细胞毒性
B7-H6、NKp30 和自然杀伤细胞
与其他 B7 家族蛋白不同,在稳态条件下,B7-H6 不会在正常人体组织中表达,但在炎性应激下会被诱导表达。1相应地,B7-H6 已被证明会在各种不同的肿瘤组织上表达。1B7-H6 会与自然杀伤细胞上的 NKp30 激活受体结合,诱导细胞毒性,从而促进抗肿瘤免疫应答。1-2与此相对的是,研究还显示可溶性 B7-H6(可由 ADAM 介导的胞外域脱落产生)与某些癌症中的 NKp30 表达减少和自然杀伤细胞功能障碍相关。3此外,在利用人乳腺癌或神经胶质瘤细胞系开展的研究中发现,B7-H6 可促进肿瘤细胞增殖并抑制细胞凋亡,这进一步表明 B7-H6 可能参与了肿瘤发生。4, 5同样,B7-H6 在人卵巢癌中的高水平表达与肿瘤进展和转移呈正相关。6所有这些观察结果表明,B7-H6 可能是极具前景的治疗靶标。
B7-H6 通过与 NKp30 激活受体结合诱导自然杀伤细胞的细胞毒性
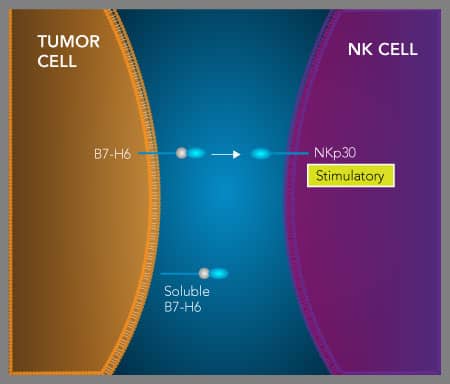
B7-H6 与自然杀伤细胞上的 NKp30 激活受体结合。B7-H6 在炎症条件下会被诱导表达,并且在肿瘤中经常会观察到 B7-H6 过表达。虽然 B7-H6 会与自然杀伤细胞上表达的激活受体 NKp30 结合,但肿瘤组织中 B7-H6 的高水平表达通常与肿瘤进展相关。同样,可溶性 B7-H6 也被证明可下调自然杀伤细胞上的 NKp30 表达并抑制自然杀伤细胞活性,这表明 B7-H6 在某些条件下可能负向调节免疫应答。
R&D Systems 重组人 B7-H6 与 NKp30 蛋白的结合分析

NKp30 与 B7-H6 结合。固定 1 μg/mL(100 μL/孔)的重组人 B7-H6(R&D Systems,目录号 9309-B7),并添加指定浓度的重组人 NKp30/NCR3 Fc 嵌合体(R&D Systems,目录号 1849-NK)。重组人 NKp30 结合的 ED50 为 0.02-0.1 μg/mL。
R&D Systems 重组人 B7-H6 蛋白生物活性评估

B7-H6 诱导 NK-92 细胞中的 IFN-γ 分泌。用指定浓度的重组人 B7-H6 Fc 嵌合体(R&D Systems,目录号 7144-B7)处理 NK-92 人自然杀伤淋巴瘤细胞。使用人 IFN-γ QuantikineTM ELISA 试剂盒(R&D Systems,目录号 DIF50)测定 IFN-γ 分泌。这一作用的 ED50 通常为 0.6-3 μg/mL。
-
Kaifu, T. et al. (2011) B7-H6/NKp30 interaction: a mechanism of alerting NK cells against tumors. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 68:3531. PMID: 21877119.
-
Kellner, C. et al. (2012) Mimicking an induced self phenotype by coating lymphomas with the NKp30 ligand B7-H6 promotes NK cell cytotoxicity. J. Immunol. 189:5037. PMID: 23066150.
-
Schlecker, E. et al. (2014) Metalloprotease-mediated tumor cell shedding of B7-H6, the ligand of the natural killer cell-activating receptor NKp30. Cancer Res. 74:3429. PMID: 24780758.
-
Jiang, T. et al. (2017) High expression of B7-H6 in human glioma tissues promotes tumor progression. Oncotarget 8:37435. PMID: 28415577.
-
Zhang, B. et al. (2018) Knockdown of B7H6 inhibits tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 16:91. PMID: 29963127.
-
Zhou, Y. et al. (2015) B7-H6 expression correlates with cancer progression and patient's survival in human ovarian cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 8:9428. PMID: 26464699.