Chemokines Regulate Cell Migration Under Homeostatic and Inflammatory Conditions

Chemokine Ligand-Receptor Interactions
Chemokines are a large family of small, secreted or cell surface-localized proteins that bind to seven transmembrane, G protein-coupled receptors and regulate cell migration, including chemotaxis, haptotaxis, chemokinesis, haptokinesis, cell adhesion, and chemorepulsion. Chemokines function by establishing concentration gradients, which are formed either by soluble chemokines or by chemokines immobilized on cell surfaces or in the extracellular matrix due to their interactions with glycosaminoglycans. These chemokine gradients direct the movement of target cells expressing the corresponding chemokine receptor towards areas of high chemokine concentration. This is crucial for the recruitment of immune cells to sites of infection or tissue damage and is also required for directing immune cell trafficking under homeostatic conditions to mediate immune surveillance in healthy tissues. Besides directing cell migration, chemokine signaling has been found to regulate a wide variety of other biological processes in leukocytes, such as cell survival, proliferation, differentiation, degranulation, cytokine production, and phagocytosis. Additionally, chemokines contribute to the regulation of some important processes involving non-immune cell types, such as organogenesis, angiogenesis, and tumor cell trafficking.
Chemokine Subfamilies
The chemokine superfamily is divided into four subfamilies (C, CC, CX3C, and CXC) based on the spacing between two conserved cysteine residues located in their amino-terminal ends. Intramolecular disulfide bonds formed between these N-terminal cysteine residues and additional conserved cysteine residues located downstream help to establish the tertiary structure of the proteins. Members of each chemokine subfamily bind to conventional chemokine receptors that are named according to the chemokine subfamily that they bind (XCR, CCR, CX3CR, and CXCR). Within each subfamily, there is significant promiscuity, so many chemokine receptors are capable of interacting with more than one chemokine to drive intracellular signaling.
C Chemokines
Chemokines belonging to the C chemokine subfamily, which are also known as gamma-chemokines, have a single N-terminal cysteine residue that forms an intramolecular disulfide bridge with a downstream cysteine residue. In contrast to the other chemokine subfamilies, the C chemokines are missing the first and third conserved cysteine residues that form the second disulfide bridge common to other chemokines. To date, there are only two C chemokine subfamily proteins that have been identified in humans and only one in mice. In humans, these include XCL1 and XCL2, while only XCL1 has been found in mice. Both XCL1 and XCL2 bind to the XCR receptor.
CC Chemokines
The CC chemokines, also known as beta-chemokines, have two adjacent cysteine residues directly next to each other in their amino-terminal ends. Members of this chemokine subfamily bind to one or more of ten different conventional CC chemokine receptors, known as CCRs. CC chemokines act as critical mediators of inflammatory responses due to their ability to promote the migration of multiple different immune cell types, including monocytes, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and T cells. In addition to binding conventional chemokine receptors, some members of the CC chemokine subfamily bind to the atypical chemokine receptors, D6, DARC, or CCRL1, which are primarily expressed by non-hematopoietic cell types. These atypical receptors are typically unable to activate G protein signaling and have been suggested to play a role in the regulating the resolution of inflammatory responses.
CX3C Chemokines
CX3CL1 is the only member of the CX3C chemokine subfamily, which are also known as delta-chemokines. CX3CL1 has three amino acid residues between its two conserved N-terminal cysteine residues. CX3CL1 binds to CX3CR1 and regulates both cell migration and cell adhesion.
CXC Chemokines
The final chemokine subfamily is the CXC chemokines, also known as alpha-chemokines. These chemokines have a single variable amino acid between the two N-terminal cysteine residues. Members of the CXC subfamily are further divided based on the presence or absence of a glutamic acid-leucine-arginine (ELR) motif located immediately upstream of the CXC motif. ELR+ CXC chemokines function primarily as neutrophil chemoattractants, while ELR- CXC chemokines function as lymphocyte chemoattractants. Additionally, ELR+ CXC chemokines are potent angiogenic factors, while ELR- CXC chemokines are angiostatic. CXC chemokines bind to one or more of six different CXC receptors, known as CXCRs, and select members also bind to the atypical chemokine receptors, DARC and CXCR7.
Chemokine Classification Based on Function
In addition to their classification as C, CC, CX3C, or CXC chemokines, chemokines are also classified based on whether they are homeostatic, inflammatory, or dual-functioning chemokines. Homeostatic chemokines are constitutively expressed under normal physiological conditions and play roles in development and organogenesis, immunosurveillance, and tissue renewal and regeneration. In contrast, inflammatory chemokines are induced in response to inflammatory stimuli and are involved in promoting the migration of immune cells to sites of infection or injury to eliminate pathogens and prevent microbial spread. Some chemokines play a role in both homeostatic and inflammatory processes and thus, have been categorized as dual-function chemokines.
Chemokines and Disease
Although chemokines play essential roles in guiding development, maintaining homeostasis, and promoting inflammation in response to infections or injuries, chemokine signaling is also thought to contribute to the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, atherosclerosis, asthma, and neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, chemokines have also been suggested to contribute to cancer progression both in terms of promoting the recruitment of pro- or anti-tumor immune cells to the tumor microenvironment and in regulating tumor cell metastasis and tumor-associated angiogenesis. As a result, specific chemokines and chemokine receptors are being investigated as potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of these diseases.
Bio-Techne offers a wide selection of bioactive R&D Systems™ recombinant chemokines for studying chemokine functions, along with antibodies for investigating chemokine and chemokine receptor expression, and single and multianalyte immunoassays for quantifying chemokines or analyzing their effects on other inflammatory mediators.
C Chemokines
C Chemokines and Receptors - Products by Molecule
CC Chemokines
CC Chemokines - Products by Molecule
CC Chemokine Receptors - Products by Molecule
| CCR1 | CCR2 | CCR3 | CCR4 | CCR5 | CCR6 |
| CCR7 | CCR8 | CCR9 | CCR10 | CCR11 | CCR1L1 |
| CCRL2 | CCRL2/CRAM-A/B | CCRL2/LCCR | D6 | DARC | Chemokine Receptor Agonists |
| Chemokine Receptor Antagonists |
CC Viral Chemokine Homologs - Products by Molecule
CC Chemokine-Binding Proteins - Products by Molecule
Chemotaxis Induced by R&D Systems Recombinant Human CCL20 and Neutralization by a Mouse Anti-Human CCL20 Monoclonal Antibody

CCL20/MIP-3alpha-induced Chemotaxis is Neutralized Using a Mouse Anti-Human CCL20/MIP-3alpha Monoclonal Antibody. Recombinant Human CCL20/MIP-3alpha (R&D Systems, Catalog # 360-MP) chemoattracts the BaF3 mouse pro-B cell line transfected with human CCR6 in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). The amount of cells that migrated through to the lower chemotaxis chamber was measured by Resazurin (R&D Systems, Catalog # AR002). The ED50 for this effect is 0.5-2 ng/mL. Chemotaxis elicited by 10 ng/mL Recombinant Human CCL20/MIP-3alpha was neutralized by increasing concentrations of a Mouse Anti-Human CCL20/MIP-3alpha Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # MAB360; green line). The ND50 is typically 0.2-2 ug/mL.
Immunostaining of CCL3 in Rat Kidney Using R&D Systems Mouse Anti-Rat CCL3 Monoclonal Antibody

Detection of CCL3/MIP-1alpha in Rat Kidney. Perfusion-fixed frozen sections of rat kidney were stained for CCL3/MIP-1alpha expression using a Mouse Anti-Rat CCL3/MIP-1alpha Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # MAB66251). The tissue was stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Donkey Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # NL007; red) and counterstained with DAPI (Tocris, Catalog # 5748; blue). Specific staining was localized to the plasma membranes of epithelial cells in convoluted tubules.
Simultaneous Detection of Multiple Chemokines Using the Proteome ProfilerTM Human Chemokine Array Kit
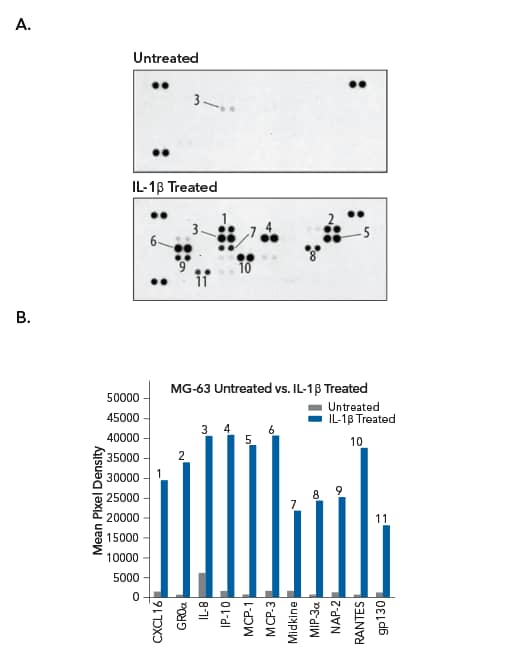
Simultaneous Detection of Multiple Chemokines in Cell Culture Supernatants from Untreated and IL-1beta-Treated Human Osteosarcoma Cells Using the Proteome Profiler Human Chemokine Array. MG-63 human osteosarcoma cells were either untreated or treated with Recombinant Human IL-1 beta (R&D Systems, Catalog # 201-LB). (A) Cell culture supernatants were removed and assayed using the Proteome Profiler Human Chemokine Array Kit (R&D Systems, Catalog # ARY017). (B) Histogram profiles for select analytes detected in the cell culture supernatants of untreated (gray bars) and IL-1 beta-treated (blue bars) cells were generated by quantifying the mean spot pixel densities from the arrays using image software analysis.
CX3C Chemokines
CX3C Chemokines and Receptors - Products by Molecule
Chemotaxis Induced by R&D Systems Recombinant Human CX3CL1 and Neutralization by a Rat Anti-Mouse CX3CL1 Monoclonal Antibody

CX3CL1/Fractalkine-induced Chemotaxis is Neutralized Using a Rat Anti-Mouse CX3CL1/Fractalkine Chemokine Domain Monoclonal Antibody. Recombinant Mouse CX3CL1/Fractalkine (R&D Systems, Catalog # 571-MF) chemoattracts the BaF3 mouse pro-B cell line transfected with human CX3CR1 in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). The amount of cells that migrated through to the lower chemotaxis chamber was measured by Resazurin (R&D Systems, Catalog # AR002). The ED50 for this effect is 0.004-0.02 ug/mL. Chemotaxis elicited by 30 ng/mL Recombinant Mouse CX3CL1/Fractalkine was neutralized with increasing concentrations of a Rat Anti-Mouse CX3CL1/Fractalkine Chemokine Domain Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # MAB571; green line). The ND50 is typically 0.75-3.5 ug/mL.
CXC Chemokines
CXC Chemokines - Products by Molecule
CXC Chemokine Receptors - Products by Molecule
| CXCR1/IL-8RA | CXCR2/IL-8RB | CXCR3 | CXCR4 | CXCR5 |
| CXCR6 | CXCR7/RDC-1 | DARC | Chemokine Receptor Agonists | Chemokine Receptor Antagonists |
CXC Viral Chemokine Homologs - Products by Molecule
Chemotaxis Induced by R&D Systems Recombinant Human CXCL8/IL-8 and Neutralization by a Mouse Anti-Human CXCR1/IL-8 RA Monoclonal Antibody

CXCL8/IL-8-induced Chemotaxis is Neutralized Using a Mouse Anti-Human CXCR1/IL-8 RA Monoclonal Antibody. Recombinant Human CXCL8/IL-8 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 208-IL) chemoattracts the BaF3 mouse pro-B cell line transfected with human CXCR1/IL-8 RA in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). The amount of cells that migrated through to the lower chemotaxis chamber was measured by Resazurin (R&D Systems, Catalog # AR002). Chemotaxis elicited by 1 ng/mL Recombinant Human CXCL8/IL-8 was neutralized with increasing concentrations of a Mouse Anti-Human CXCR1/IL-8 RA Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # MAB330; green line). The ND50 is typically 0.4-2.0 ug/mL.
Chemotaxis Induced by R&D Systems Recombinant Human CXCL12 and Inhibition by AMD 3100 Octahydrochloride

CXCL12/SDF-1alpha-induced Chemotaxis is Antagonized by AMD 3100 Octahydrochloride. Recombinant Human/ Rhesus Macaque/Feline CXCL12/SDF-1alpha (R&D Systems, Catalog # 350-NS) chemoattracts the BaF3 mouse pro-B cell line transfected with human CXCR4 in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). The amount of cells that migrated through to the lower chemotaxis chamber was measured by Resazurin (R&D Systems, Catalog # AR002). The ED50 for this effect is 0.15-0.6 ng/mL. Chemotaxis elicited by 1 ng/mL Recombinant Human/Rhesus Macaque/Feline CXCL12/SDF-1alpha was antagonized with increasing concentrations of the highly selective CXCR4 inhibitor, AMD 3100 octahydrochloride (Tocris, Catalog # 3299; blue line).
Detection of CD19+CXCR5+ Human Peripheral Blood Cells by Flow Cytometry

Detection of CXCR5 in Human Peripheral Blood Cells by Flow Cytometry. Human peripheral blood cells were stained with an APC-conjugated Mouse Anti-Human CD19 Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # FAB4867A) and either an (A) Alexa Fluor™ 488-conjugated Mouse Anti-Human CXCR5 Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog FAB190G) or an (B) Alexa Fluor™ 488-conjugated Mouse IgG2B Isotype Control (R&D Systems, Catalog # IC0041G).
Atypical Chemokine Receptors
Other Chemokine-like Proteins
Featured Chemokine Products

Proteome Profiler Chemokine Antibody Arrays
Proteome Profiler Chemokine Antibody Arrays
The Proteome Profiler Human and Mouse Chemokine Arrays offer a simple and inexpensive method to simultaneously detect multiple analytes in a single sample, using chemiluminescence and standard Western blotting equipment. Utilize these multiplex membrane-based assays for your early stage chemokine discovery research.

Modified Recombinant Chemokines
Modified Recombinant Chemokines
Naturally occurring chemokine modifications, such as N-terminal truncations, can affect their biological potency and receptor specificity. Bio-Techne exclusively offers a wide selection of R&D Systems™ modified chemokines with increased activity or altered specificity for investigating the effects of these modifications.

Chemokine Blocking and Neutralizing Antibodies
Chemokine Blocking and Neutralizing Antibodies
Blocking and neutralizing antibodies bind to their targets and either directly interfere with their functions or negatively regulate their downstream cellular effects. Bio-Techne offers a large selection of R&D Systems™ blocking or neutralizing antibodies against specific chemokines or chemokine receptors, which have been validated to block the activities of specific chemokines in chemotaxis assays.
Chemokine Resources

Chemokine Superfamily Poster
Chemokine Superfamily Poster
Chemokines and their receptors control cell migration during both homeostasis and inflammation and are associated with a diverse array of pathological conditions. Learn more about chemokine ligand-receptor interactions, chemokine signaling pathways, and chemokine receptors implicated in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases with our Chemokine Superfamily poster.

Chemokine Research Product Guide
Chemokine Research Product Guide
Download this guide to learn more about our portfolio of reagents for chemokine research. From bioactive proteins and antibodies qualified for multiple applications, to single and multianalyte immunoassays, we have the products that you need to investigate the effects of different chemokines under homeostatic and inflammatory conditions.

Periodic Table of Cytokine & Chemokine Families Wall Poster
Periodic Table of Cytokine & Chemokine Families Wall Poster
Learn about the members of different cytokine and chemokine families with our periodic table wall poster. This poster includes information on the structures, receptors, and native molecular weights of each cytokine, and will serve as a great reference tool and colorful addition to your lab space.