Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) is the trans-differentiation of stationary epithelial cells into motile mesenchymal cells. During EMT, epithelial cells lose their junctions and apical-basal polarity, reorganize their cytoskeleton, undergo a change in the signaling cascade that defines cell shape and reprograms gene expression. Collectively, these changes increase the motility of individual cells and enables the development of an invasive phenotype. At the molecular signaling level, EMT is regulated through several pathways which are triggered by TGF-beta, HGF, EGF, FGF, VEGF, Wnt, SHH, IL6, HIF1 alpha, and other proteins. At the transcription level, SNAI1/Snail, ZEB1/ZEB2 and basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors (bHLH) drive EMT progression. Accumulating evidence has established involvement of EMT in several biological processes including (but not limited to) embryonic and post-embryonic development, tissue regeneration/wound healing, stem cell homeostasis, and in pathophysiology of fibrosis and malignancies.
Having trouble in generating high quality data in EMT and stemness experiments? Read through our scientific and technical answers to ~ 20 frequently asked questions on EMT/stemness signaling, markers, induction and troubleshooting:
In line with the growth and expansion of this research area, there has been a growing need for high quality antibodies against established as well as new markers for EMT studies. Bio-Techne offers a range of antibodies for Epithelial Phenotype Markers, Mesenchymal Phenotype (Stemness) Markers and other major EMT signaling players. Some of our most popular targets are:
| Epithelial Markers | Mesenchymal Markers | Other Major EMT Players |
|---|---|---|
| Collagen IV alpha 1 | Alpha-SMA | beta-Catenin |
| Cytokeratin (pan) | Fibronectin | Cadherin-11 |
| Desmoglein-3 | N-Cadherin | GSK-3 beta |
| E-Cadherin | S100A4 | MMP2 |
| Laminin | Slug | SUMO2 |
| MUC-1 | Snail | Twist-1 |
| Syndecan-1 | Vimentin | ZEB1 |
Bio-Techne antibodies are rigorously validated in multiple species/applications, and for addressing the multiplexing needs, we provide antibodies in unconjugated as well as 21+ conjugated formats (custom conjugations also available). The validation data of some of the above mentioned targets is shown below:

E Cadherin was detected in immersion fixed D3 mouse embryonic stem cell line using Goat Anti-Human/Mouse E Cadherin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog #AF748) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell surfaces. View protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Stem Cells on Coverslips on R&D Systems.
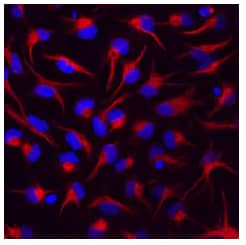
Vimentin Antibody (280618) [MAB2105]
ICC/IF staining of Vimentin in rat cortical stem cells using MAB2105 with NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated secondary antibody (red; Catalog # NL013) and counterstaining using DAPI (blue). Note the specific staining of Vimentin localized to the cytoskeleton.
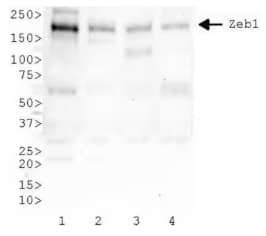
ZEB1 Antibody [NBP2-13159]
WB analysis of lysates from (1) HeLa, (2) COS7, (3) HepG2, and (4) Ntera-2 cells using rabbit polyclonal ZEB1 antibody. The signal was developed using HRP-conjugated secondary and ECL detection method. The antibody detected specific bands of ZEB1 in all of the tested cell lines with highest expression HeLa cells.