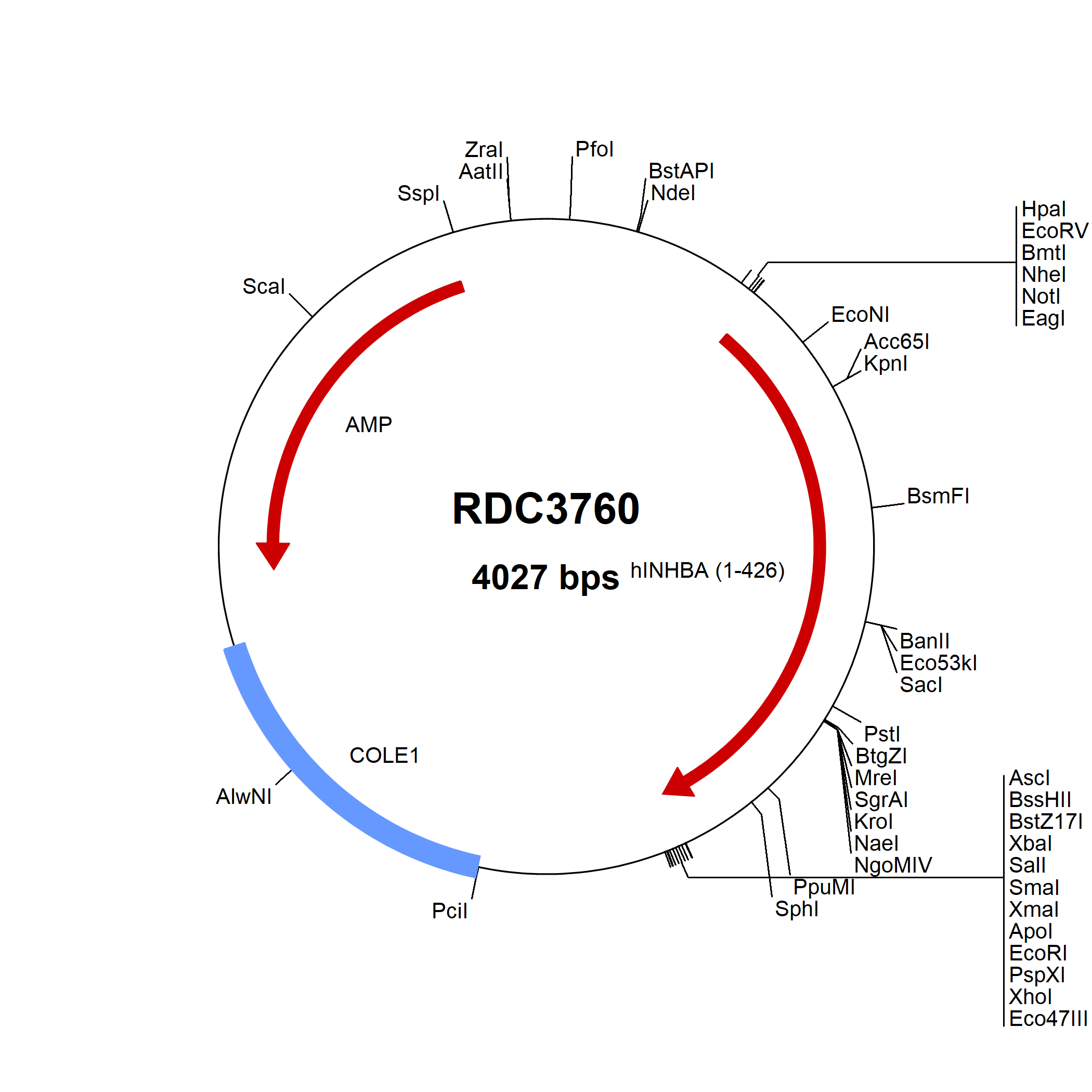
Activin A: cDNA Clones
Activin A is an important member of the TGF-beta superfamily that is produced by many different cell types and is essential for proper development. Bioactive Activin A exists as a disulfide-linked homodimer that recognizes and binds to four Activin receptors, Activin RIA and RIB, and Activin RIIA and RIIB. This ligand-receptor binding event triggers activation of SMAD signaling pathways ultimately regulating a wide variety of functions including stem cell maintenance, self-renewal, and differentiation, B-cell differentiation and proliferation, wound healing, metabolism, and gonadal development.
Activin A is first produced as a precursor protein containing a propeptide that gets proteolytically cleaved off leaving the mature A chain. Two A chains assemble by disulfide bond formation creating the bioactive homodimer. The bioavailability of Activin A is regulated by cell-associated decoy molecules (BAMBI, Betaglycan, Cripto), secreted proteins (a2-Macroglobulin, Follistatin, FLRG), and intracellular incorporation of the beta A subunit into Activin AC or Inhibin A. Experimentally, recombinant Activin A is commonly used to maintain the proliferative potential of human induced pluripotent stem cells and to promote differentiation of embryonic stem cells into endoderm and pancreatic B cells.
Products:
1 result for "Activin A cDNA Clones" in Products
1 result for "Activin A cDNA Clones" in Products
Activin A: cDNA Clones
Activin A is an important member of the TGF-beta superfamily that is produced by many different cell types and is essential for proper development. Bioactive Activin A exists as a disulfide-linked homodimer that recognizes and binds to four Activin receptors, Activin RIA and RIB, and Activin RIIA and RIIB. This ligand-receptor binding event triggers activation of SMAD signaling pathways ultimately regulating a wide variety of functions including stem cell maintenance, self-renewal, and differentiation, B-cell differentiation and proliferation, wound healing, metabolism, and gonadal development.
Activin A is first produced as a precursor protein containing a propeptide that gets proteolytically cleaved off leaving the mature A chain. Two A chains assemble by disulfide bond formation creating the bioactive homodimer. The bioavailability of Activin A is regulated by cell-associated decoy molecules (BAMBI, Betaglycan, Cripto), secreted proteins (a2-Macroglobulin, Follistatin, FLRG), and intracellular incorporation of the beta A subunit into Activin AC or Inhibin A. Experimentally, recombinant Activin A is commonly used to maintain the proliferative potential of human induced pluripotent stem cells and to promote differentiation of embryonic stem cells into endoderm and pancreatic B cells.
Products: