Additional p53-related Compounds: Small Molecules and Peptides
p53 is well known for its key role as a tumor suppressor protein. It is 393 amino acids (aa) in length with a predicted molecular weight of 44 kDa. It belongs to the p53 family that also includes p63 and p73. Structurally, p53 is characterized by an N-terminal transactivation domain, central DNA-binding and oligomerization domains, and a C-terminal regulatory domain. It is thought to exist as a homotetramer, and it exhibits approximately 72% and 76% aa identity with its mouse and rat orthologs, respectively. Mutations in the p53 gene are one of the most frequent genomic events accompanying oncogenic transformation. p53 responds to signals such as DNA damage or cell stress primarily through its actions as a transcription factor. Among its gene targets are a range factors that promote DNA repair mechanisms or apoptosis including cell cycle regulatory proteins and members the Bcl-2 family. Because of its critical role in genomic homeostasis, p53 activities are tightly regulated by a network of protein-protein interactions, microRNAs, and a range of post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, and ubiquitination. A widely studied regulator is Murine Double Minute 2 (MDM2). MDM2 is known to suppress p53 activity through direct binding or through its actions as a Ubiquitin ligase (E3) that catalyzes p53 ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation.
4 results for "Additional p53-related Compounds Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
4 results for "Additional p53-related Compounds Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
Additional p53-related Compounds: Small Molecules and Peptides
p53 is well known for its key role as a tumor suppressor protein. It is 393 amino acids (aa) in length with a predicted molecular weight of 44 kDa. It belongs to the p53 family that also includes p63 and p73. Structurally, p53 is characterized by an N-terminal transactivation domain, central DNA-binding and oligomerization domains, and a C-terminal regulatory domain. It is thought to exist as a homotetramer, and it exhibits approximately 72% and 76% aa identity with its mouse and rat orthologs, respectively. Mutations in the p53 gene are one of the most frequent genomic events accompanying oncogenic transformation. p53 responds to signals such as DNA damage or cell stress primarily through its actions as a transcription factor. Among its gene targets are a range factors that promote DNA repair mechanisms or apoptosis including cell cycle regulatory proteins and members the Bcl-2 family. Because of its critical role in genomic homeostasis, p53 activities are tightly regulated by a network of protein-protein interactions, microRNAs, and a range of post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, and ubiquitination. A widely studied regulator is Murine Double Minute 2 (MDM2). MDM2 is known to suppress p53 activity through direct binding or through its actions as a Ubiquitin ligase (E3) that catalyzes p53 ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation.
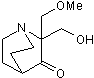
Restores mutant p53 activity
| Alternate Names: | APR-246 |
| Chemical Name: | 2-(Hydroxymethyl)-2-(methoxymethyl)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Restores mutant p53 activity; proapoptotic
| Chemical Name: | 1-[(1-Oxopropoxy)methyl]-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione |
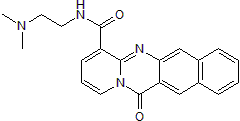
RNA polymerase I inhibitor; also p53 pathway activator
| Chemical Name: | N-[2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl]-12-oxo-12H-benzo[g]pyrido[2,1-b]quinazoline-4-carboxamide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
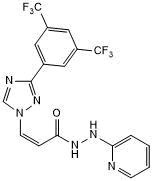
Selective exportin-1 (XPO1/CRM1) inhibitor
| Chemical Name: | (2Z)-3-[3-[3,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]-2-propenoic acid 2-(2-pyridinyl)hydrazide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |