CARD8: Proteins and Enzymes
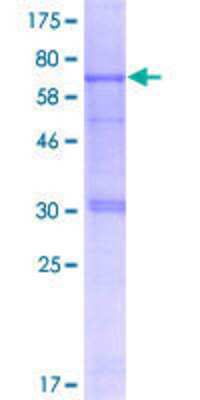
TUCAN (also known as CARD8 and CARDINAL) is a CARD domain containing protein. TUCAN stands for tumor-up-regulated CARD-containing antagonist of caspase nine. Proteins containing a CARD (caspase-associated recruitment domain) domain are key regulators of cell death, cell survival and cytokine production (reviewed in Damiano and Reed, 2004). CARD domains are found in the N-terminal pro-domains of certain caspases, a family of apoptotic and pro-inflammatory proteases, as well as in a diversity of other proteins including TUCAN. CARD domains are homotypic protein interaction motifs that enable networks of proteins to communicate via CARD-CARD interactions. TUCAN is an anti-apoptotic CARD protein that can protect tumors from cell death stimuli, and is overexpressed in certain forms of cancer. The role of TUCAN in tumor biology remains to be fully elucidated, and there appears to be be various mechanisms by TUCAN can potentially contribute to apoptosis resistance (reviewed in Checinska et al, 2006). For example, TUCAN has been shown to inhibit caspase-9 activation by binding to the CARD region of pro-caspase-9, thereby suppressing the formation of the Apaf-1-caspase-9 apoptotic complex and apoptosis. Additionally, a TUCAN isoform has been described that blocks both caspase-8 and caspase-9 mediated apoptosis. However, in some tumors, TUCAN does not appear to interact with caspase-9 and may play a role in modulating NF-kB transcription factor survivial signaling pathways. In this regard a CARD-independent interaction of TUCAN with Ikkg has been described, resulting in the inhibition of interleukin-1 and TNF-induced NF-kB activation. Human TUCAN is a 431 amino acid protein according to GenBank no. gi|14424229|sp|Q9Y2G2|CARD8_HUMAN, and migrates at ~45-49 kDa on SDS-PAGE.
Show More
6 results for "CARD8 Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
6 results for "CARD8 Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
CARD8: Proteins and Enzymes
TUCAN (also known as CARD8 and CARDINAL) is a CARD domain containing protein. TUCAN stands for tumor-up-regulated CARD-containing antagonist of caspase nine. Proteins containing a CARD (caspase-associated recruitment domain) domain are key regulators of cell death, cell survival and cytokine production (reviewed in Damiano and Reed, 2004). CARD domains are found in the N-terminal pro-domains of certain caspases, a family of apoptotic and pro-inflammatory proteases, as well as in a diversity of other proteins including TUCAN. CARD domains are homotypic protein interaction motifs that enable networks of proteins to communicate via CARD-CARD interactions. TUCAN is an anti-apoptotic CARD protein that can protect tumors from cell death stimuli, and is overexpressed in certain forms of cancer. The role of TUCAN in tumor biology remains to be fully elucidated, and there appears to be be various mechanisms by TUCAN can potentially contribute to apoptosis resistance (reviewed in Checinska et al, 2006). For example, TUCAN has been shown to inhibit caspase-9 activation by binding to the CARD region of pro-caspase-9, thereby suppressing the formation of the Apaf-1-caspase-9 apoptotic complex and apoptosis. Additionally, a TUCAN isoform has been described that blocks both caspase-8 and caspase-9 mediated apoptosis. However, in some tumors, TUCAN does not appear to interact with caspase-9 and may play a role in modulating NF-kB transcription factor survivial signaling pathways. In this regard a CARD-independent interaction of TUCAN with Ikkg has been described, resulting in the inhibition of interleukin-1 and TNF-induced NF-kB activation. Human TUCAN is a 431 amino acid protein according to GenBank no. gi|14424229|sp|Q9Y2G2|CARD8_HUMAN, and migrates at ~45-49 kDa on SDS-PAGE.
Show More
| Applications: | AC |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, MA, AP |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, MA, AP |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, MA, AP |
| Applications: | AC |
| Applications: | AC |